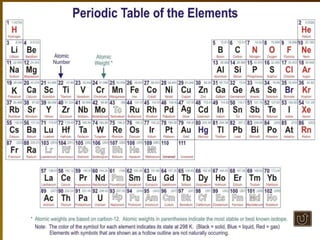
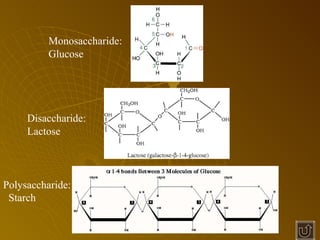
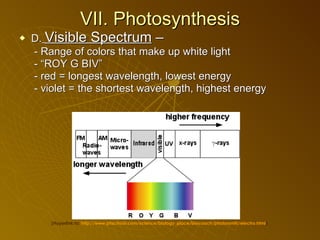
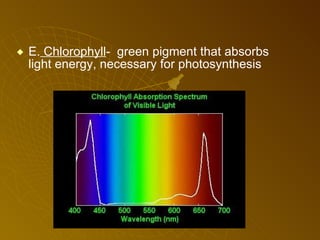
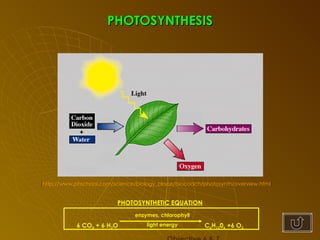
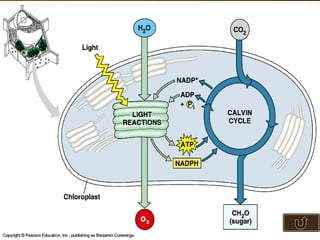
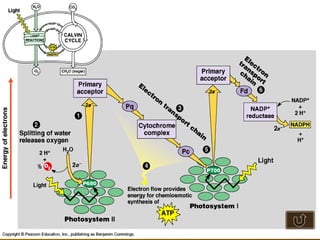
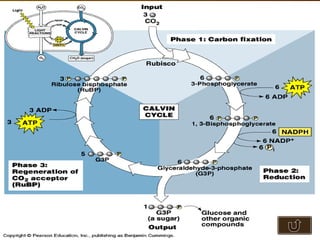
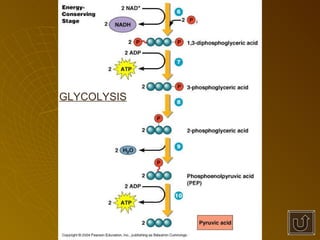
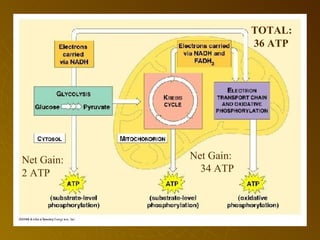
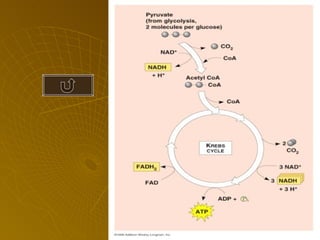
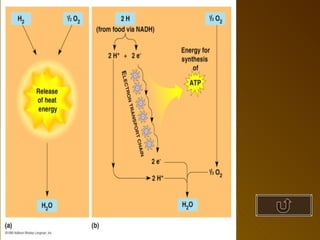
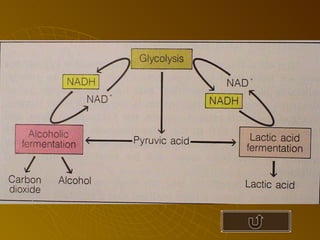
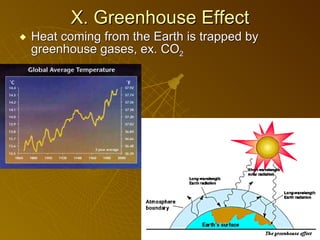
The document summarizes key concepts about photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Photosynthesis uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and glucose through two stages - the light reaction and Calvin cycle. Cellular respiration breaks down glucose to release energy through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle in the mitochondria, and the electron transport chain, using oxygen as the final electron acceptor to produce water. Both processes involve the production and consumption of ATP as an energy carrier.