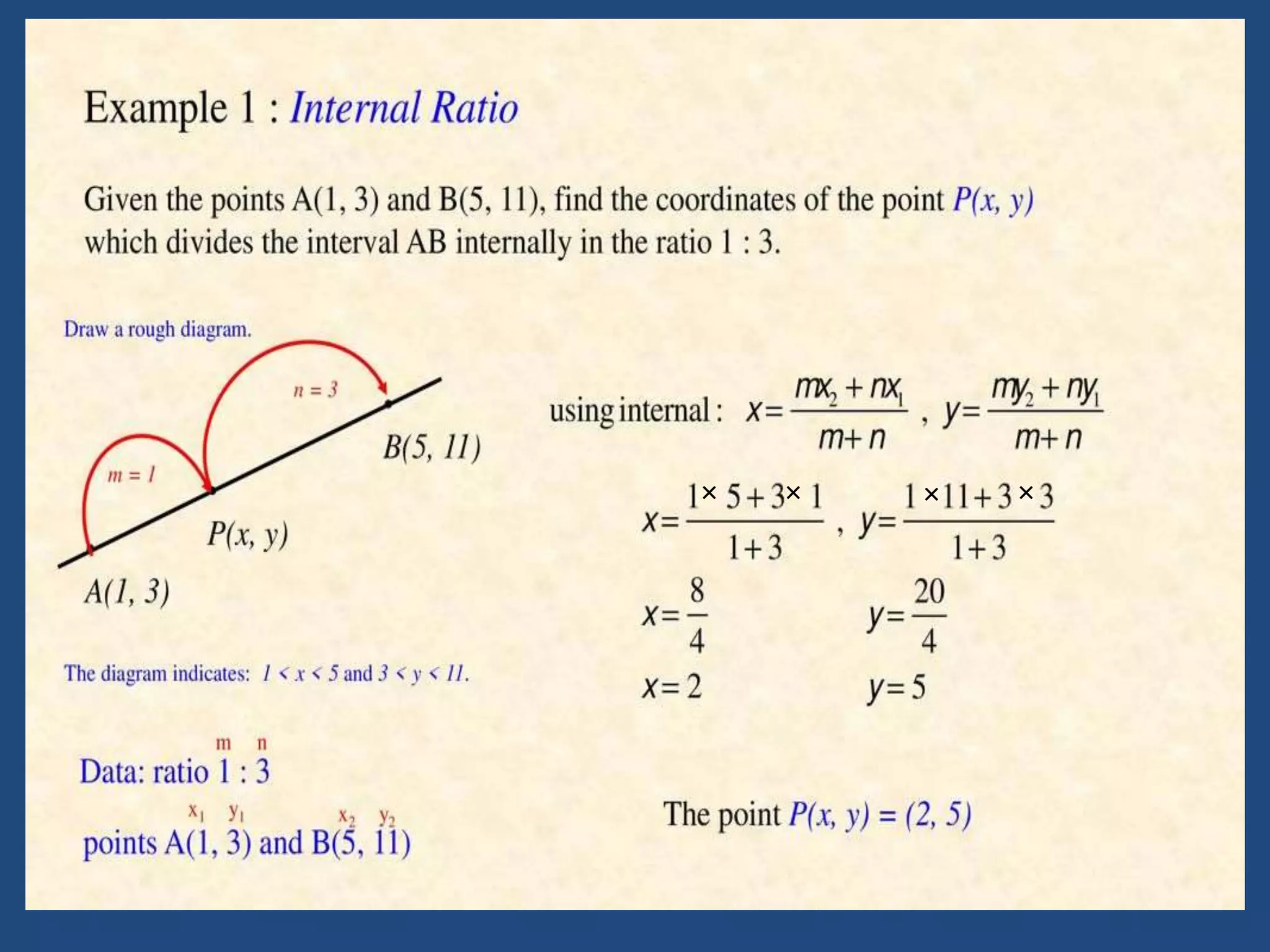
