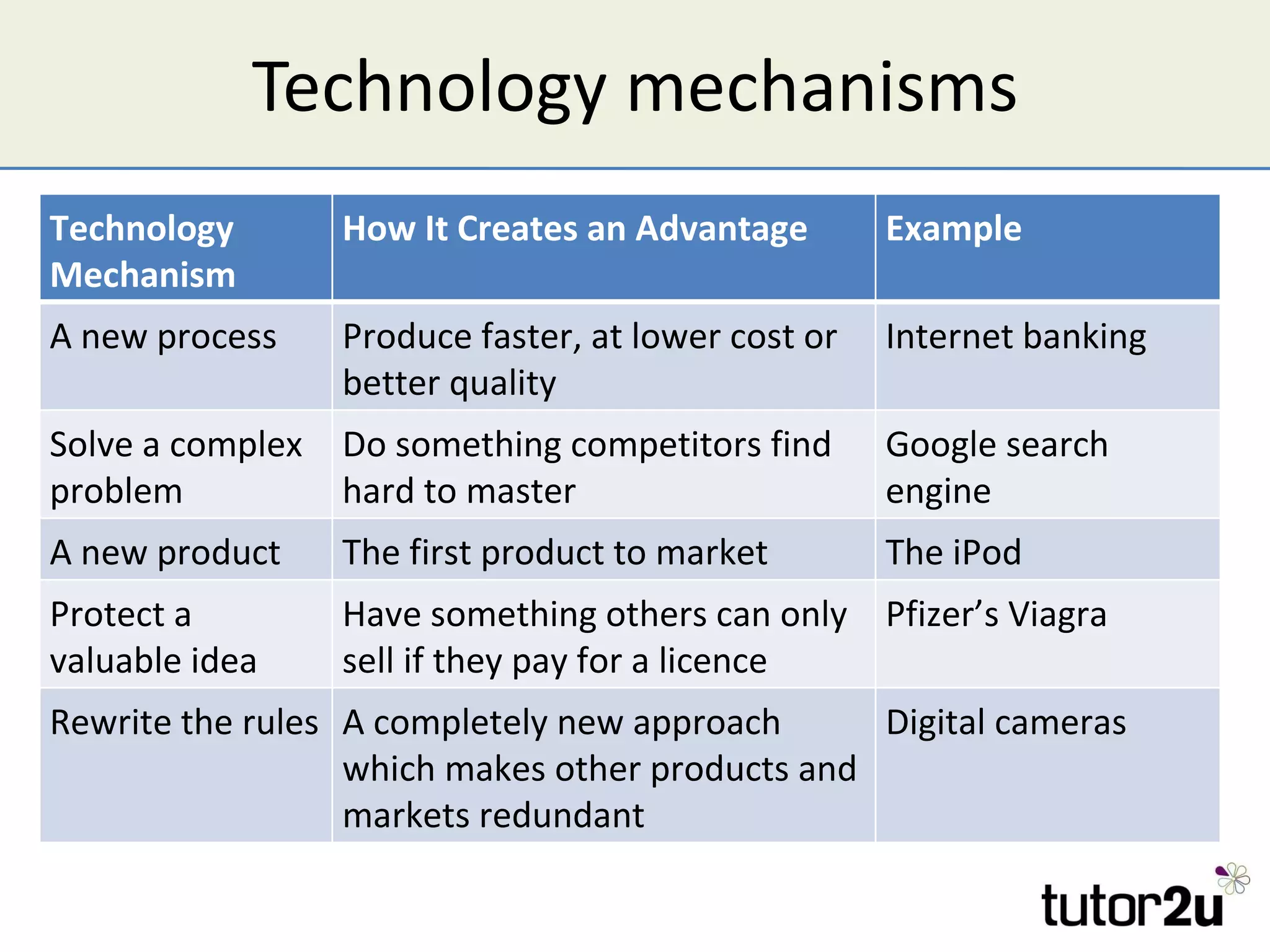
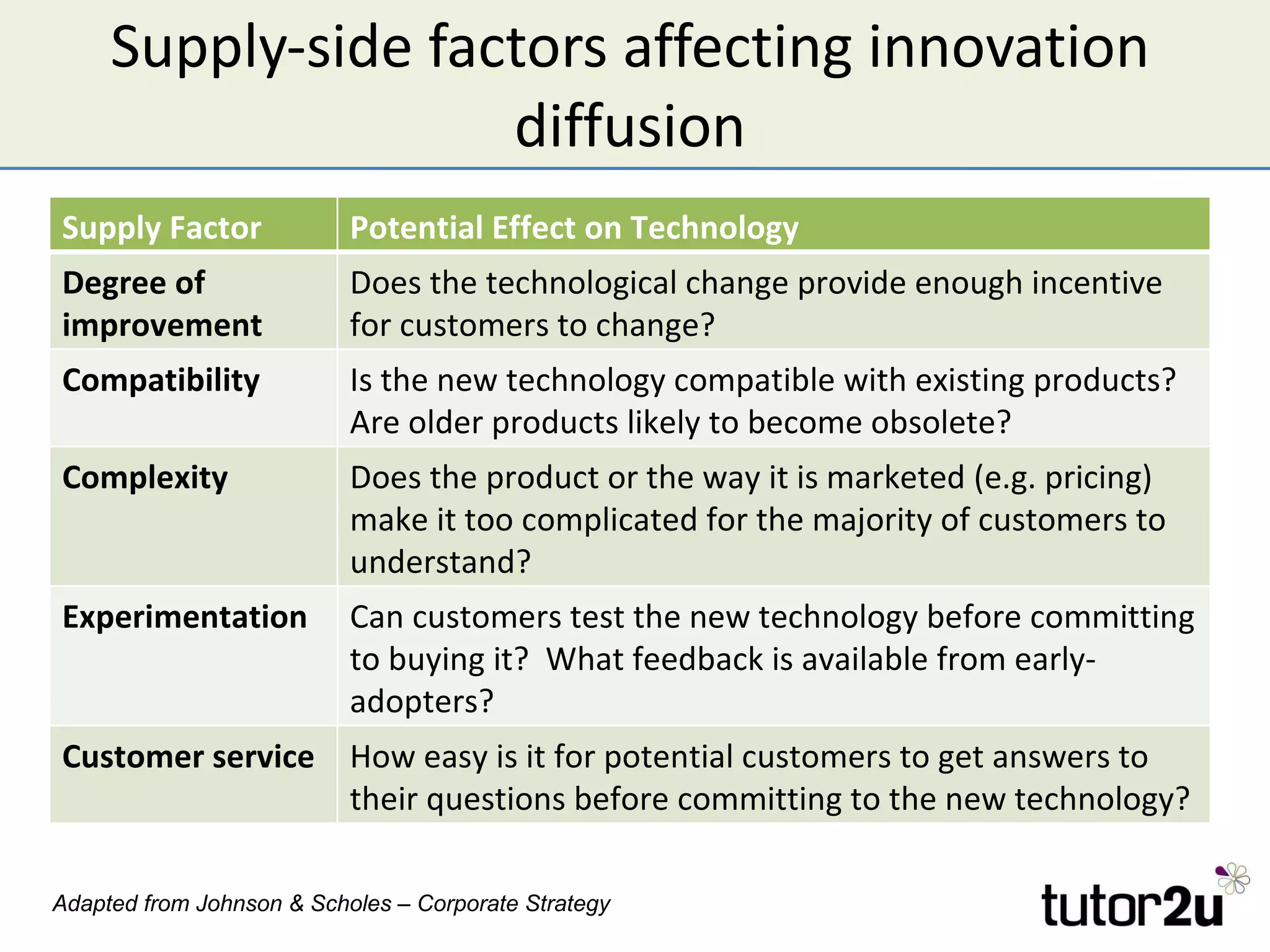
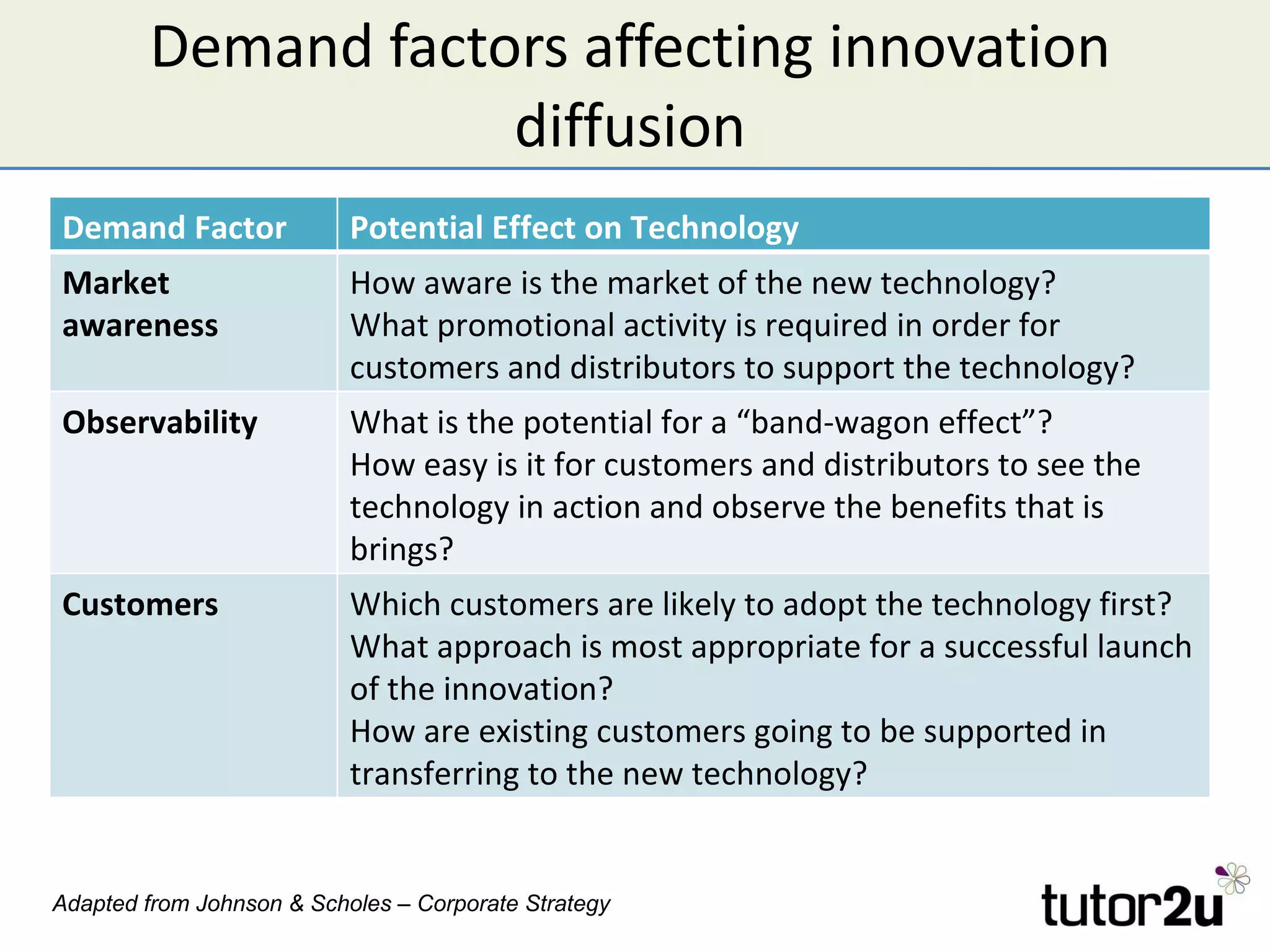
