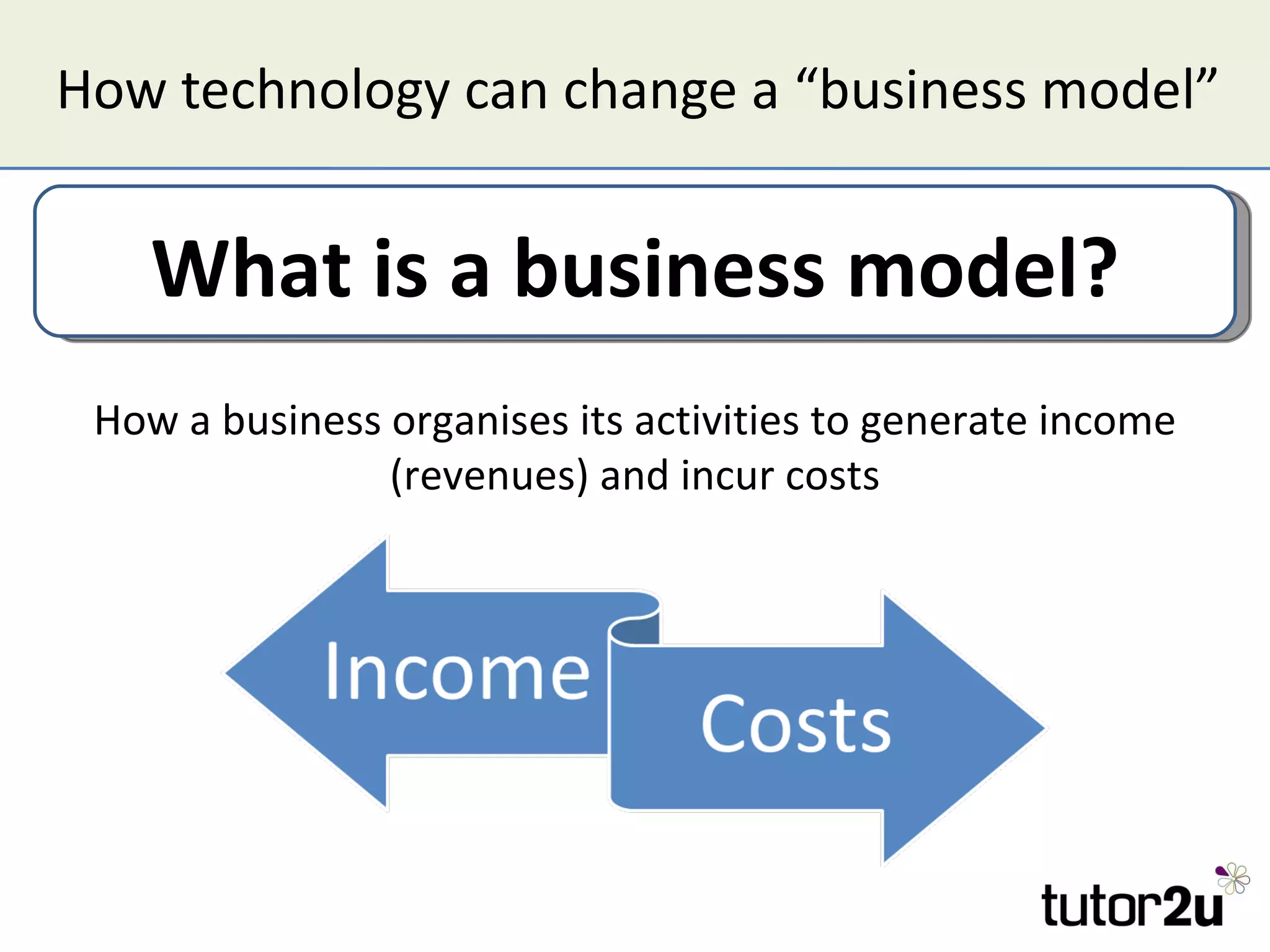
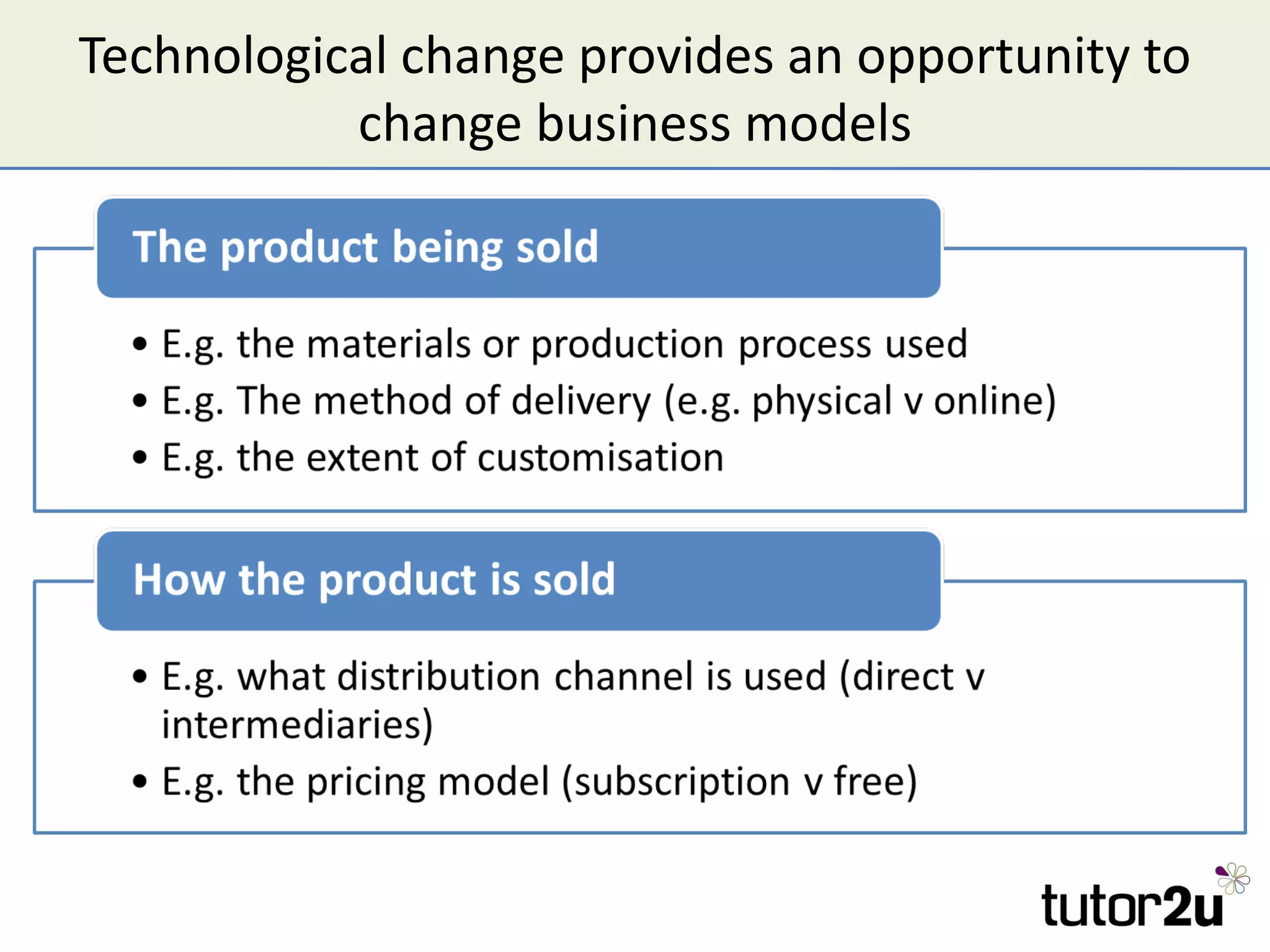
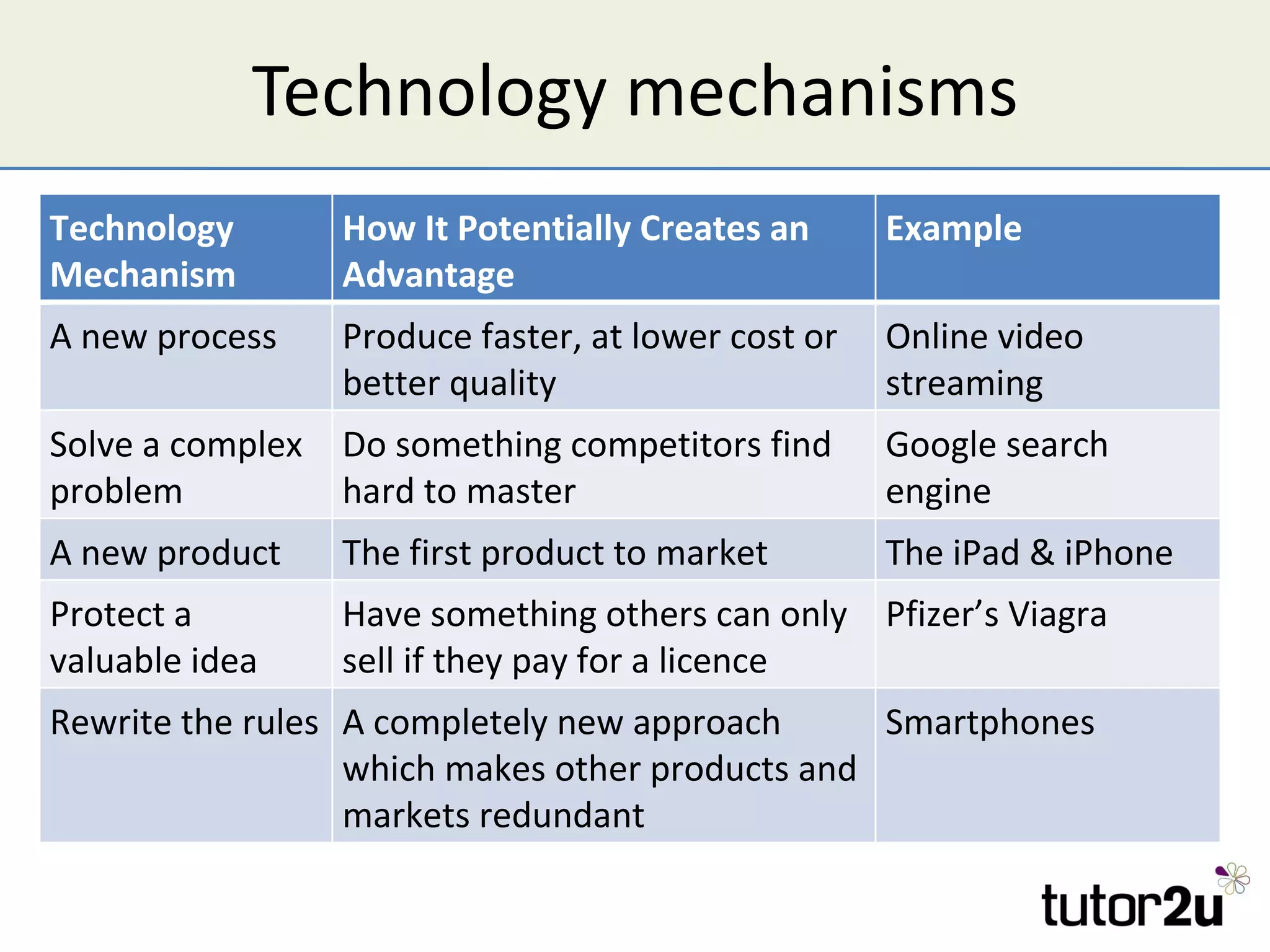
