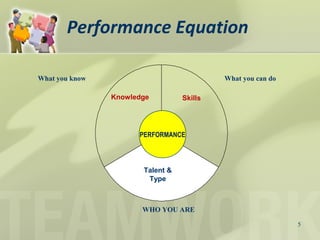
This document discusses strengths-based teamwork and how focusing on individual strengths rather than weaknesses leads to greater performance and engagement. It defines teamwork as blending individual strengths in a common direction towards meaningful goals. Strengths are refined talents combined with skill and knowledge that allow consistent top performance. However, most people spend only 17% of their time using their strengths. Focusing on weaknesses can lead to frustration, while focusing on strengths builds confidence and motivation, resulting in 73% engagement. Recognizing each person's top 34 strengths themes allows for optimizing roles. In summary, a strengths approach identifies and leverages natural talents for maximum productivity and satisfaction.