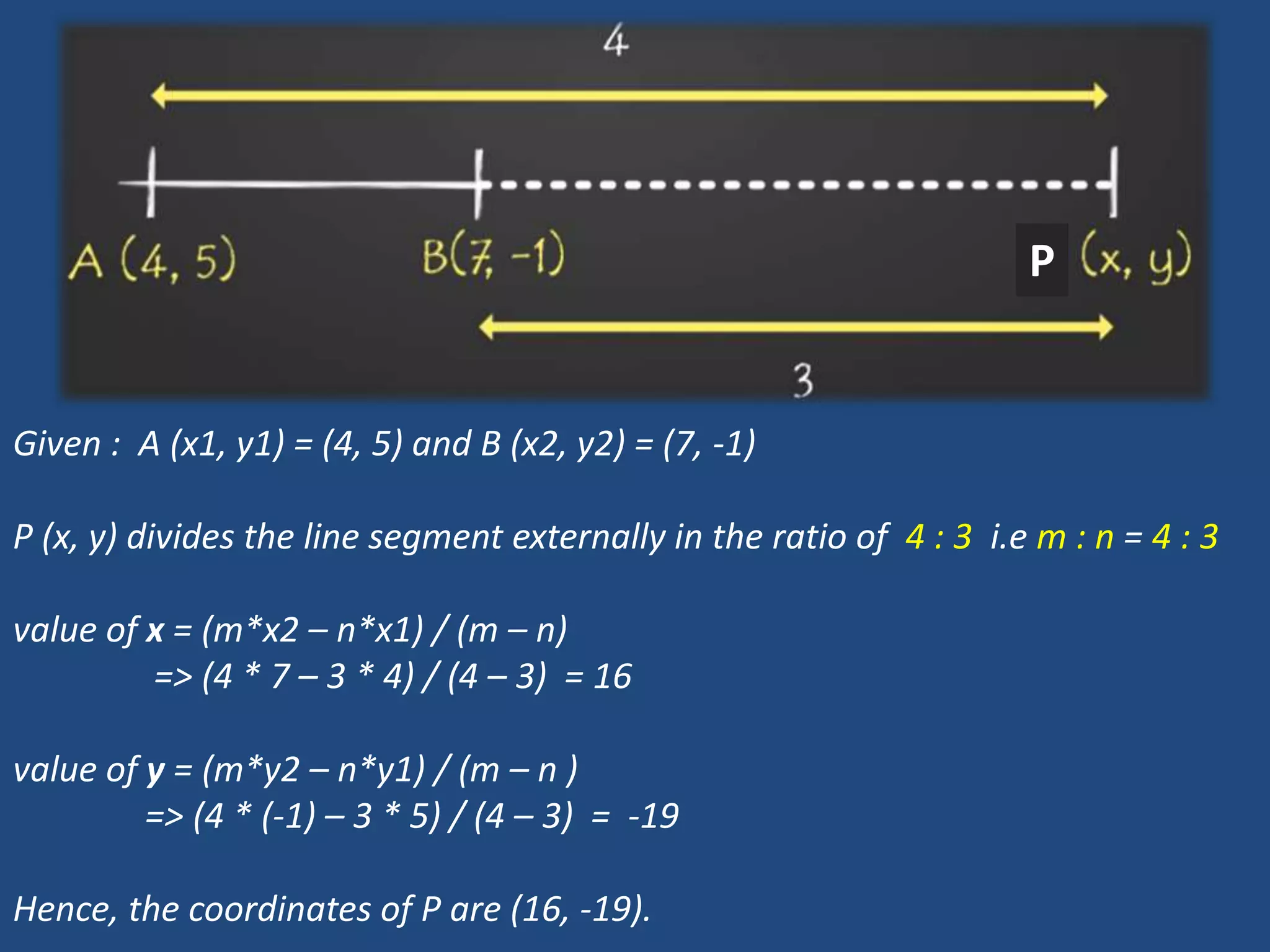
