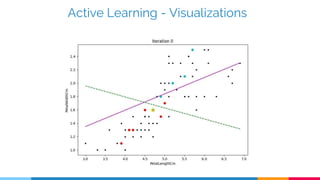
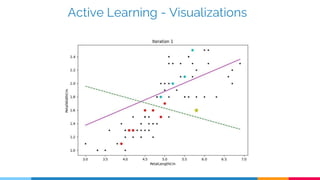
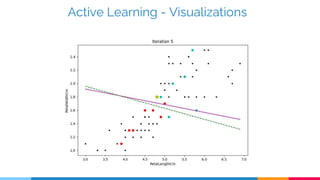
Active learning is a machine learning technique that can perform well with less training data by allowing algorithms to select the most informative samples to be labelled. It trains an initial model on labelled data, evaluates the model on unlabelled samples, and selects samples to label that will most improve the model. Common strategies to select samples include least confidence, margin sampling, and entropy sampling. Active learning is useful when labelling data is expensive and can reduce labelling requirements for tasks like natural language processing.




![What is active learning?
“The key idea behind active learning is that a machine learning algorithm
can perform better with less training if it is allowed to choose the data from
which it learns.”[1]
● It gives the samples to be labelled in such a way that with less labelled
samples, the machine learning model performs well - it chooses the
optimal set of samples to be labelled for good performance
● We could say that the model actively learns and sees what to learn next
so that it can perform better.
References:
1. Settles, Burr. Active learning literature survey. University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Computer Sciences, 2009.
2. "Active Learning (Machine Learning)". En.Wikipedia.Org, 2020,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_learning_(machine_learning)#cite_note-settles-1. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activelearning-201101051626/85/Active-learning-5-320.jpg)

![An Important Component
Oracle - person or a model that knows the correct
answer/classification/prediction to all questions/queries.[1][2]
Practically, an expert in the corresponding field would be
considered as an oracle.
1. Hosein, Stefan. "A Beginner's Guide To Active Learning". DatacampCommunity, 2020, https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/active-learning. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.
2. "Active Learning (Machine Learning)". En.Wikipedia.Org, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_learning_(machine_learning)#cite_note-settles-1. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activelearning-201101051626/85/Active-learning-7-320.jpg)



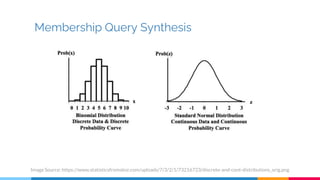




![Query Strategies
There are many query strategies.[1][2] Here are three common
strategies:
● Least Confidence
● Margin Sampling
● Entropy Sampling
1. Hosein, Stefan. "A Beginner's Guide To Active Learning". DatacampCommunity, 2020, https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/active-learning. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.
2. "Active Learning (Machine Learning)". En.Wikipedia.Org, 2020, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_learning_(machine_learning)#cite_note-settles-1. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activelearning-201101051626/85/Active-learning-16-320.jpg)



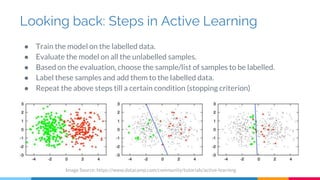

![Application Areas of Active Learning
● Natural Language Processing[1]
○ Lots of data to label
● Reinforcement Learning
● Online Learning
○ Lot of data coming in continuously
○ Spam filters, ranking of search results, job listings, etc.[2]
References
1. Hosein, Stefan. "A Beginner's Guide To Active Learning". DatacampCommunity, 2020, https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/active-learning. Accessed 31 Oct 2020.
2. https://www.oreilly.com/content/real-world-active-learning/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/activelearning-201101051626/85/Active-learning-22-320.jpg)