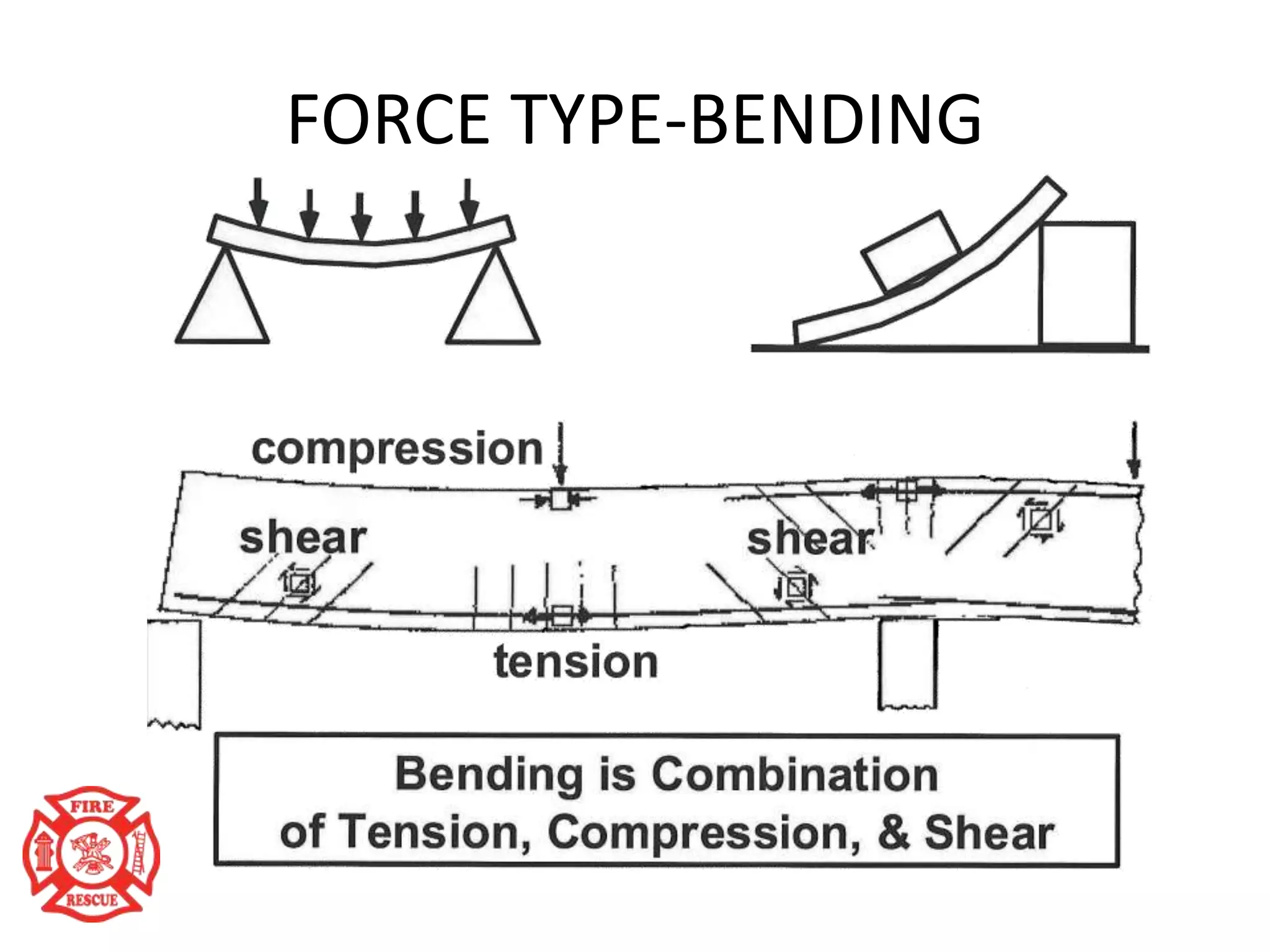
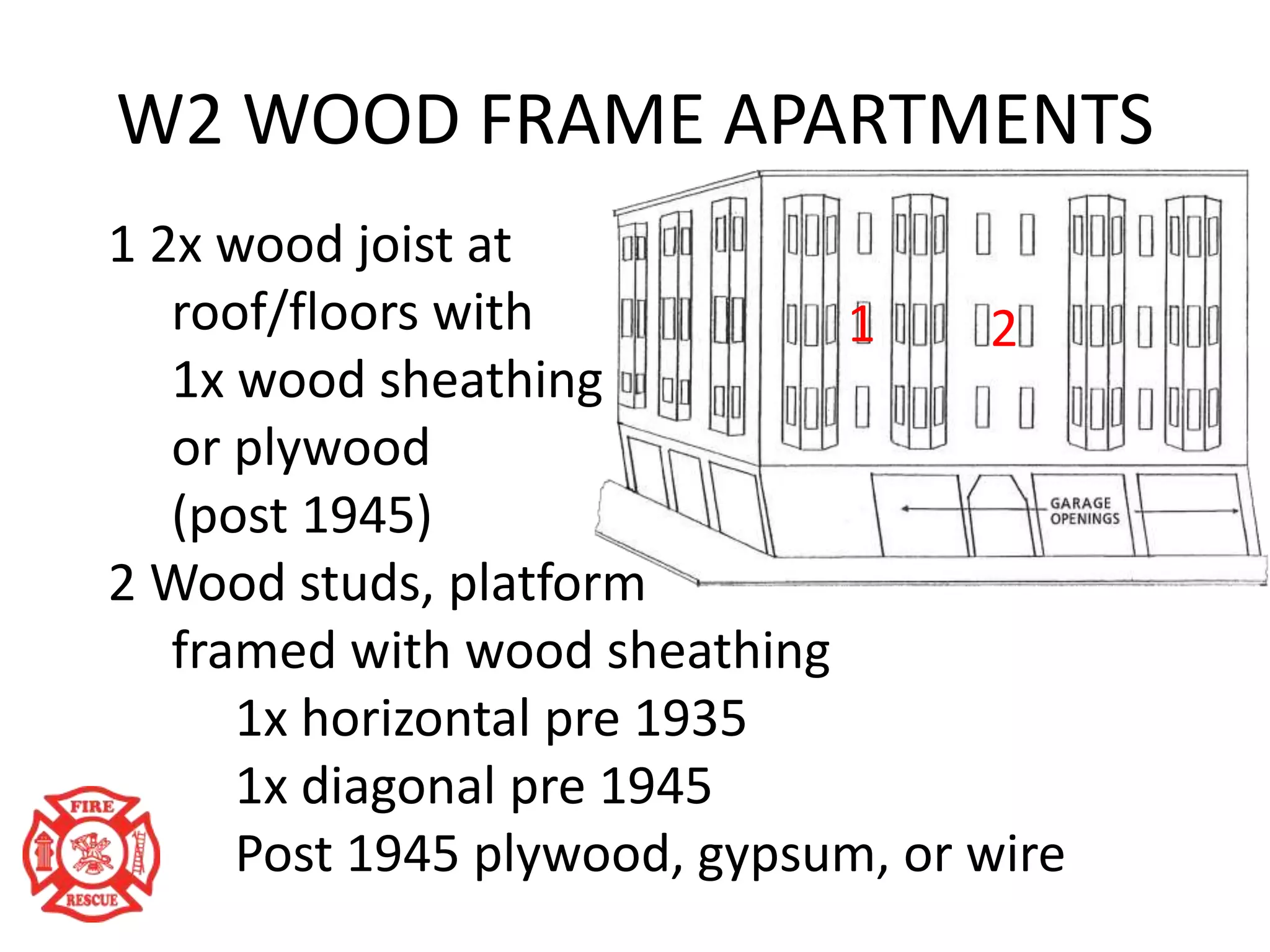
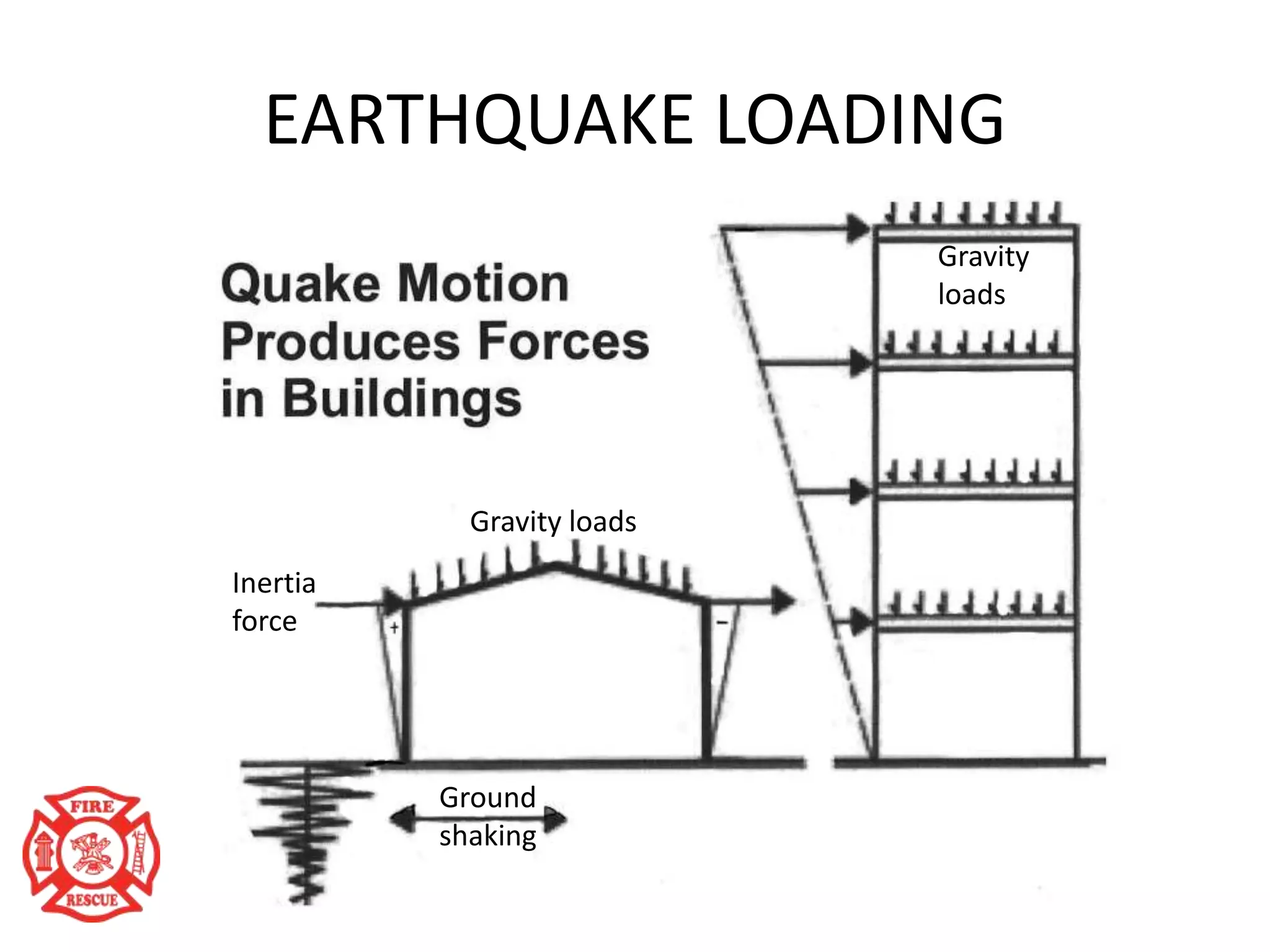