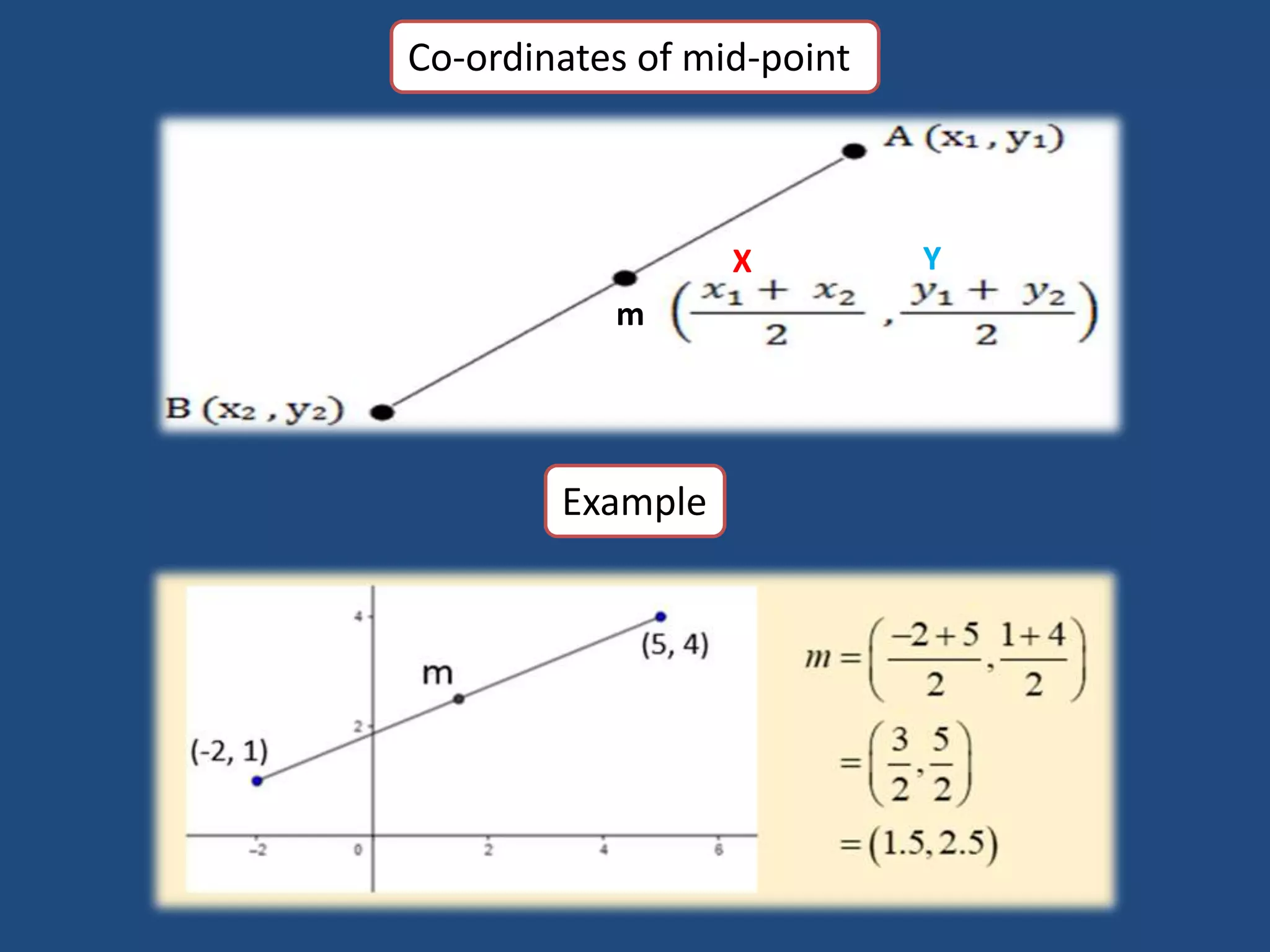