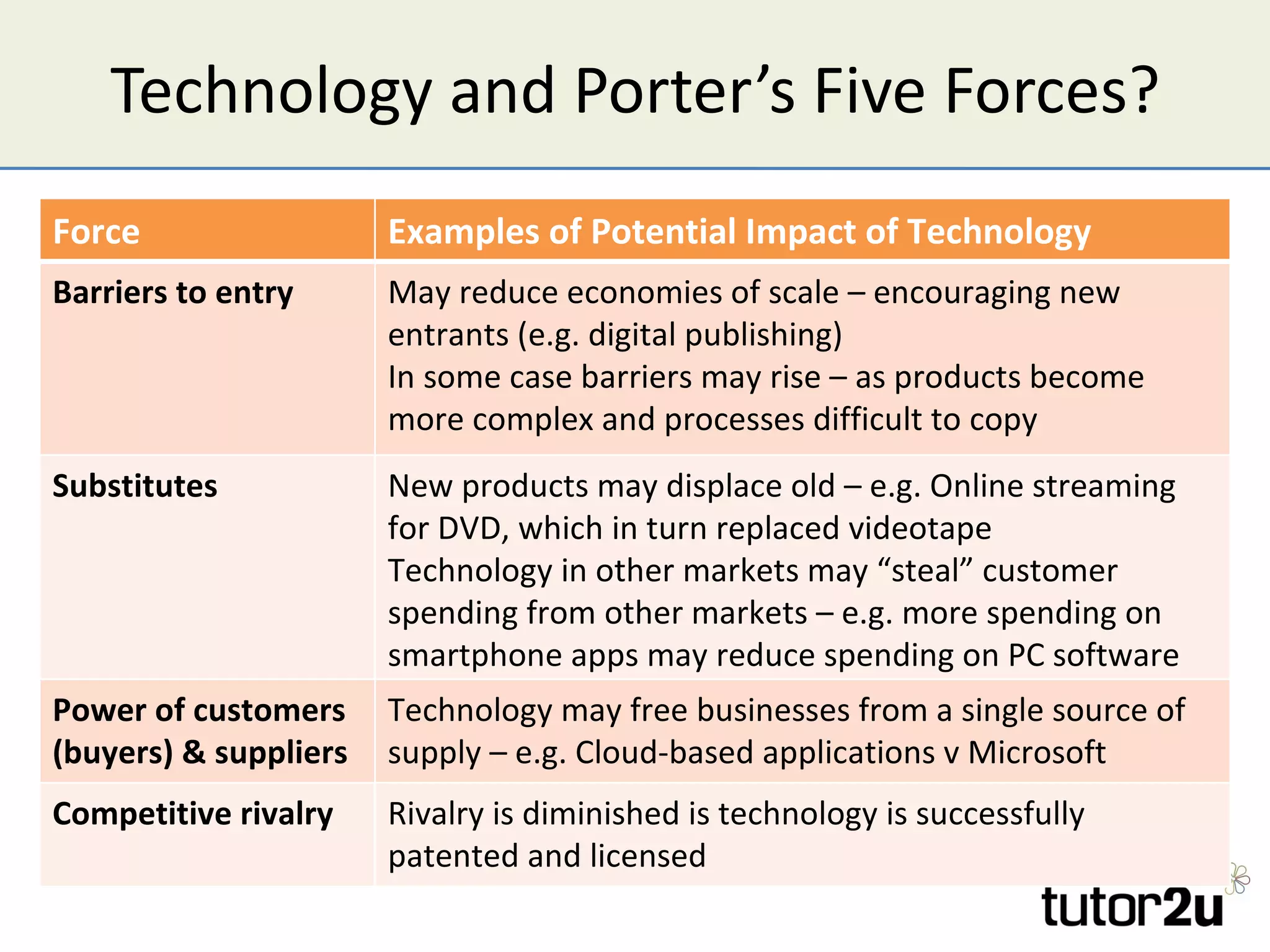
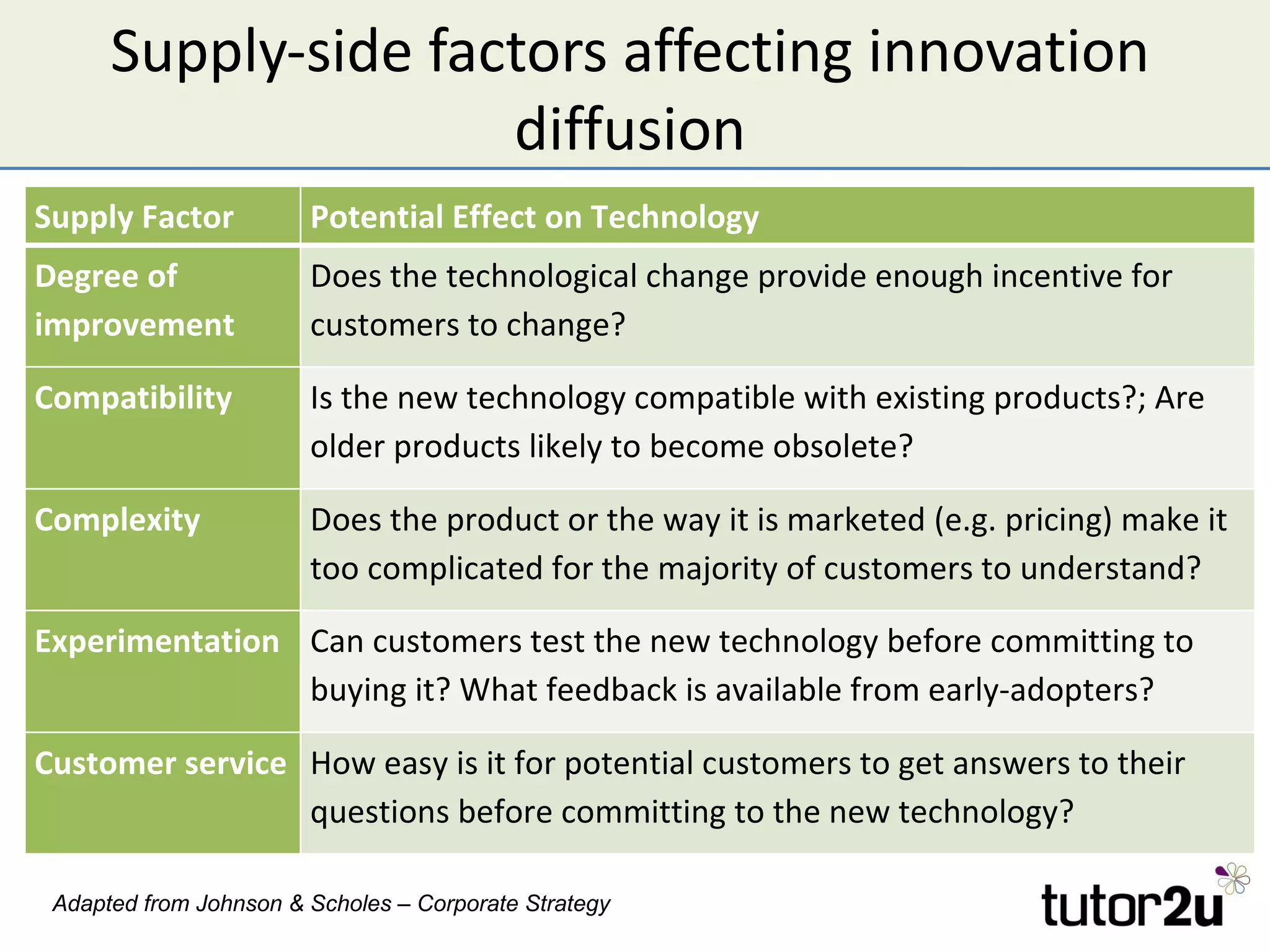
