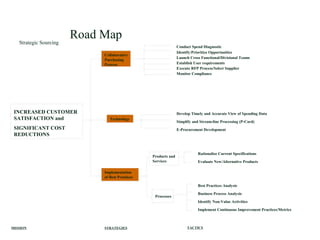
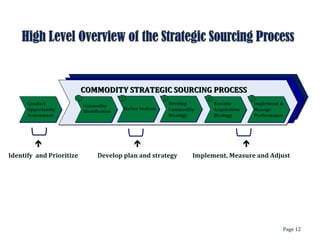
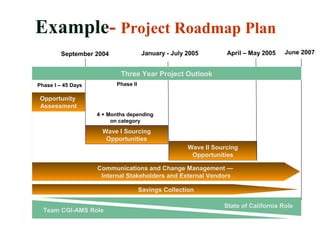
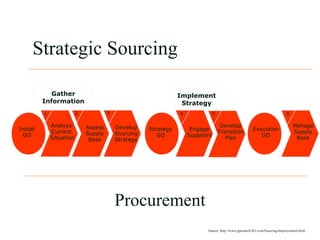
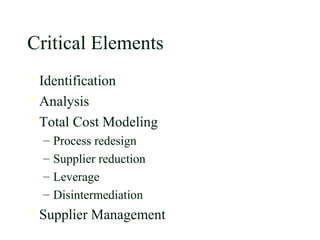
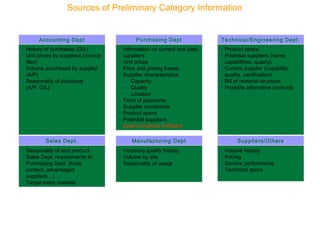
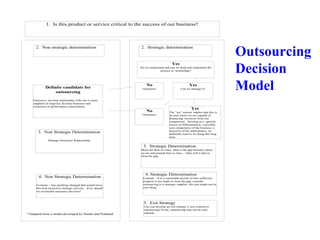
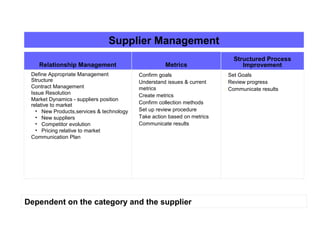
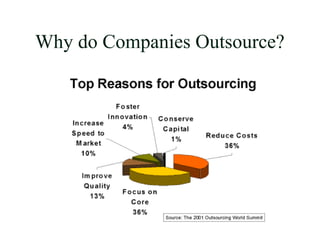
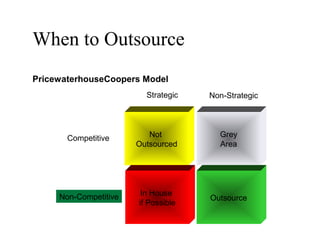
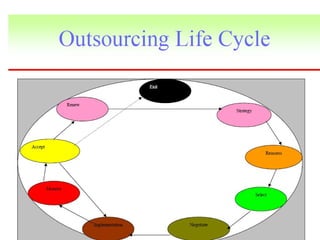
This document discusses strategic sourcing, which involves analyzing an organization's spending to make more effective business decisions about acquiring commodities and services. It outlines the mission, goals, and critical success factors of strategic sourcing, including executive sponsorship, end user involvement, data integrity, appropriate technology use, and continuous process improvement. A roadmap is provided that shows how strategic sourcing can increase customer satisfaction and significantly reduce costs through implementing best practices, identifying opportunities, and technology.