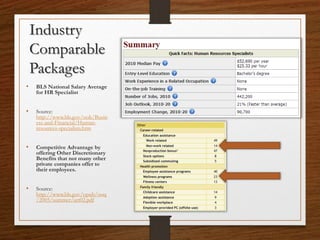
This document discusses developing a compensation and benefits package for a human resources secretary position that aligns with the organization's strategic HR goals of retaining committed experts. It recommends a pay structure that meets the local and national median salary along with discretionary benefits like health insurance, retirement contributions, and professional development incentives. The package is designed to reduce overtime, enhance performance through training and feedback, and motivate employees through goal setting while ensuring compliance with labor regulations.