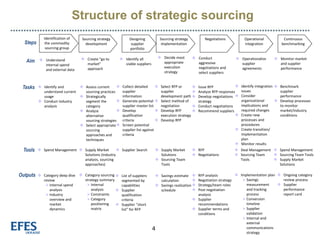
Strategic sourcing involves systematically analyzing internal and external data to develop an optimal supplier strategy. It aims to optimize spend, improve quality, increase ROI, and cut costs through partnership with a limited number of suppliers. The process identifies current spending and viable suppliers, develops sourcing approaches, issues RFPs, negotiates with suppliers, and integrates and monitors selected suppliers. Benefits include estimated 5-10% savings, collaborative spending improvements, new performance metrics, innovation, and better teamwork. Most Fortune 500 companies use strategic sourcing.