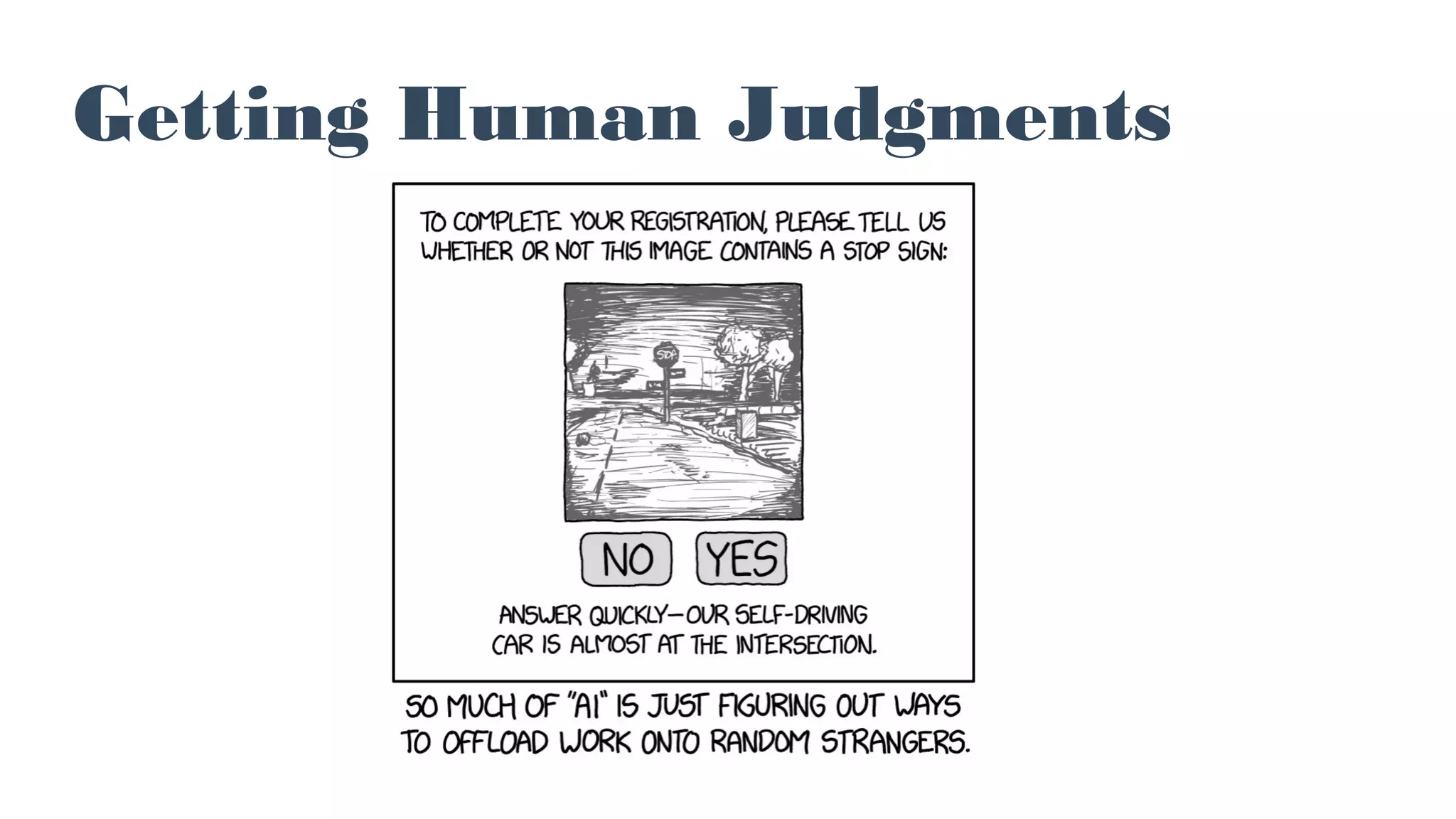
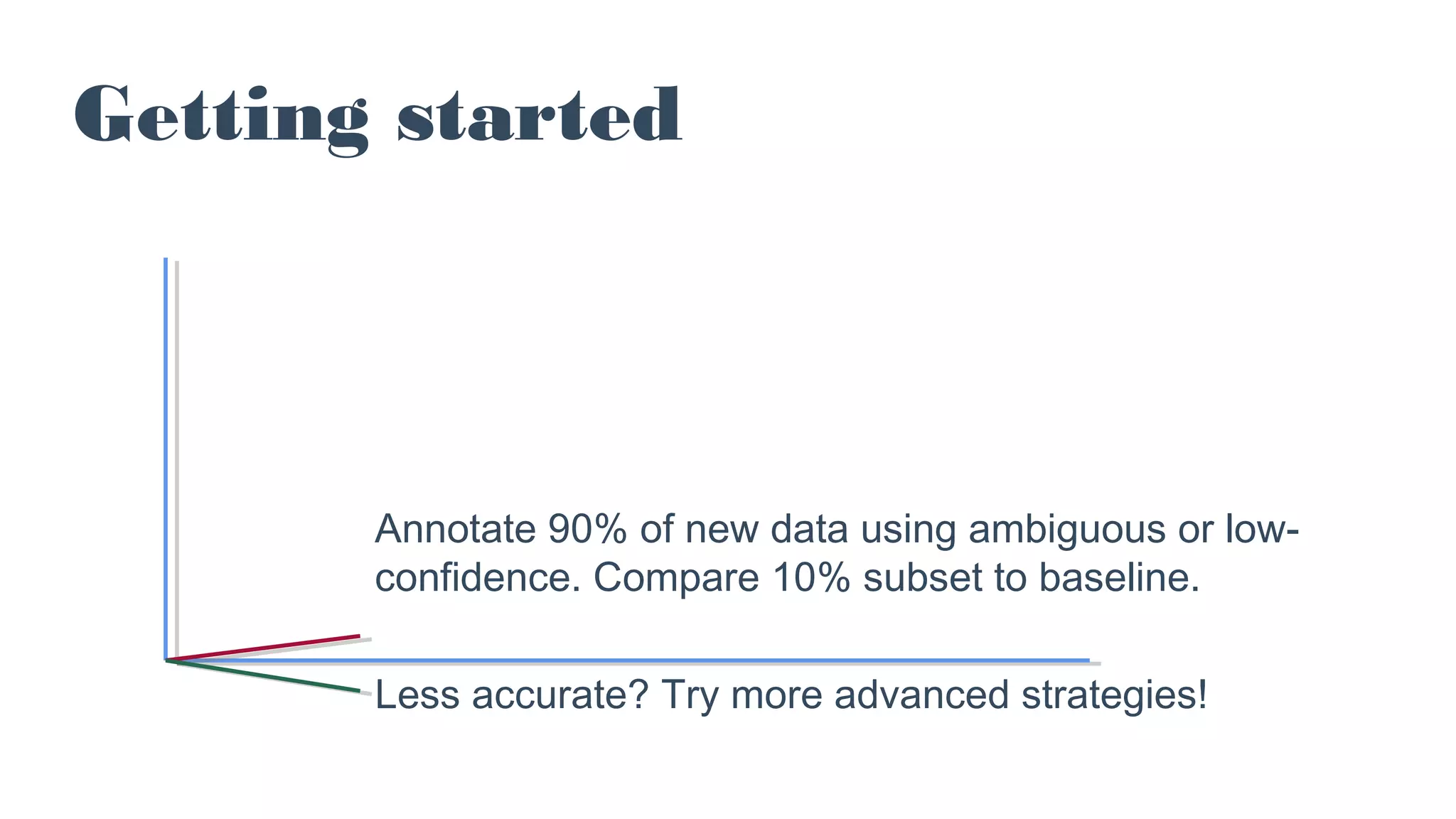
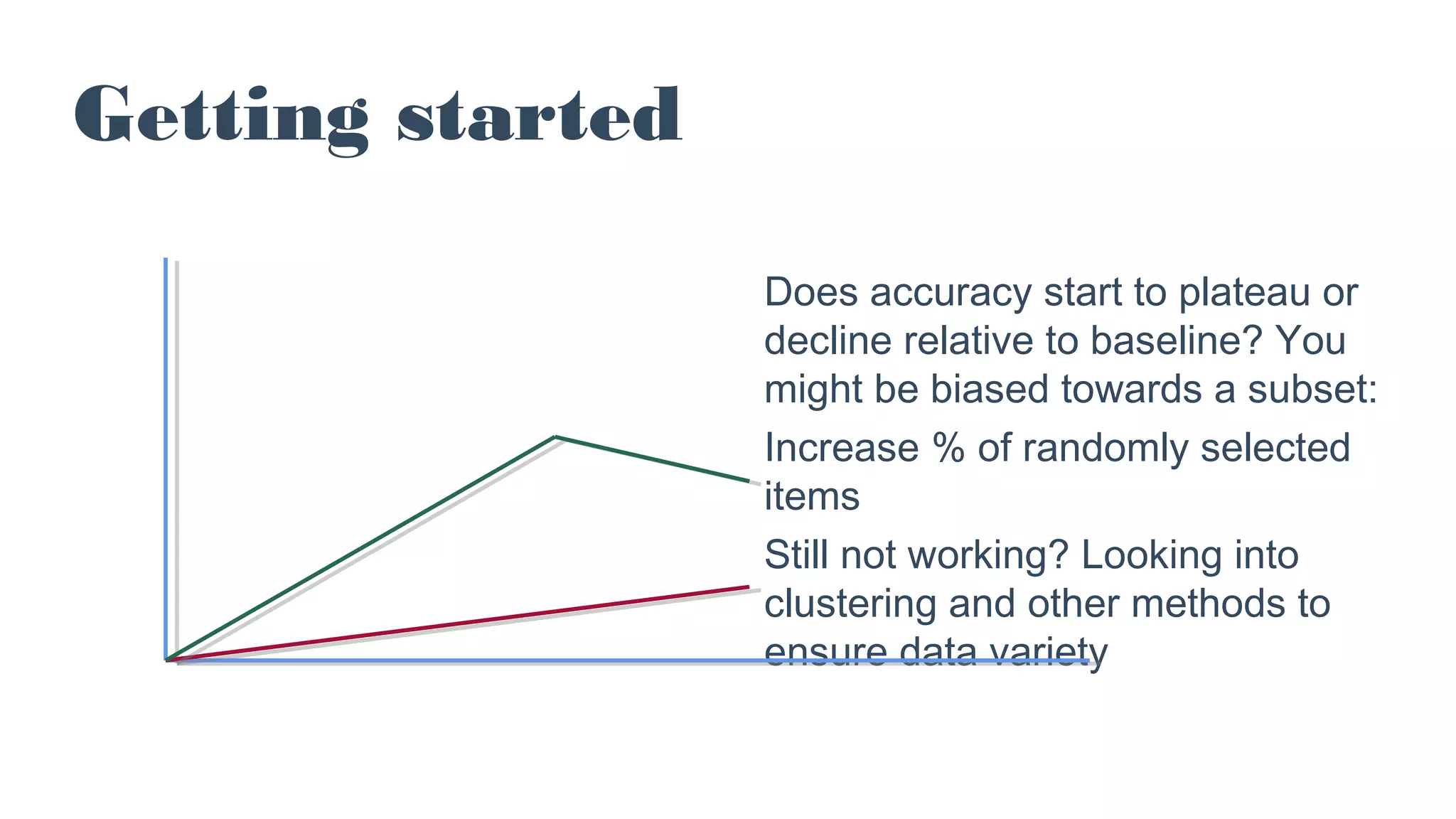
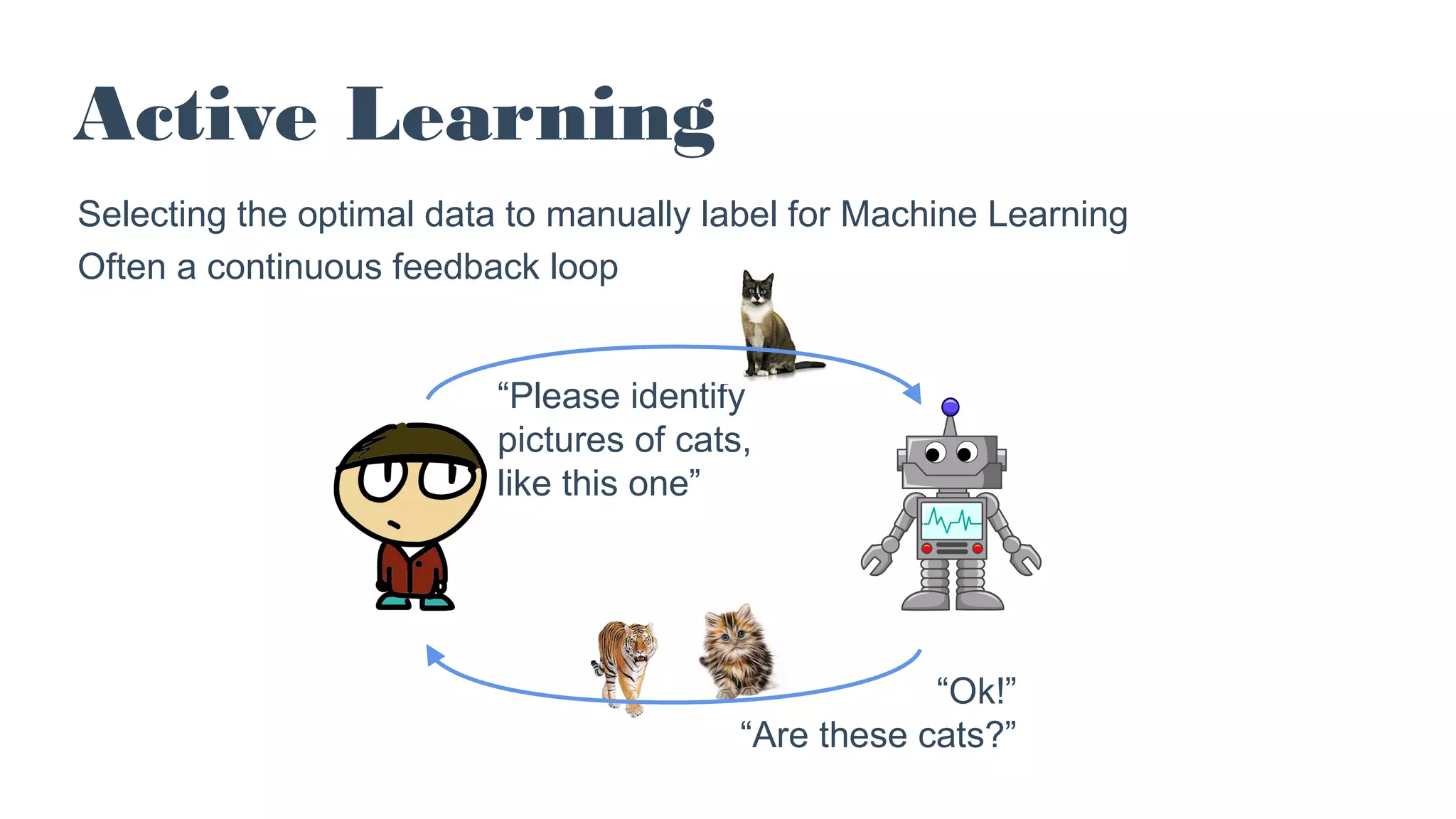
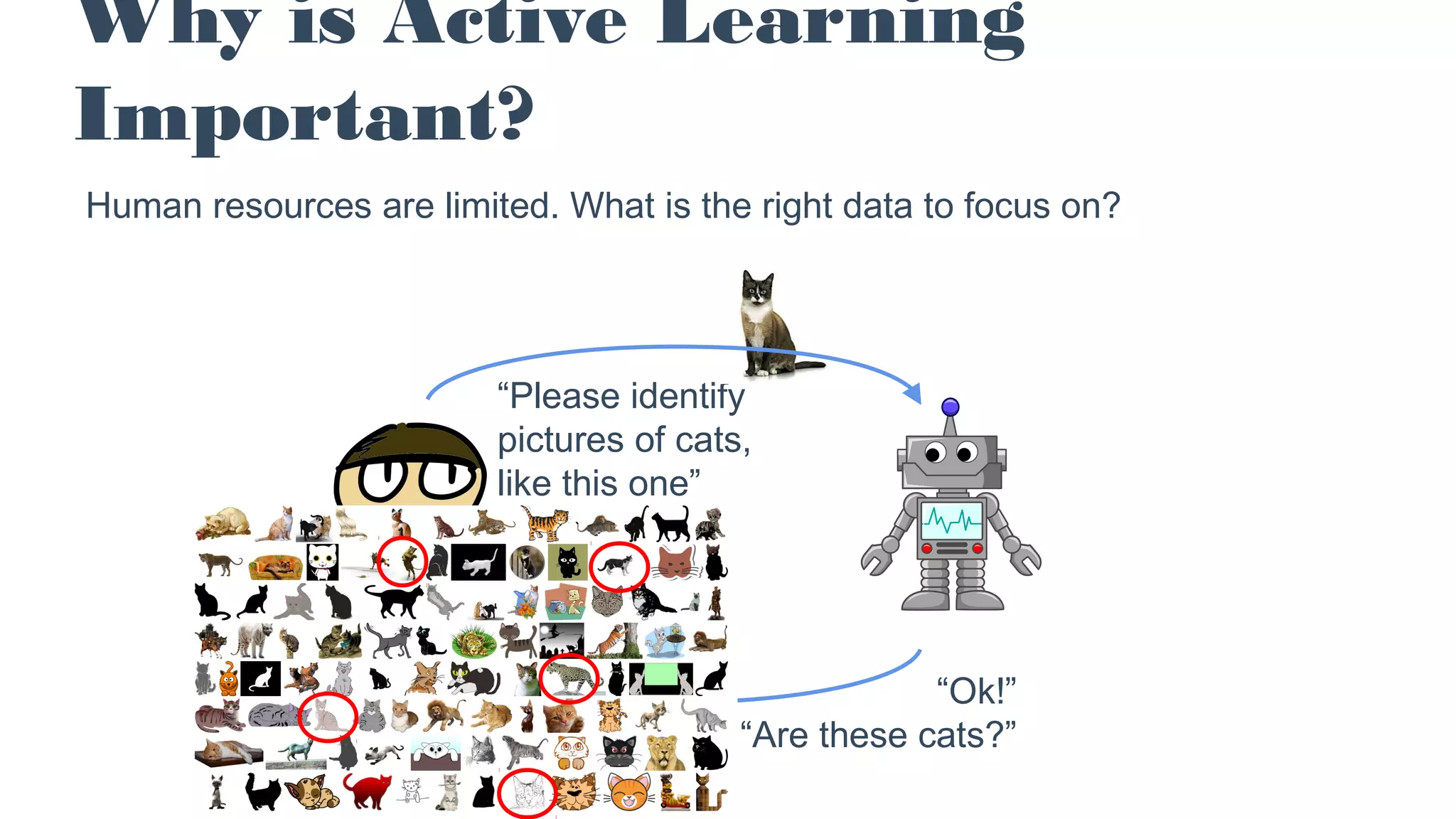
The document discusses the concept of active learning in machine learning, focusing on selecting the optimal data for manual labeling to enhance model accuracy. It highlights the importance of this approach, noting its prevalence in industry despite its limited