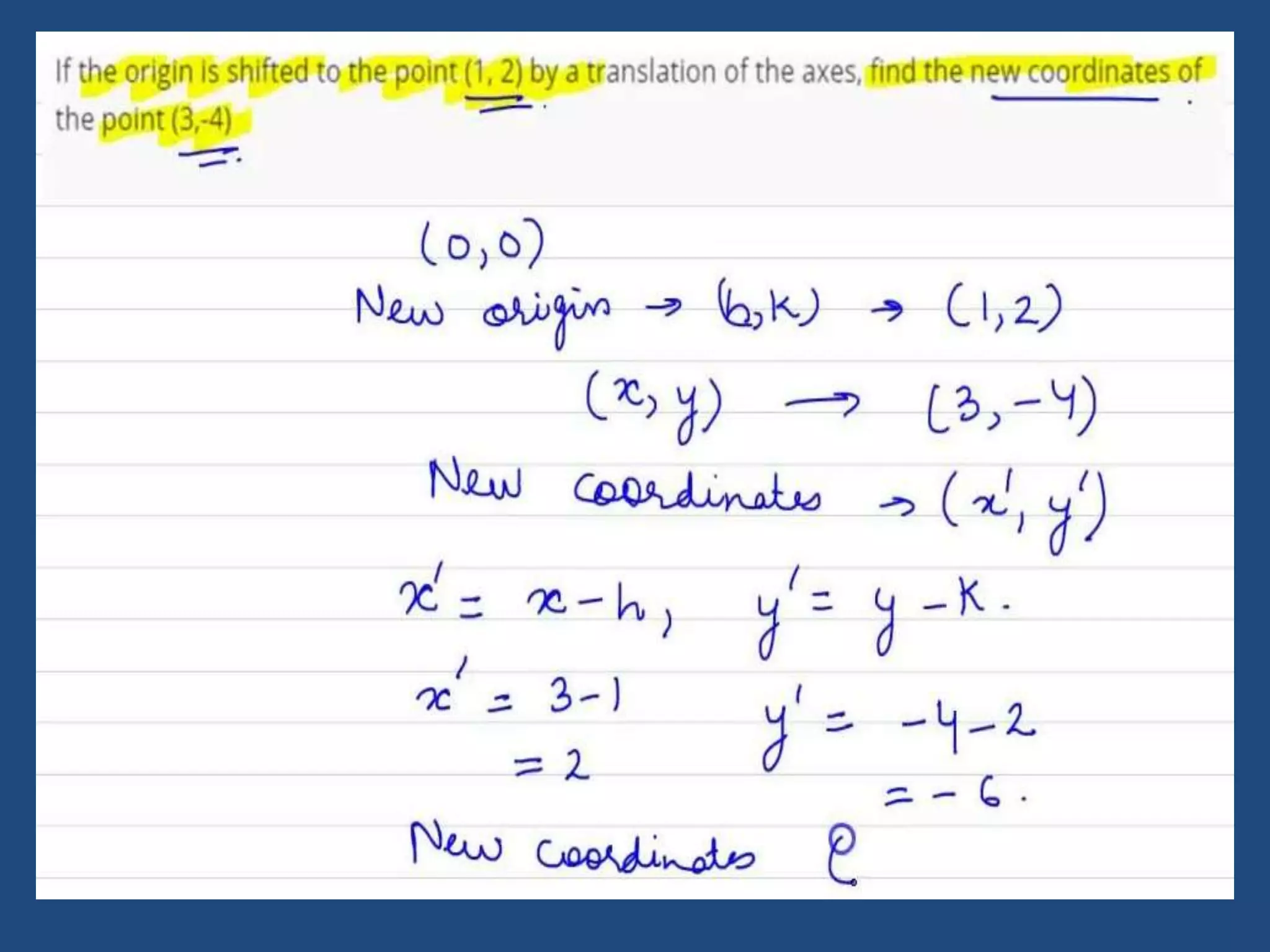
