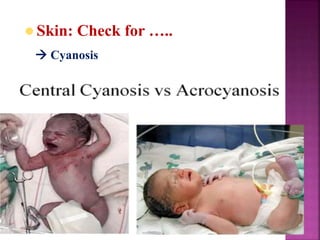
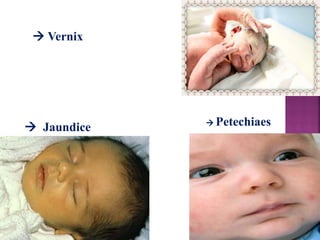
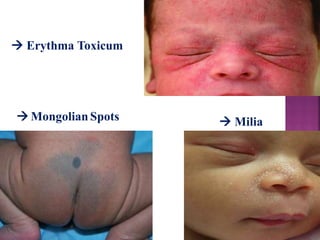
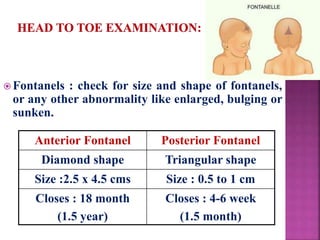
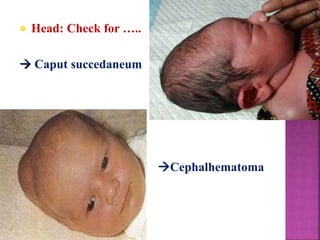
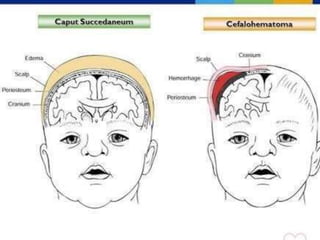
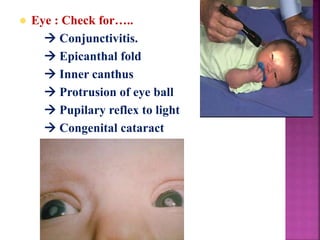
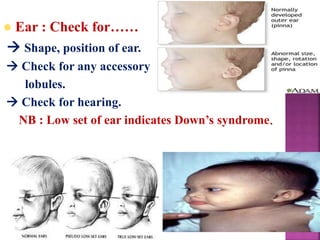
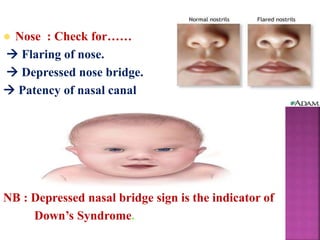
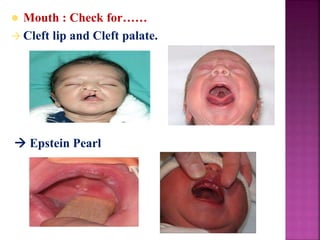
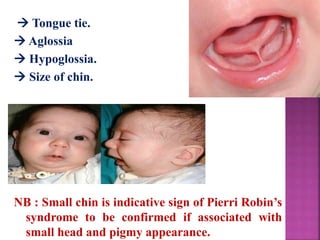
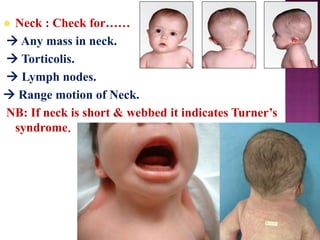
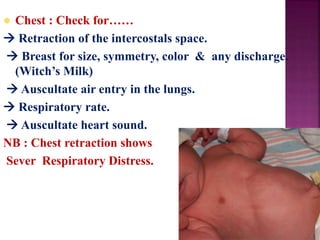
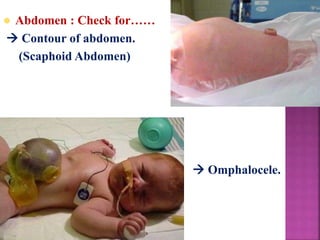
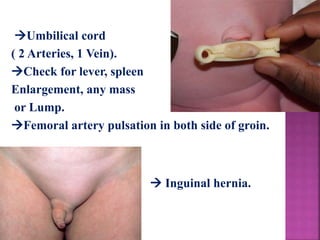
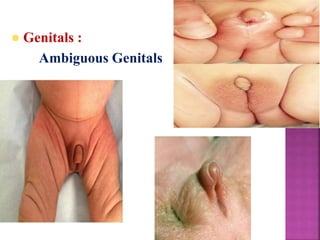
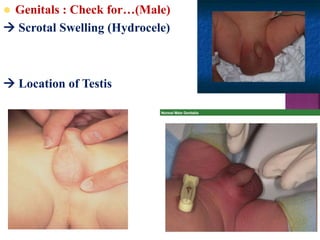
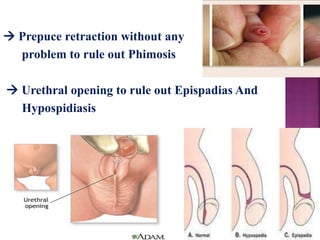
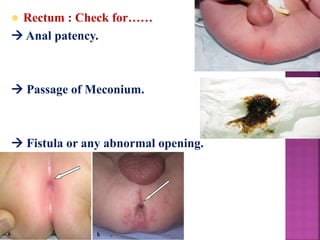
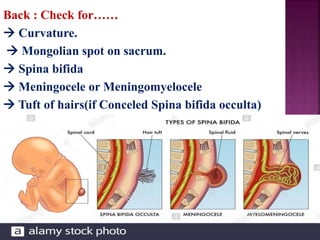
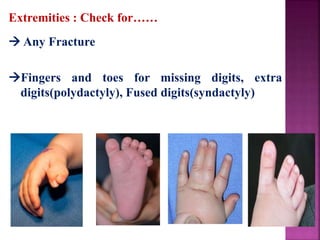
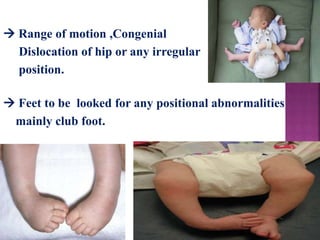
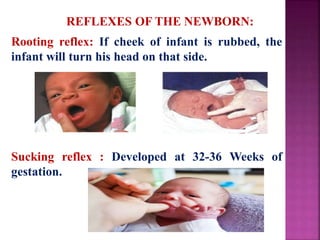
