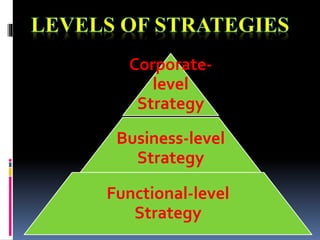
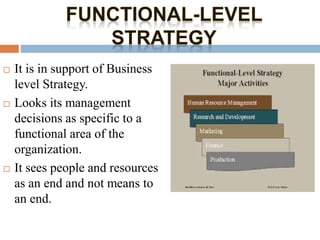
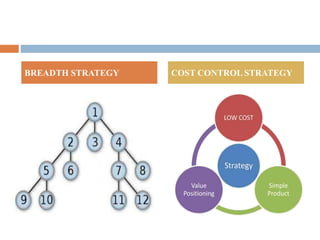
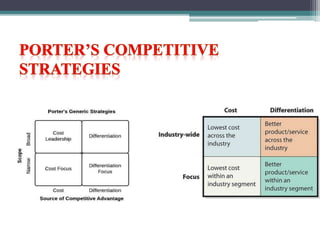
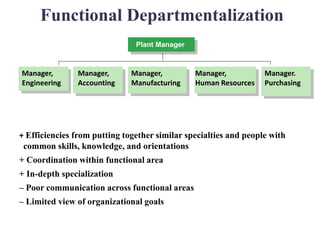
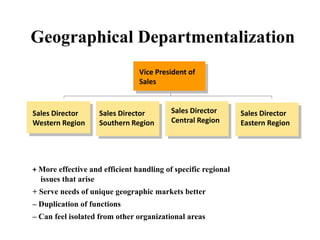
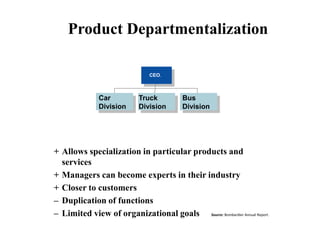
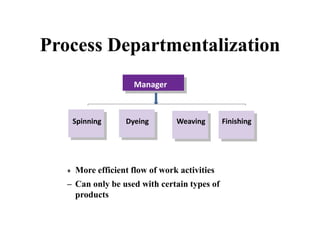
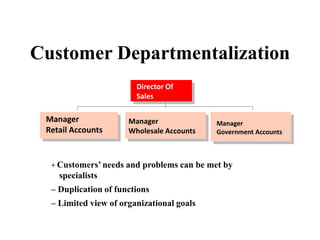
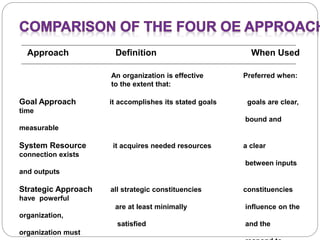
This document discusses various aspects of organizational strategy and effectiveness. It begins by defining strategy and the different levels of strategy - corporate, business, and functional. It then covers organizational design elements like work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command and Miles and Snow's strategic types. Finally, it discusses approaches to measuring organizational effectiveness like the goal, internal process, system resource and strategic approaches.