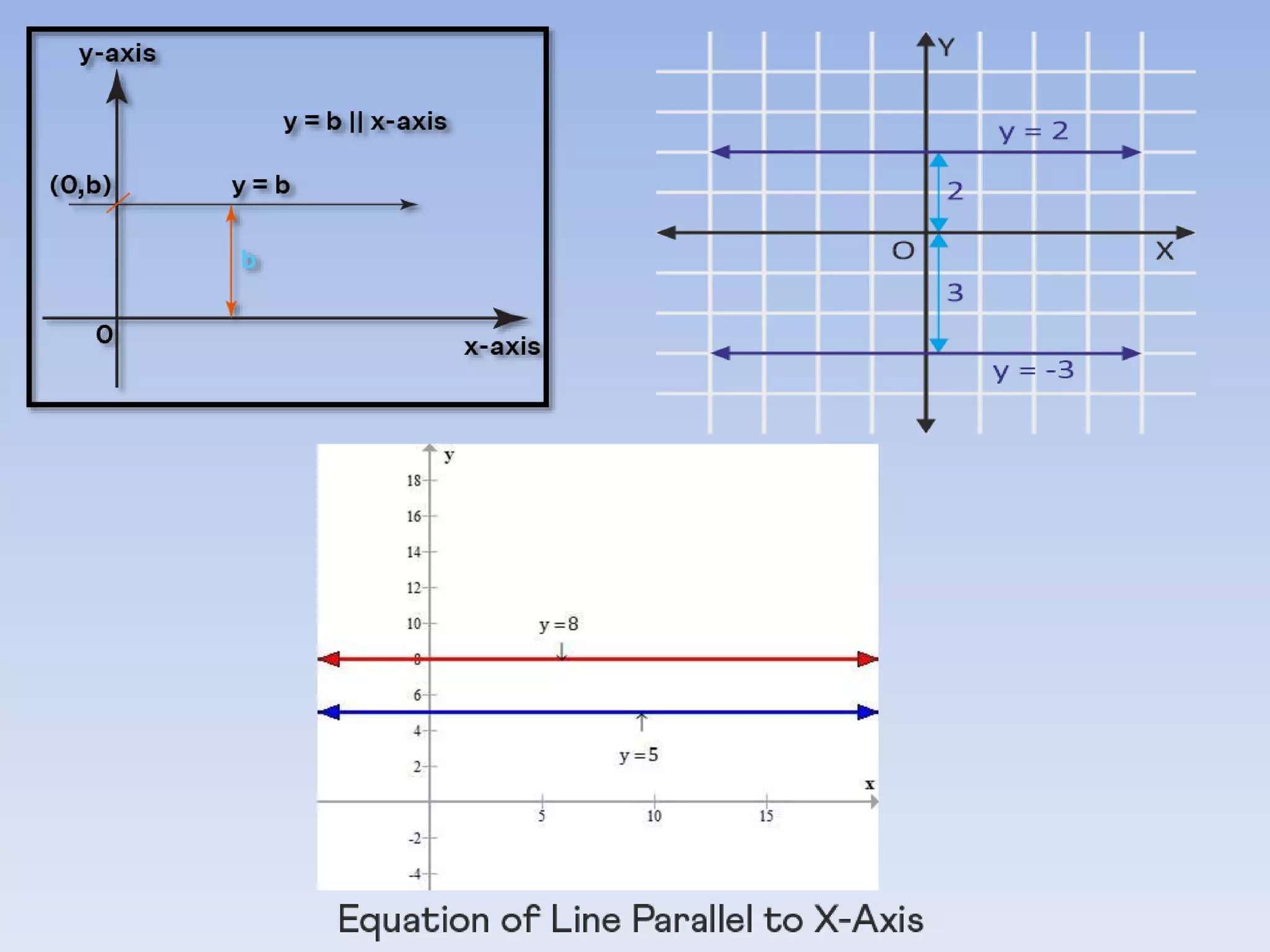
