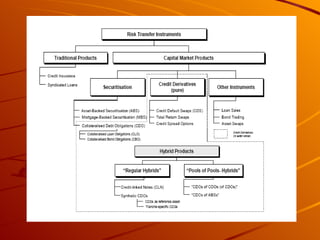
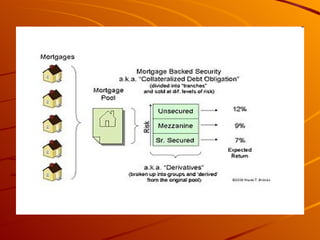
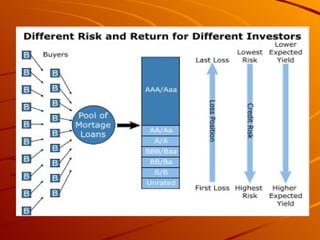
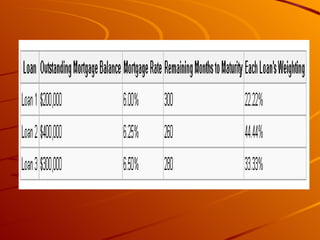
Mortgage backed securities (MBS) are asset-backed securities representing claims on the cash flows from pools of mortgage loans. MBS are created through a process called securitization where mortgages are pooled together and tranched into different risk levels. This allows risk to be transferred and spread across various tranches, generating rated securities from unrated assets. The main types of MBS include pass-through securities for residential and commercial loans, as well as collateralized mortgage obligations.