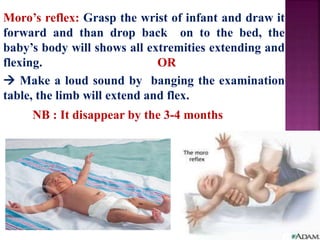
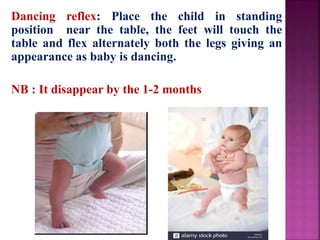
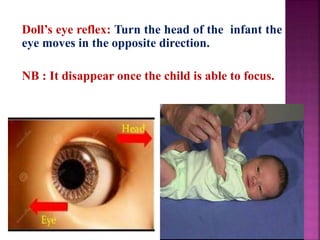
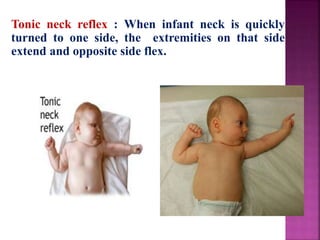
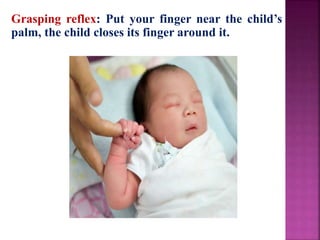
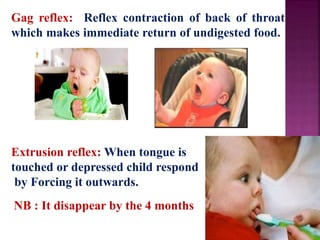
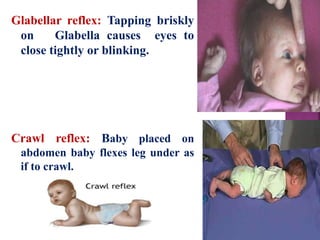
This document provides guidance on newborn examination including the purpose, procedures, vital signs, measurements, physical characteristics and abnormalities to examine for, as well as common reflexes. The examination should be done swiftly within 8-10 minutes while keeping hands clean and warm, and protecting the newborn from unnecessary exposure and drafts. Abnormalities of the skin, head, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, neck, chest, abdomen, genitals, rectum, back, and extremities should all be examined and noted. Common reflexes like rooting, sucking, Moro's, and tonic neck should also be tested. Any deviations from normal should prompt immediate action.