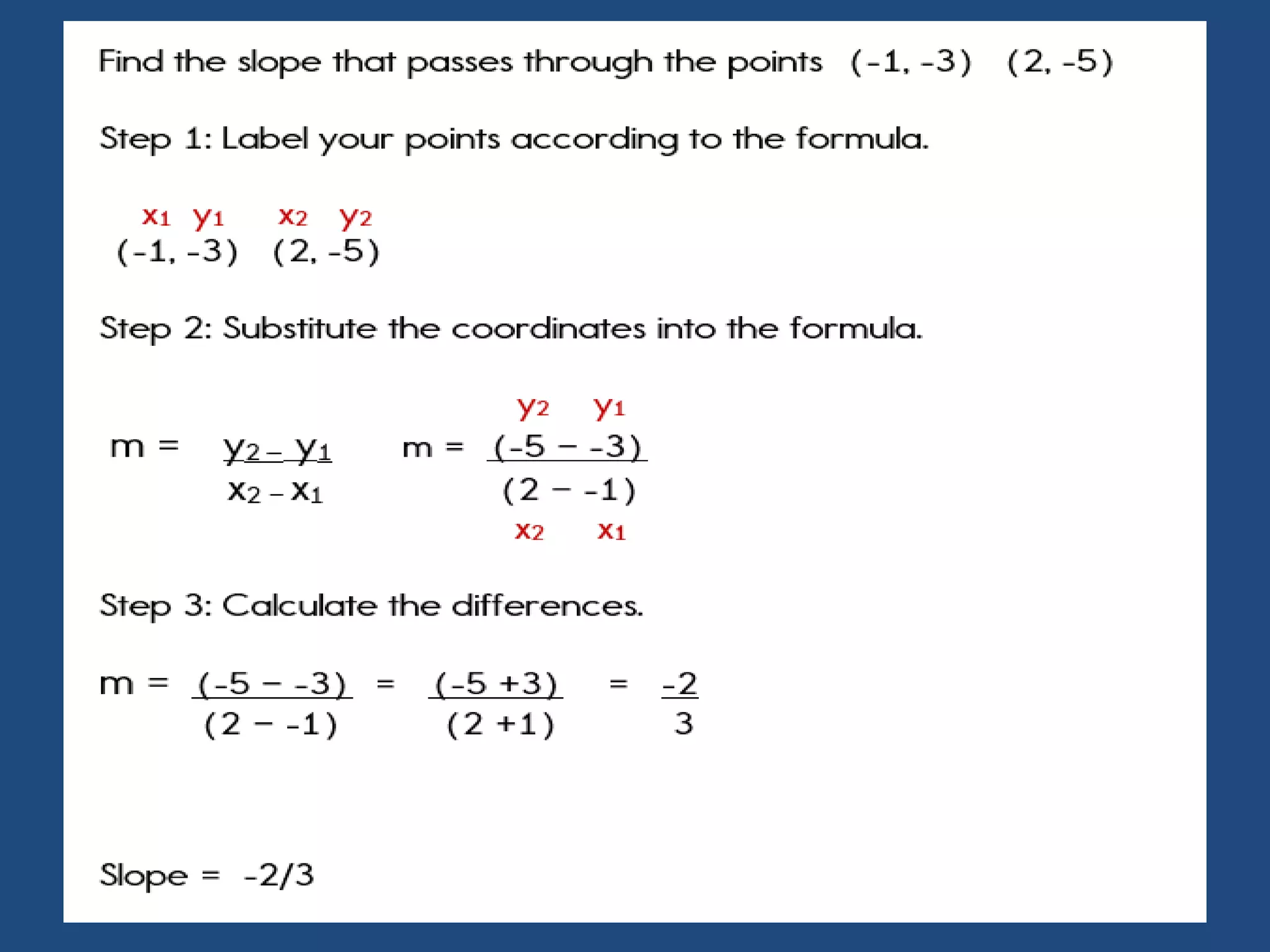
