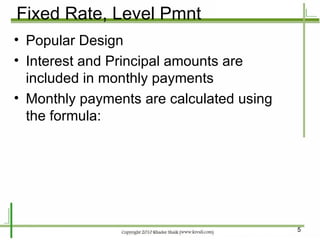
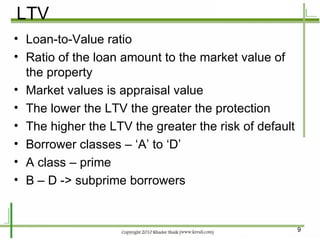
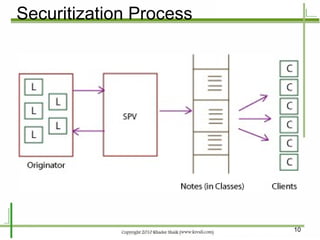
Structured financial products are created through the securitization of assets like mortgages and other loans. Mortgages are pooled together and interests in the cash flows from the pool are sold to investors in the form of mortgage-backed securities. Securitization allows originators to convert illiquid mortgages into tradable securities, replenish funds for further lending, and remove assets from their balance sheets. Common types of mortgage-backed securities include mortgage passthrough securities and collateralized mortgage obligations, which divide the cash flows from mortgage pools into different classes or tranches.