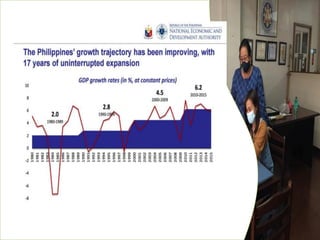
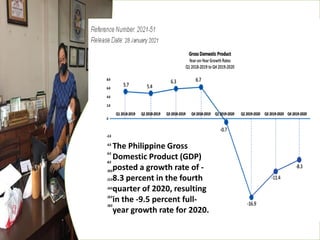
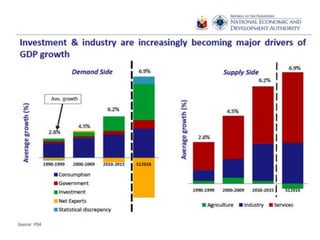
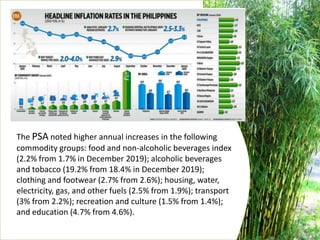
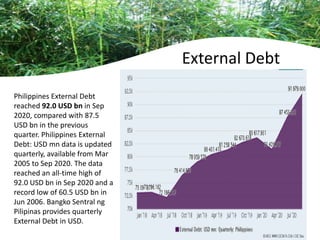
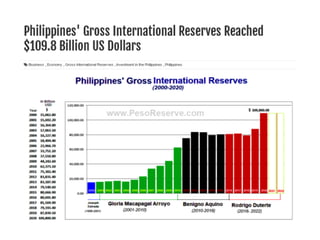
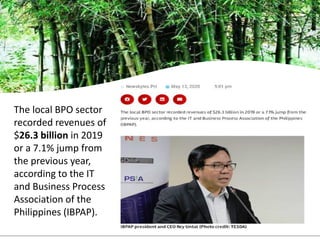
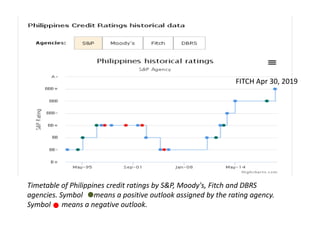
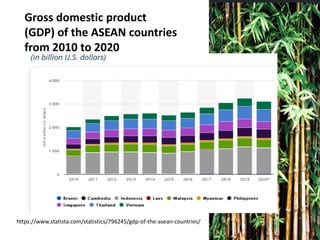
The document provides an overview of planning concepts and processes. It discusses development planning, socioeconomic factors in the Philippines like GDP growth and inflation. It also examines strategic planning approaches and rationales. Planning is presented as a process for setting goals and determining actions to achieve purposes. Strategic planning specifically involves analyzing external environments, formulating objectives and strategies, and using systematic methods to develop action plans and assess results. The document highlights the importance of planning for development and priority-setting given limited resources.