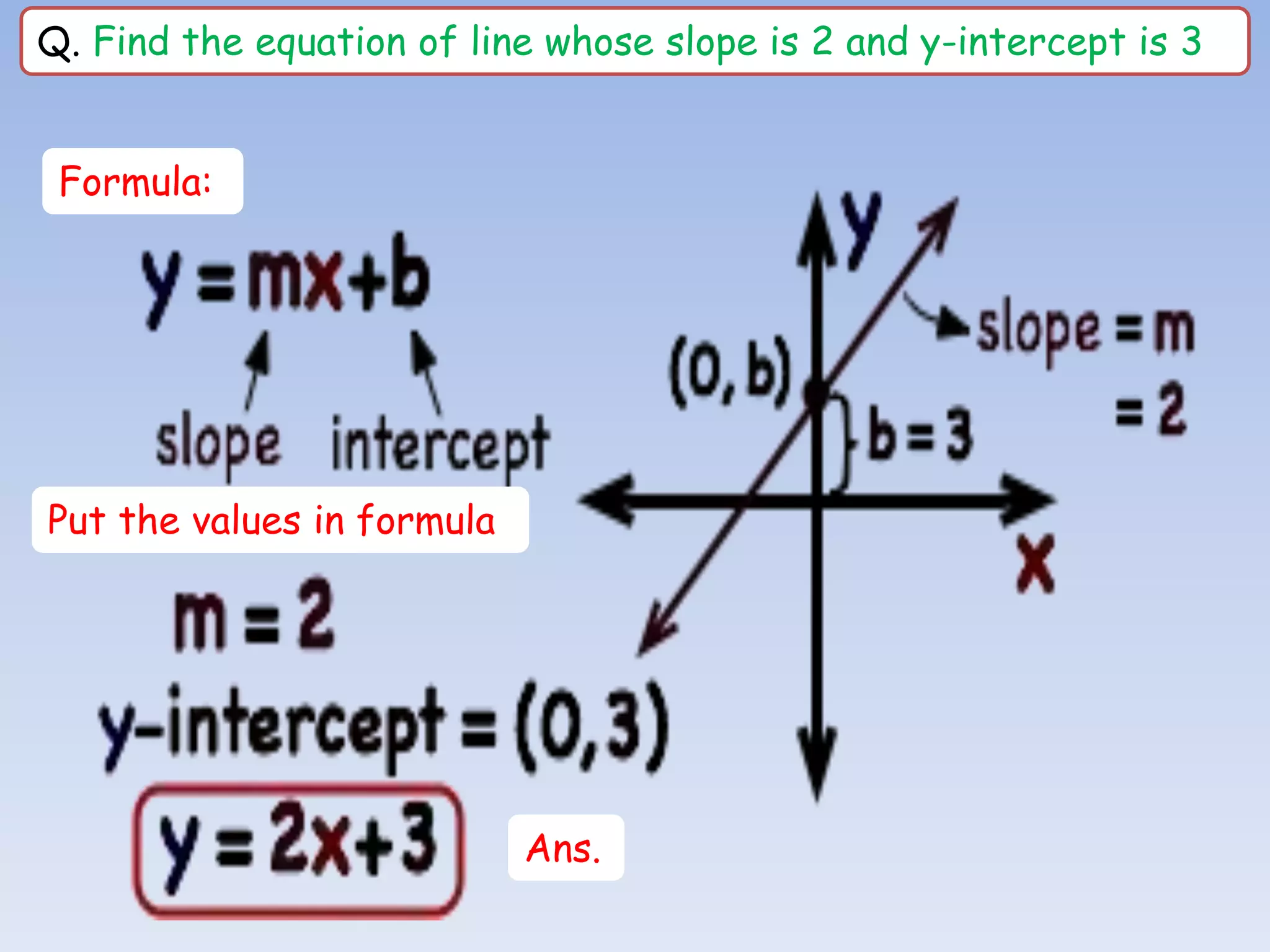
