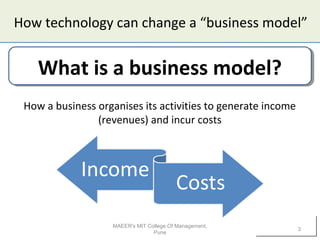
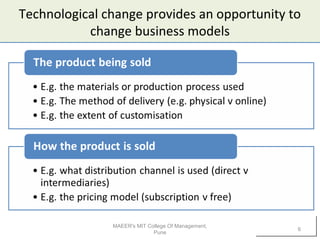
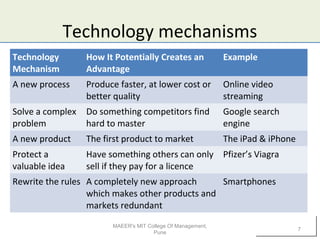
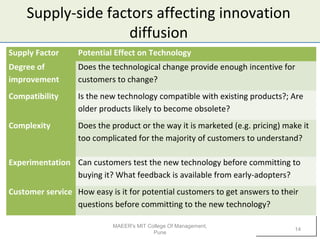
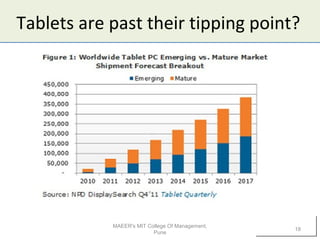
1) Technology can impact businesses by enabling new business models or changing existing ones. It allows companies to organize their activities and generate revenue differently.
2) Companies must assess whether technology presents an opportunity or threat to their competitive position. It may allow some businesses to gain an advantage while threatening others.
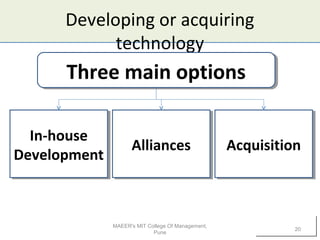
3) When developing new technologies, companies can choose between in-house development, alliances, or acquisitions, with each approach having different risks and requirements.