representation in academic literature. Additionally, it provides practical strategies, examples, and resources for implementing active learning, particularly using tools like TensorFlow and ImageNet.






![TensorFlow’s ImageNet model
Example output :
['canoe', 0.90240431], ['paddle,
boat paddle', 0.042475685],
['gondola', 0.0011620093],
['sandbar, sand bar',
0.0011261732], ['snorkel',
0.00047367468]
Predicting that this image is a
‘canoe’ with 90.2% confidence, is
a ‘paddle/boat paddle’ with 4.2%
confidence, etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robertmunroodscslides-171115223052/75/Strategies-for-Practical-Active-Learning-Robert-Munro-11-2048.jpg)


![Ambiguous items
Example:
the top two predictions have
36.9% and 32.2% confidence
[['volleyball', 0.36908466],
['balance beam, beam',
0.32213417], ['stage',
0.020542733], ['basketball',
0.019910889], ['horizontal bar,
high bar', 0.011983166]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robertmunroodscslides-171115223052/75/Strategies-for-Practical-Active-Learning-Robert-Munro-14-2048.jpg)
![Low confidence items
Example:
the top prediction has only
11.2% confidence
['parachute, chute',
0.11202857], ['geyser',
0.075139046], ['wing',
0.074320331], ['cliff, drop,
drop-off', 0.074191555],
['balloon', 0.053766355]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robertmunroodscslides-171115223052/75/Strategies-for-Practical-Active-Learning-Robert-Munro-15-2048.jpg)