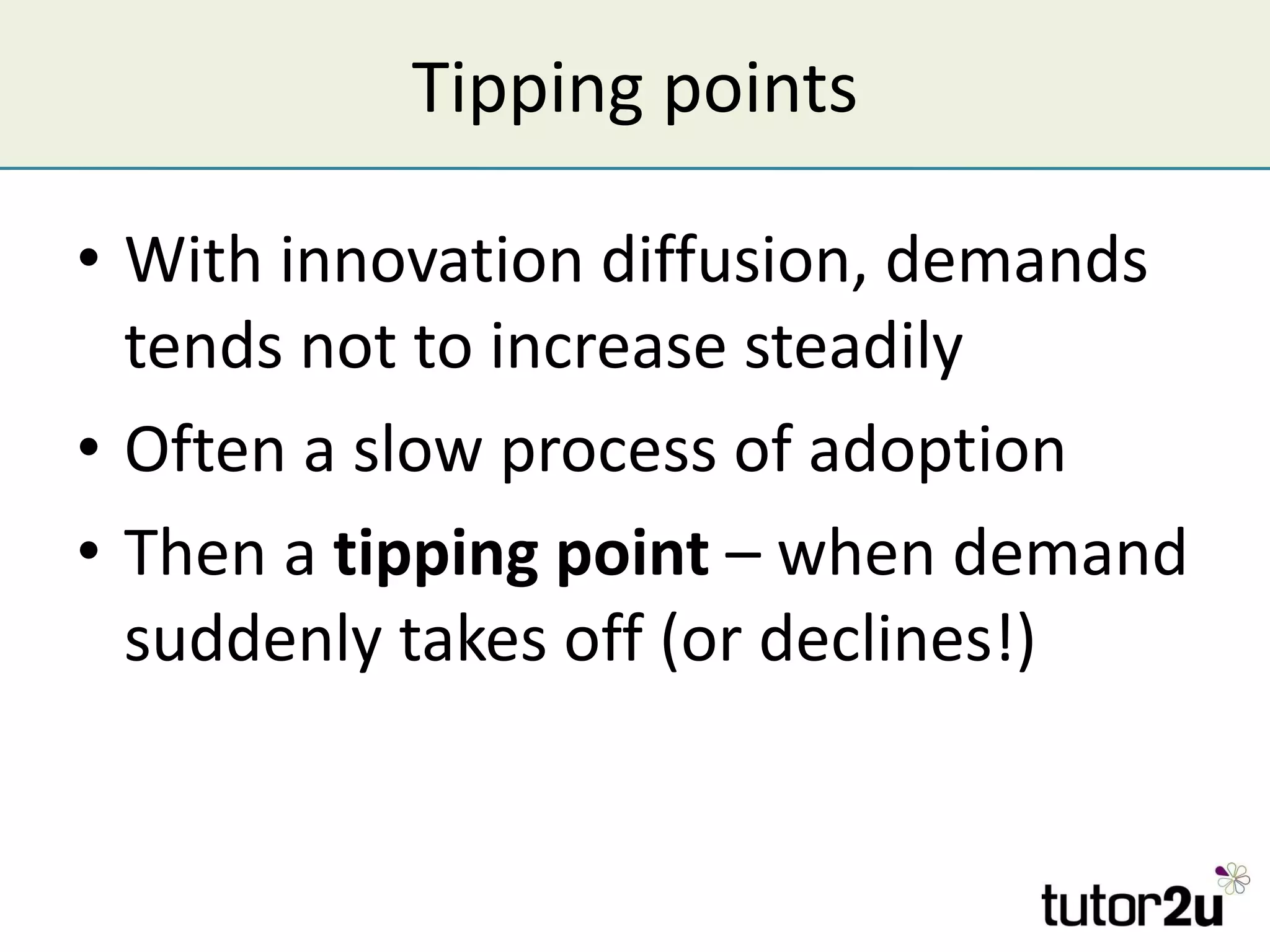
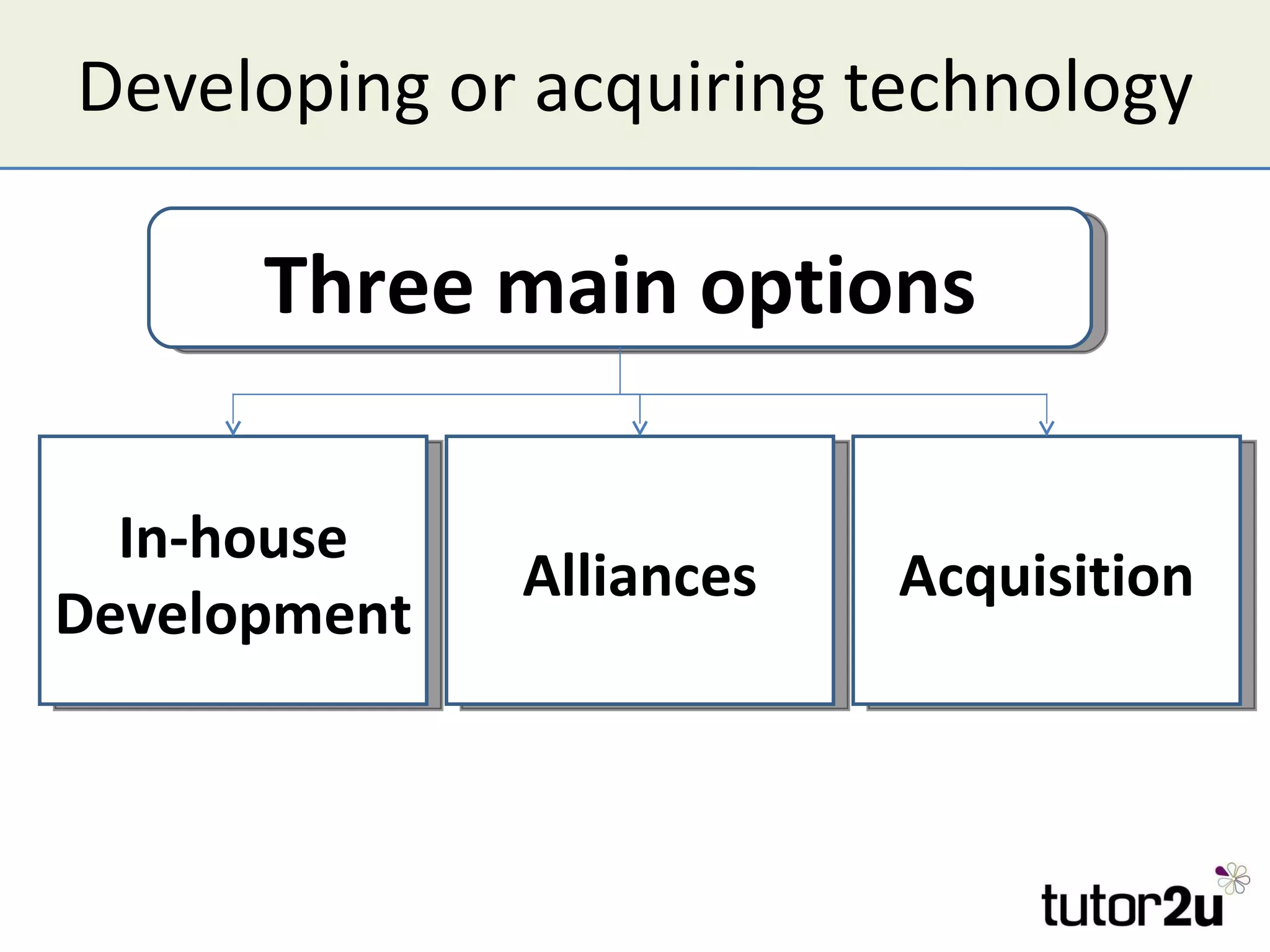
Technology can provide competitive advantages if a company can exploit it before competitors. The document discusses how technology affects Porter's Five Forces and provides examples of how new processes, products, or approaches can impact barriers to entry, substitutes, and competitive rivalry. It also examines factors that influence the adoption of new technologies like the degree of improvement, compatibility with existing products, and customer awareness and observability of the new technology.