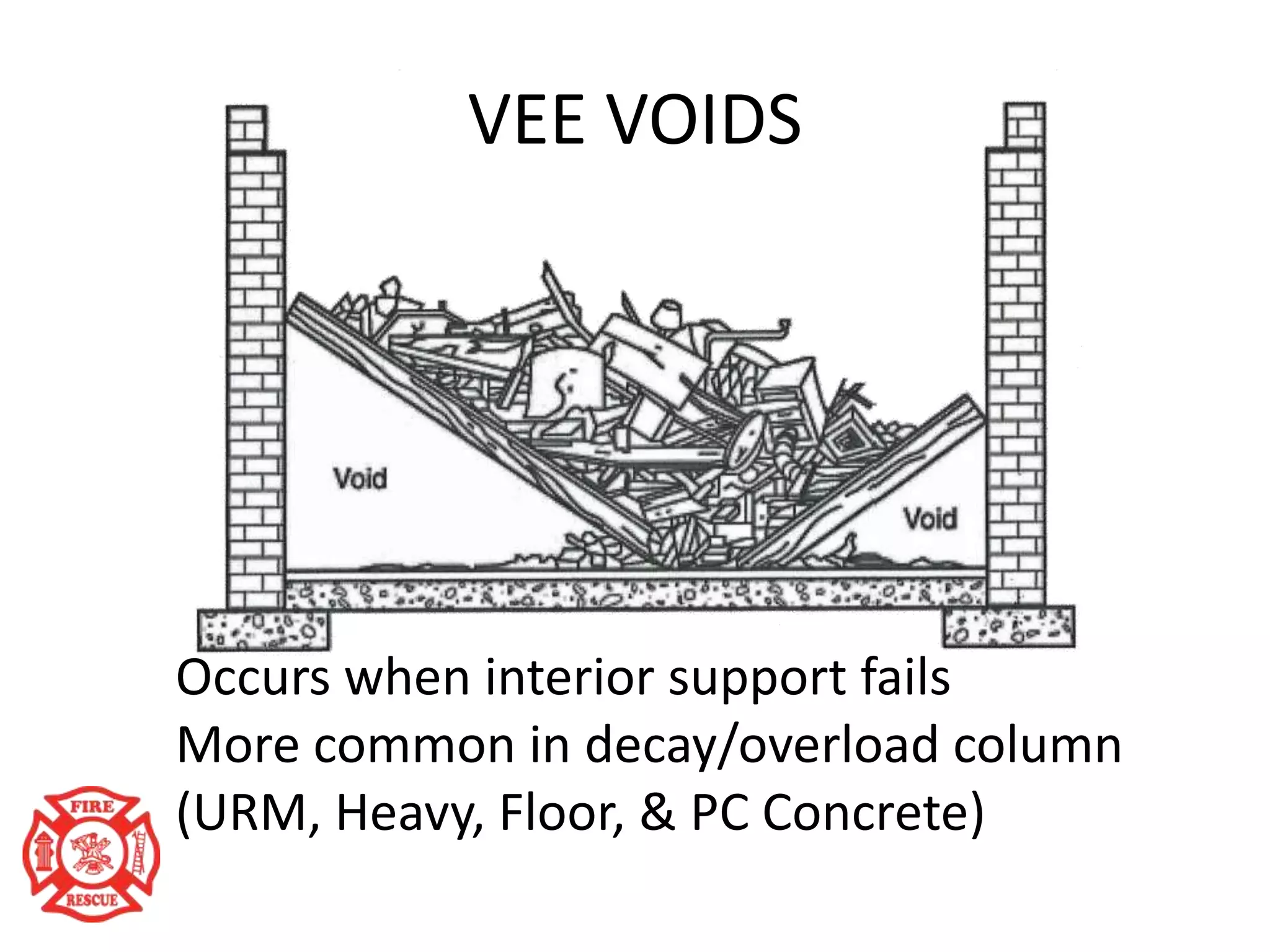
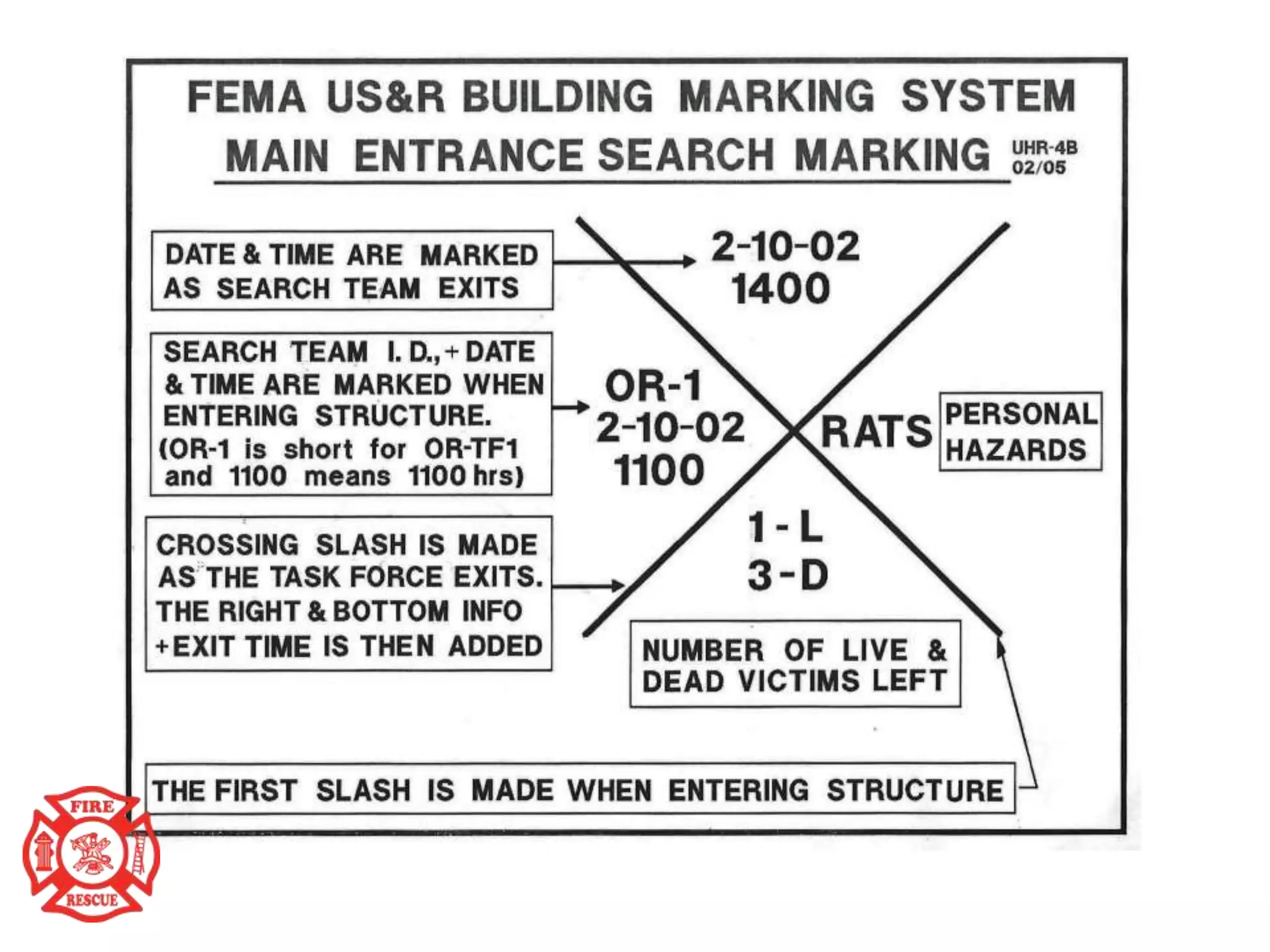
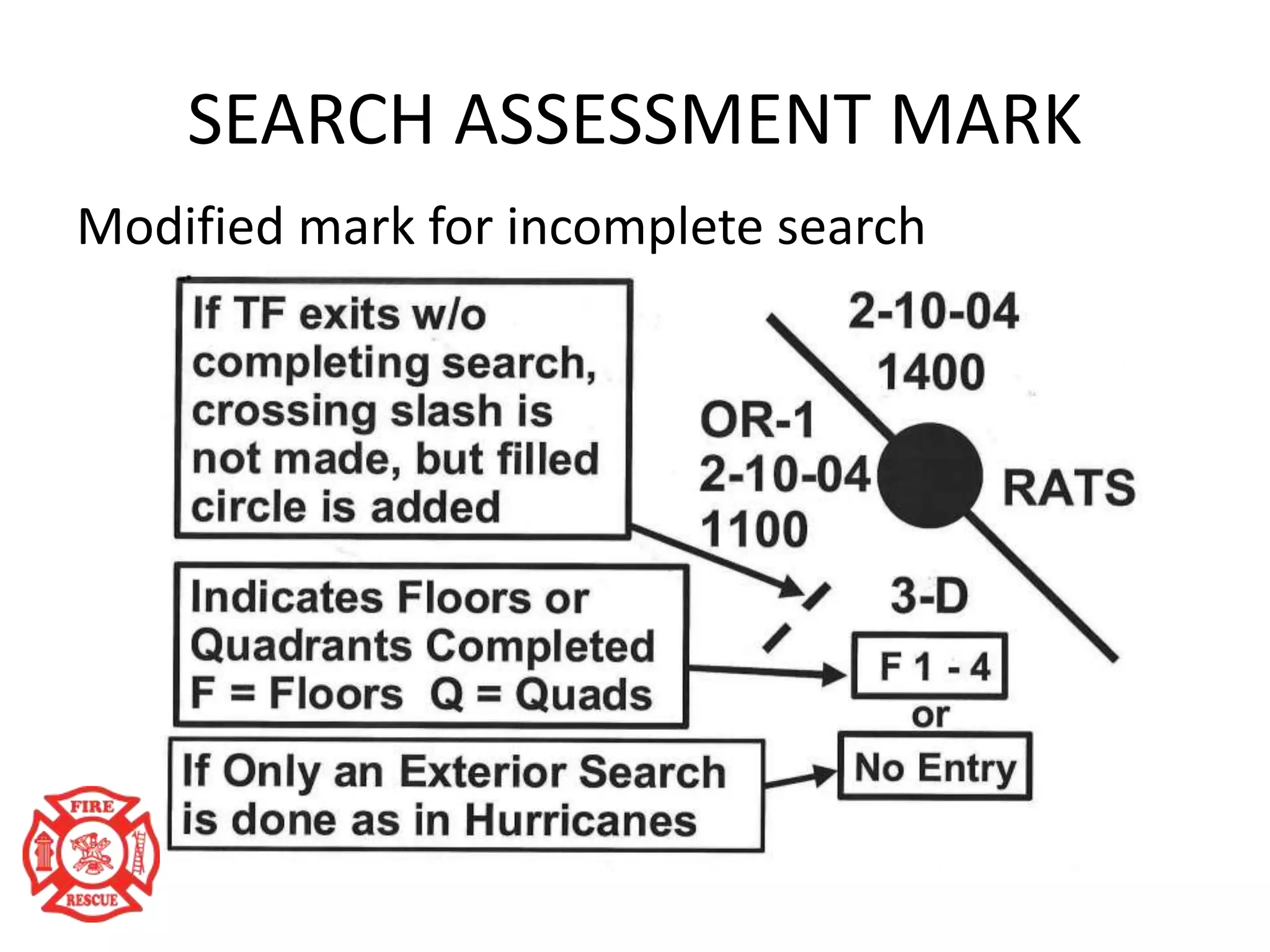
The document outlines training objectives for structural collapse rescue awareness, emphasizing familiarity with building systems, collapse patterns, and hazards. It discusses operational capabilities and necessary protective equipment, alongside the importance of swift rescue efforts to save trapped victims while minimizing risks. Key performance aspects of various building types and their characteristics, as well as potential hazards, are summarized for effective incident management.