![Randomly selected items
Evaluate accuracy on a
random set of items
The most valuable items to label
are confidently wrong
[['volleyball', 0.80830169], ['rugby
ball', 0.029293904], ['bathing cap,
swimming cap', 0.020639554],
['soccer ball', 0.020503236],
['bikini, two-piece', 0.011906843]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robertmunroodscslides-171115223052/75/Strategies-for-Practical-Active-Learning-Robert-Munro-16-2048.jpg)
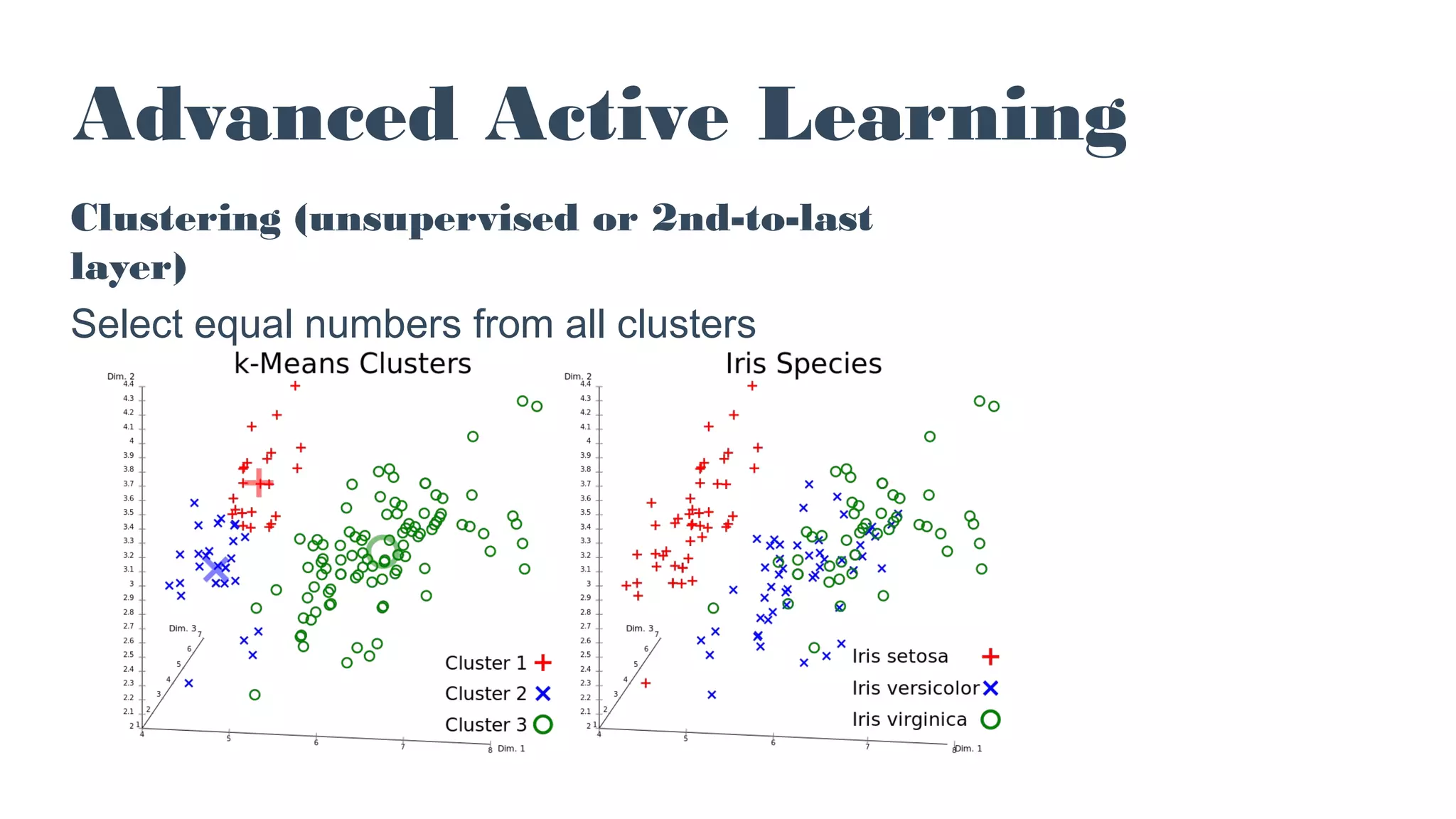
![Advanced Active Learning
Using external resources:
eg WordNet distance between top predictions
['lawn mower, mower', 0.44160703], ['crash
helmet', 0.18804552], ['vacuum, vacuum
cleaner', 0.038397752], ['go-kart',
0.03737054], ['motor scooter, scooter',
0.033097573]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/robertmunroodscslides-171115223052/75/Strategies-for-Practical-Active-Learning-Robert-Munro-18-2048.jpg)