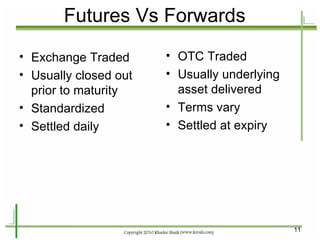
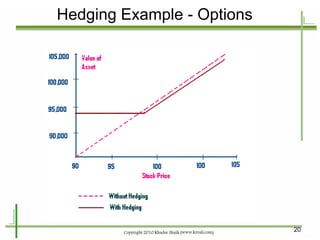
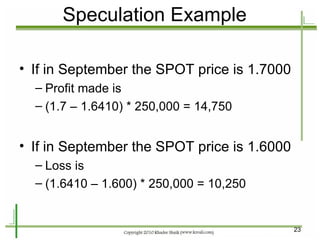
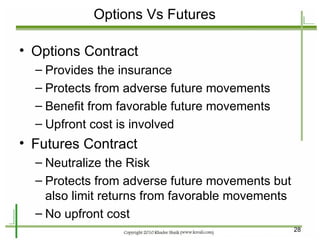
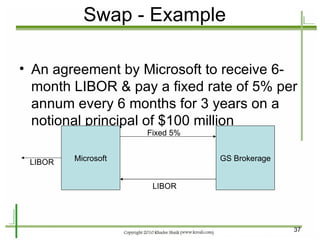
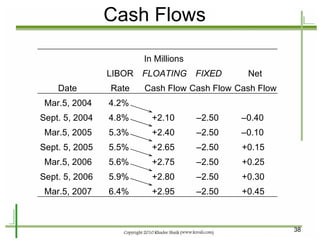
The document provides an introduction to derivatives markets. It defines derivatives as financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset. Major classes of derivatives discussed include futures, forwards, options, and swaps. Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an asset in the future. Forwards are similar but traded over-the-counter and non-standardized. Options provide the right to buy or sell the underlying asset. Swaps involve exchanging one set of cash flows for another. Derivatives are used for hedging risk, speculation, and arbitrage opportunities.