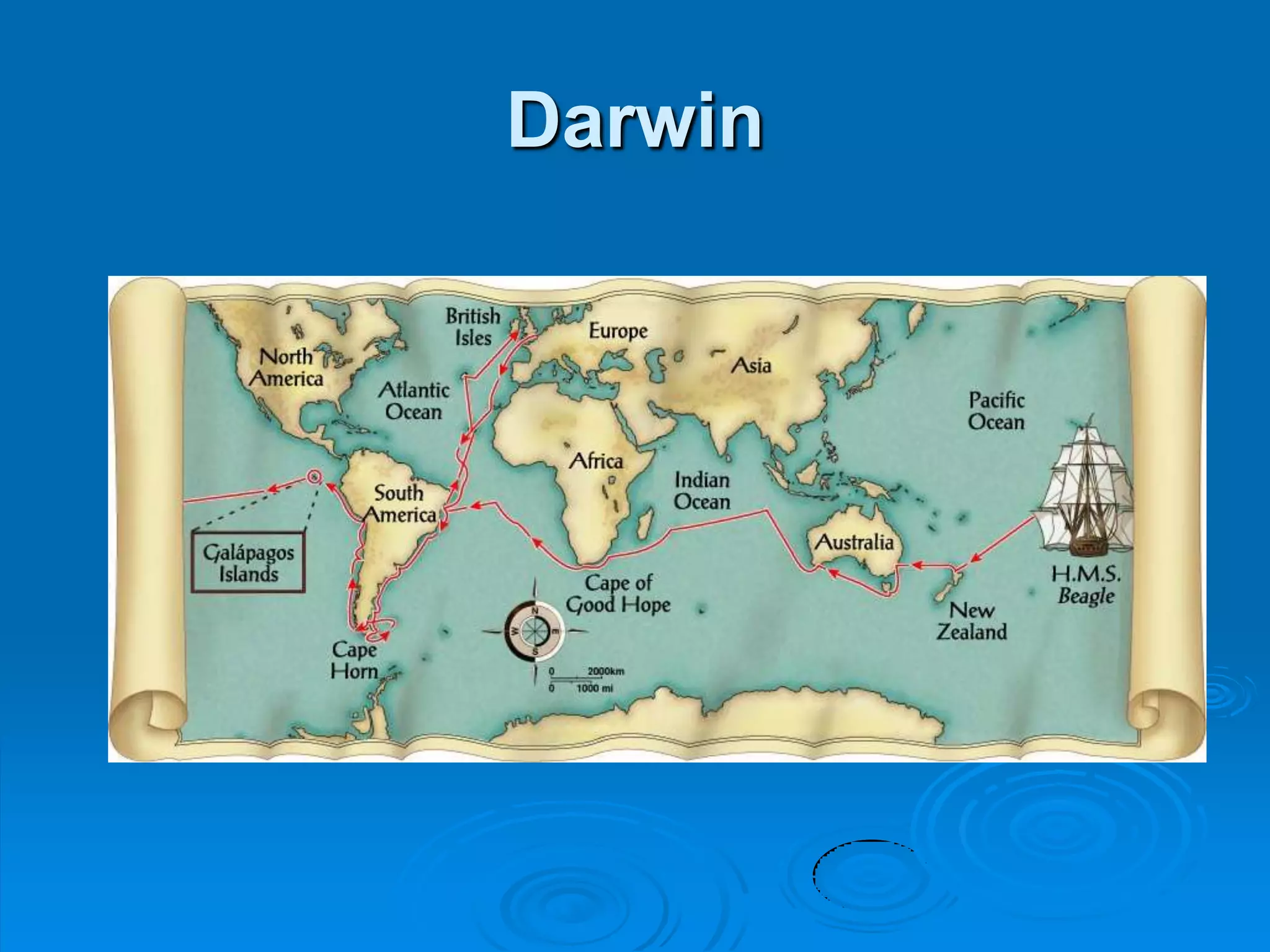
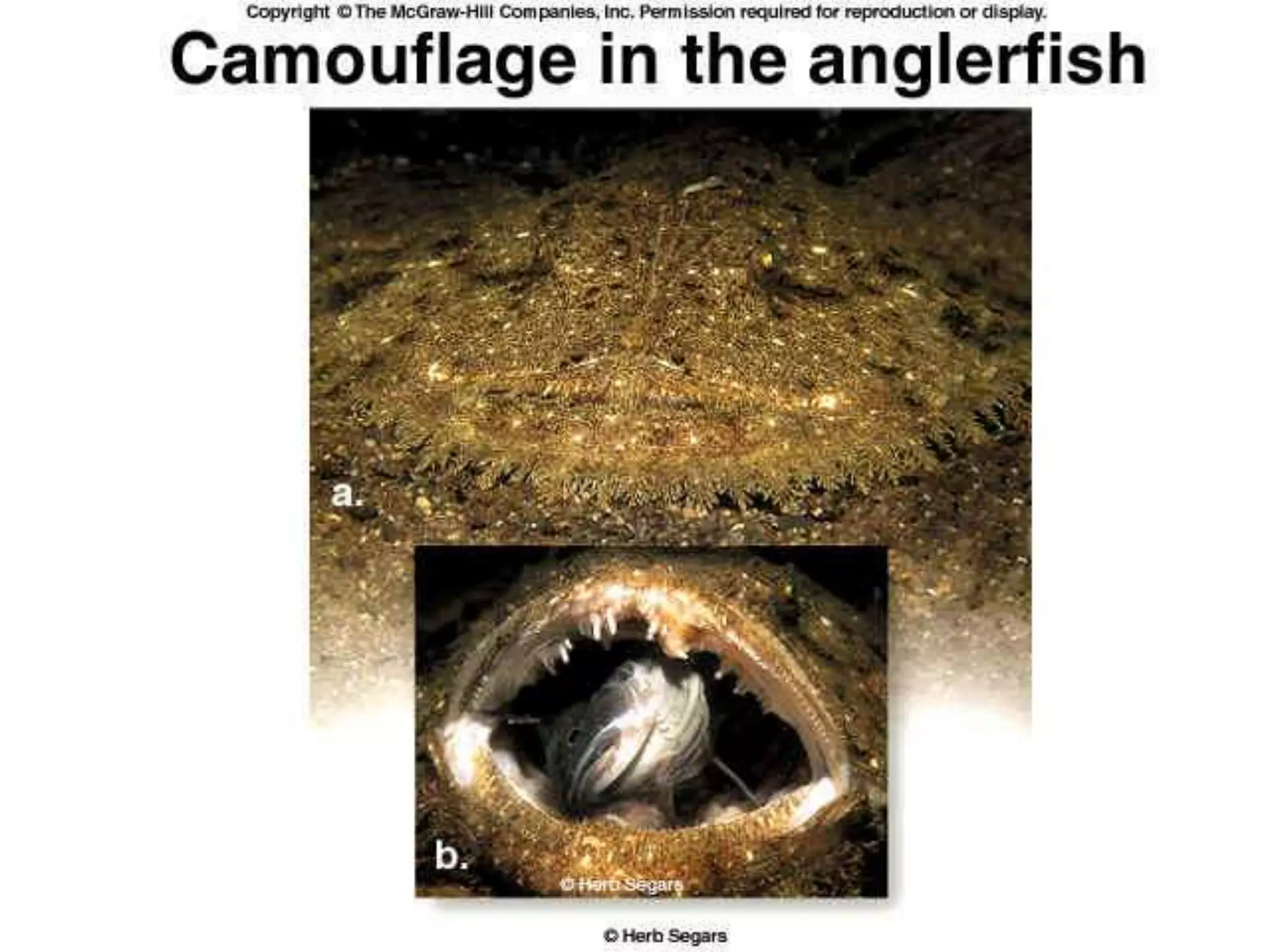
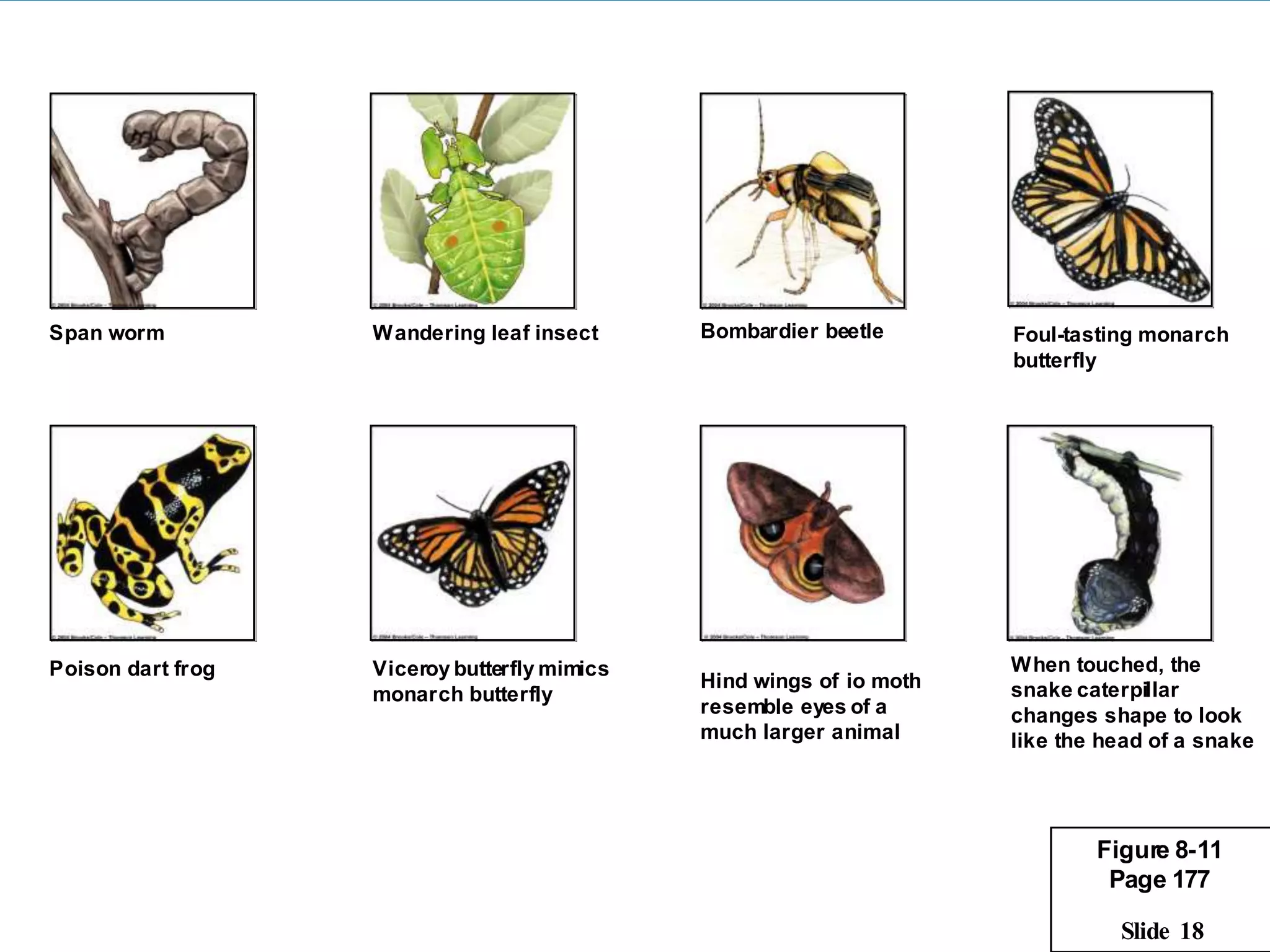
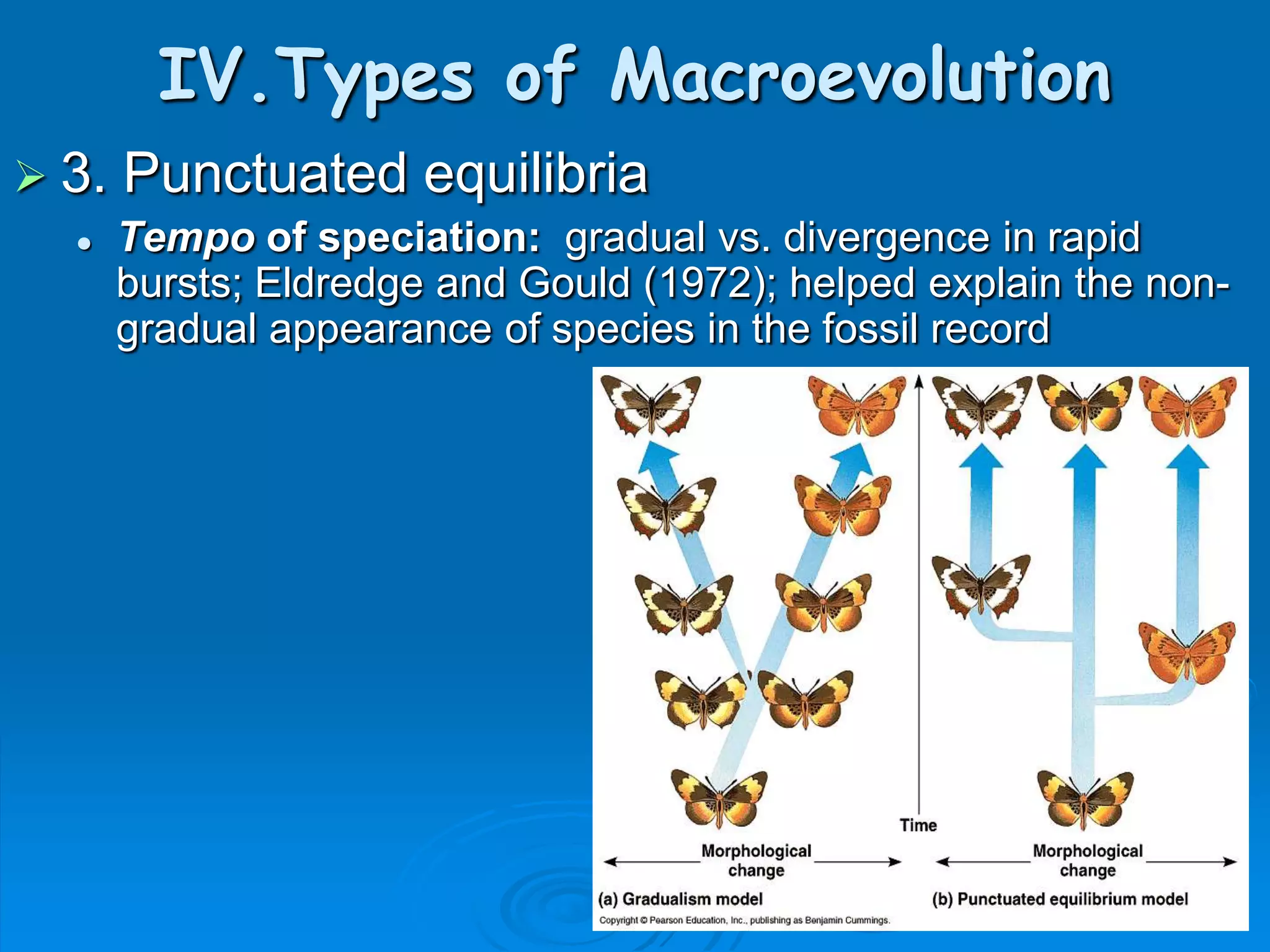
This document provides an overview of evolution and related topics. It defines evolution as any change in allele frequencies in a gene pool over time. The ancient Earth had an atmosphere without oxygen which allowed for the formation of complex organic molecules like amino acids. The first cells were anaerobic and prokaryotic around 3.5 billion years ago. Evidence for evolution includes the fossil record, similarities in living organisms, and DNA/biochemical evidence. Theories of evolution include Lamarck's theory of acquired characteristics and natural selection proposed by Darwin involving variation and the survival of the fittest. Evolution can occur through microevolution within a species or macroevolution leading to new species through gradualism, divergence, or convergent evolution.