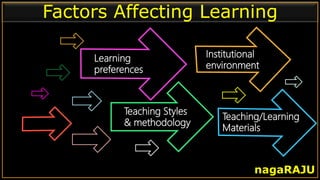
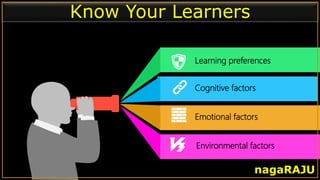
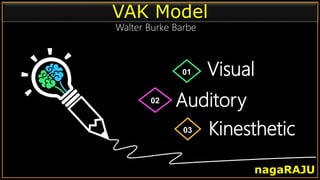
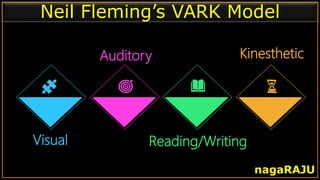
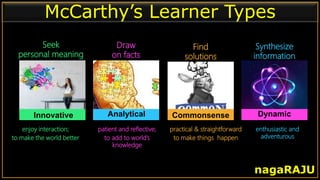
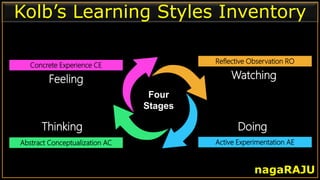
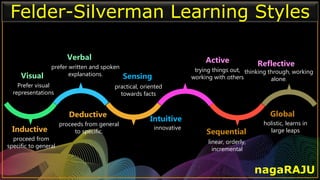
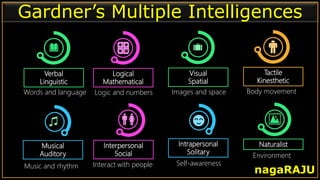
The document discusses various learning styles and their implications for teaching, emphasizing that students learn differently based on biological, cognitive, social, and emotional factors. It outlines different models of learning styles, such as the VAK model, Kolb’s inventory, and Gardner’s multiple intelligences, and suggests pedagogic strategies tailored to each style. The conclusion highlights the importance of using diverse resources and strategies in teaching to accommodate individual learning preferences.