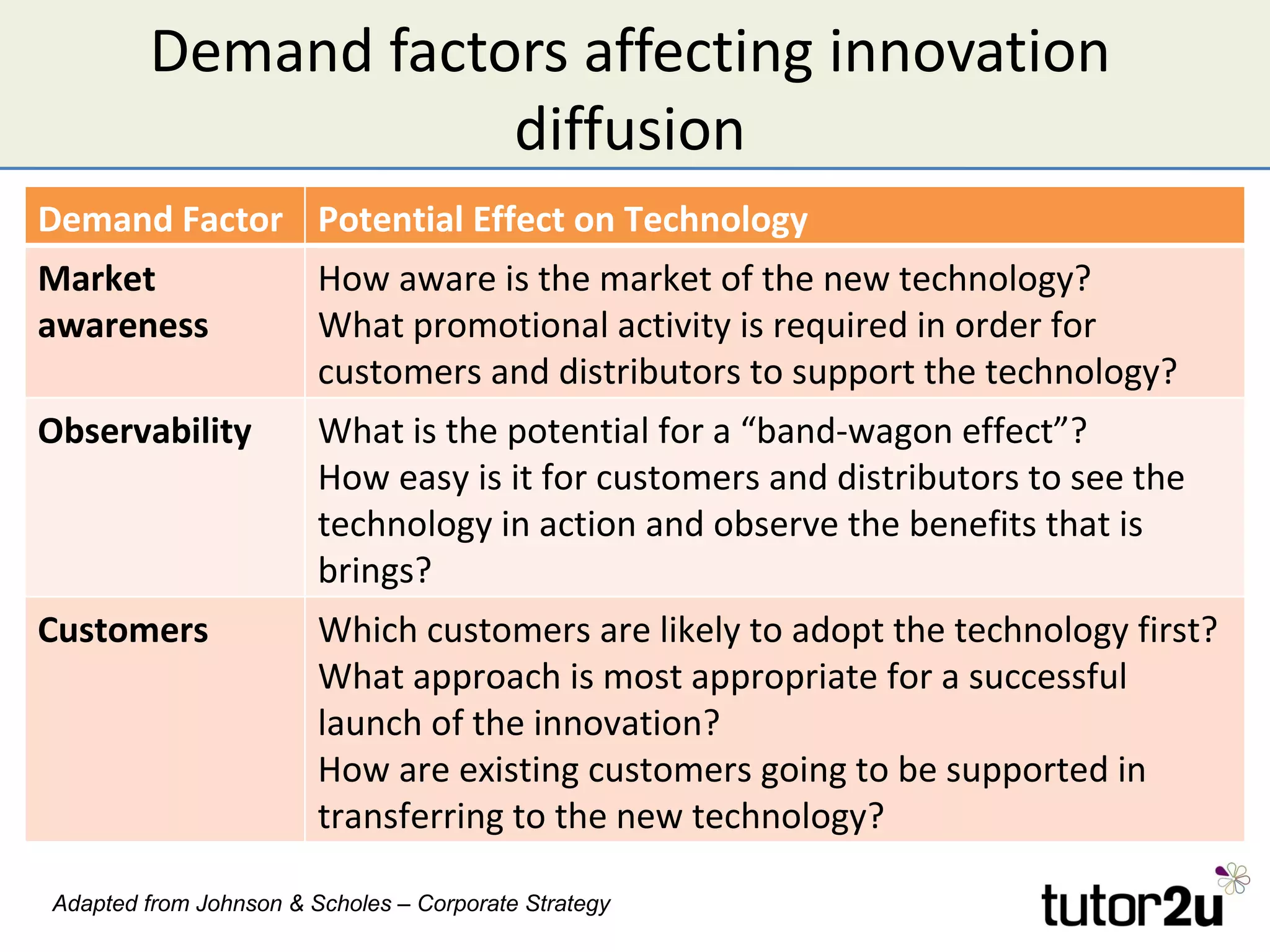
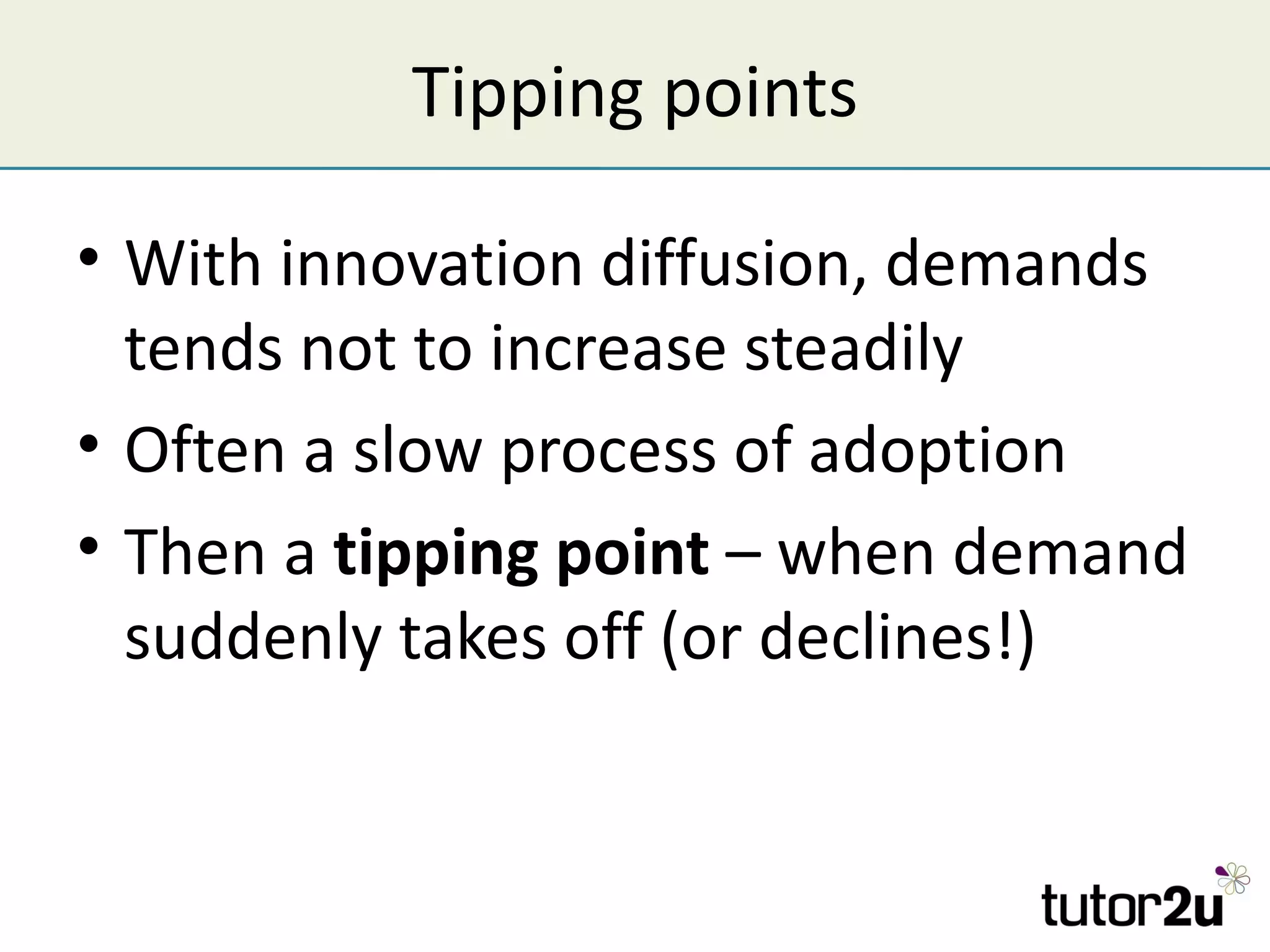
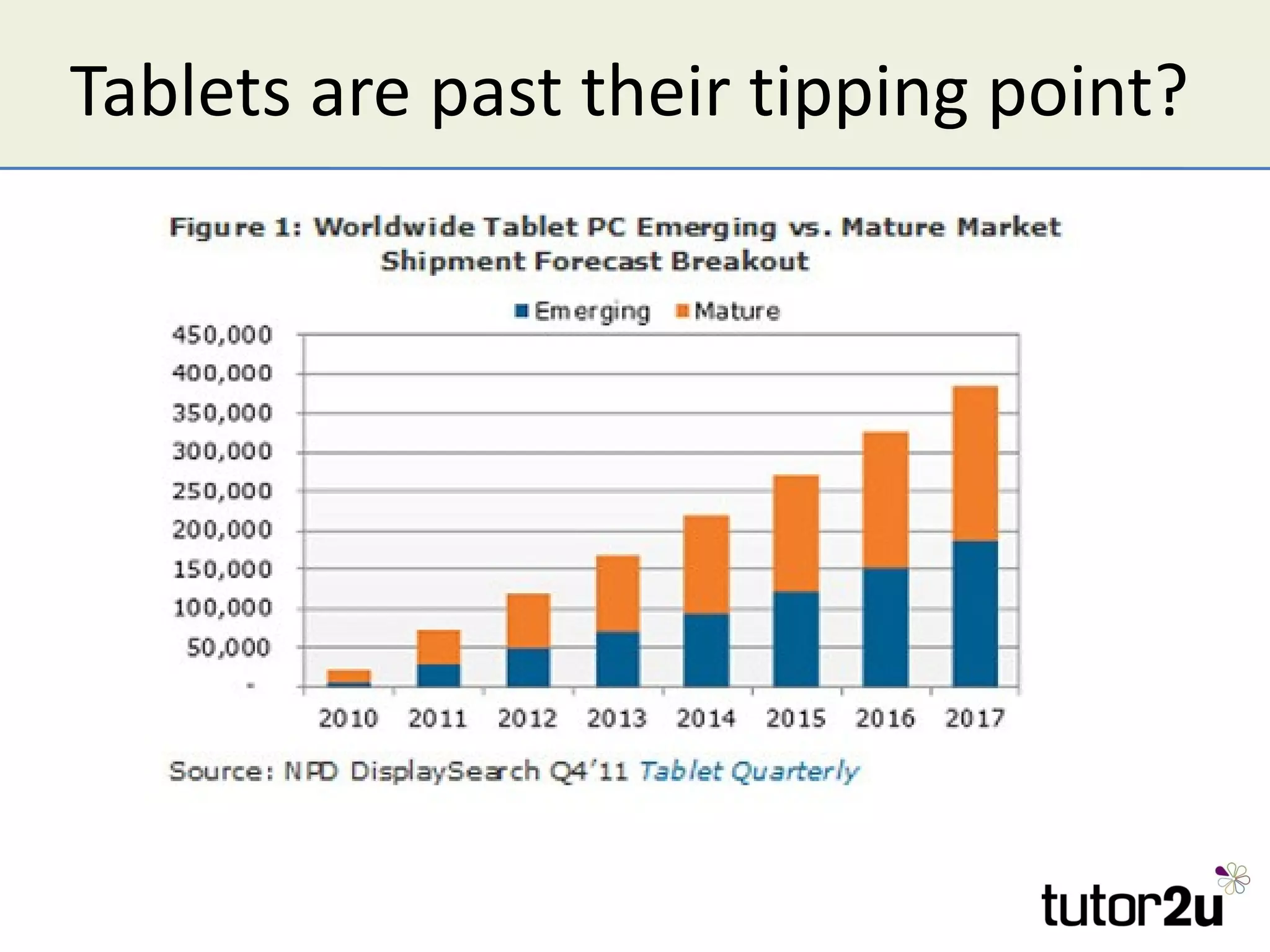
The document discusses the strategic importance of technology in business, emphasizing that while it can drive competitive advantage, rapid technological change can also pose significant challenges. It outlines how technology can transform business models, introduces concepts like innovation diffusion and tipping points, and explores options for acquiring new technology, including in-house development, alliances, and acquisitions. Additionally, it examines the impact of technology on competitive forces such as barriers to entry and the power of customers.