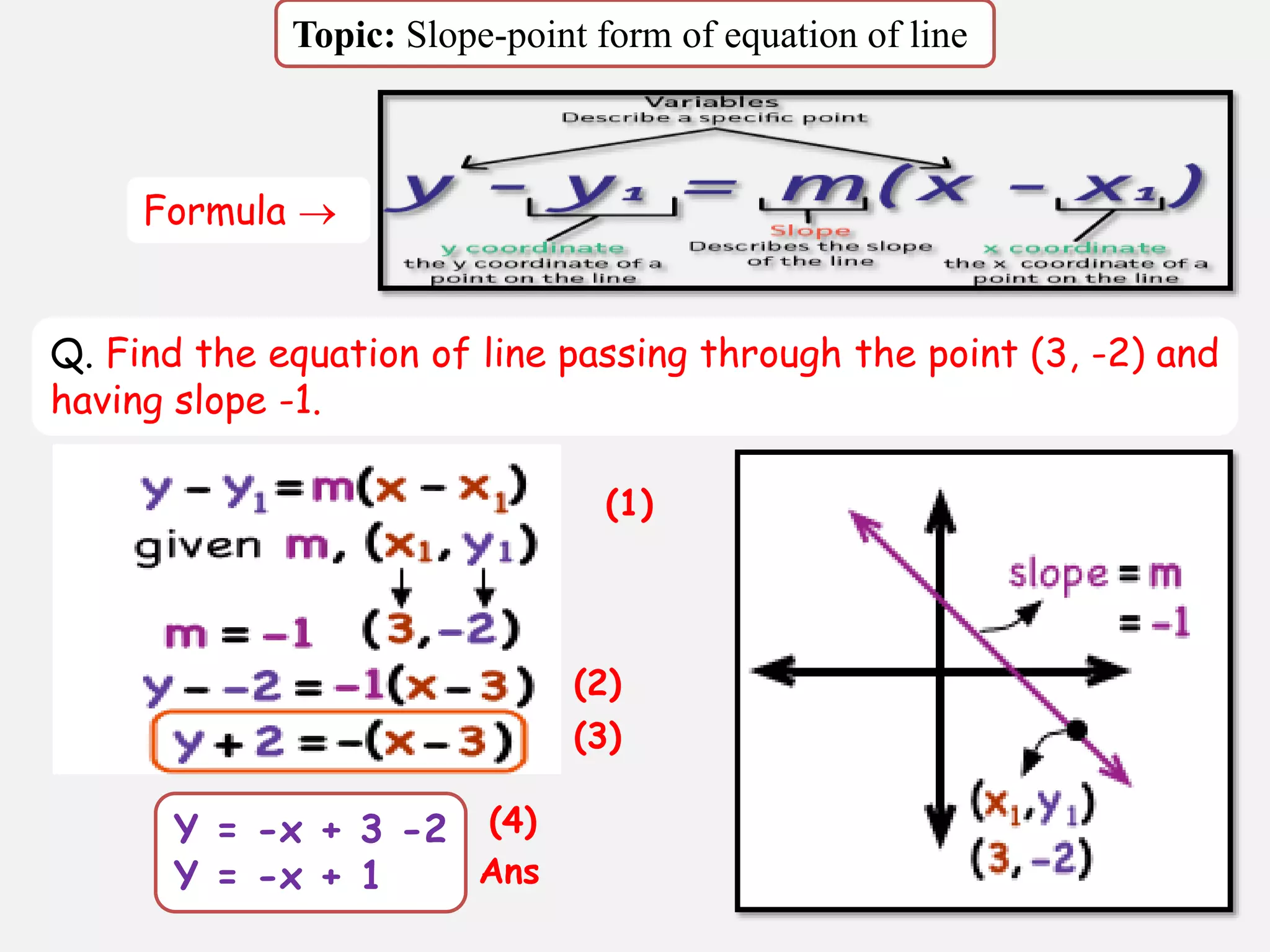
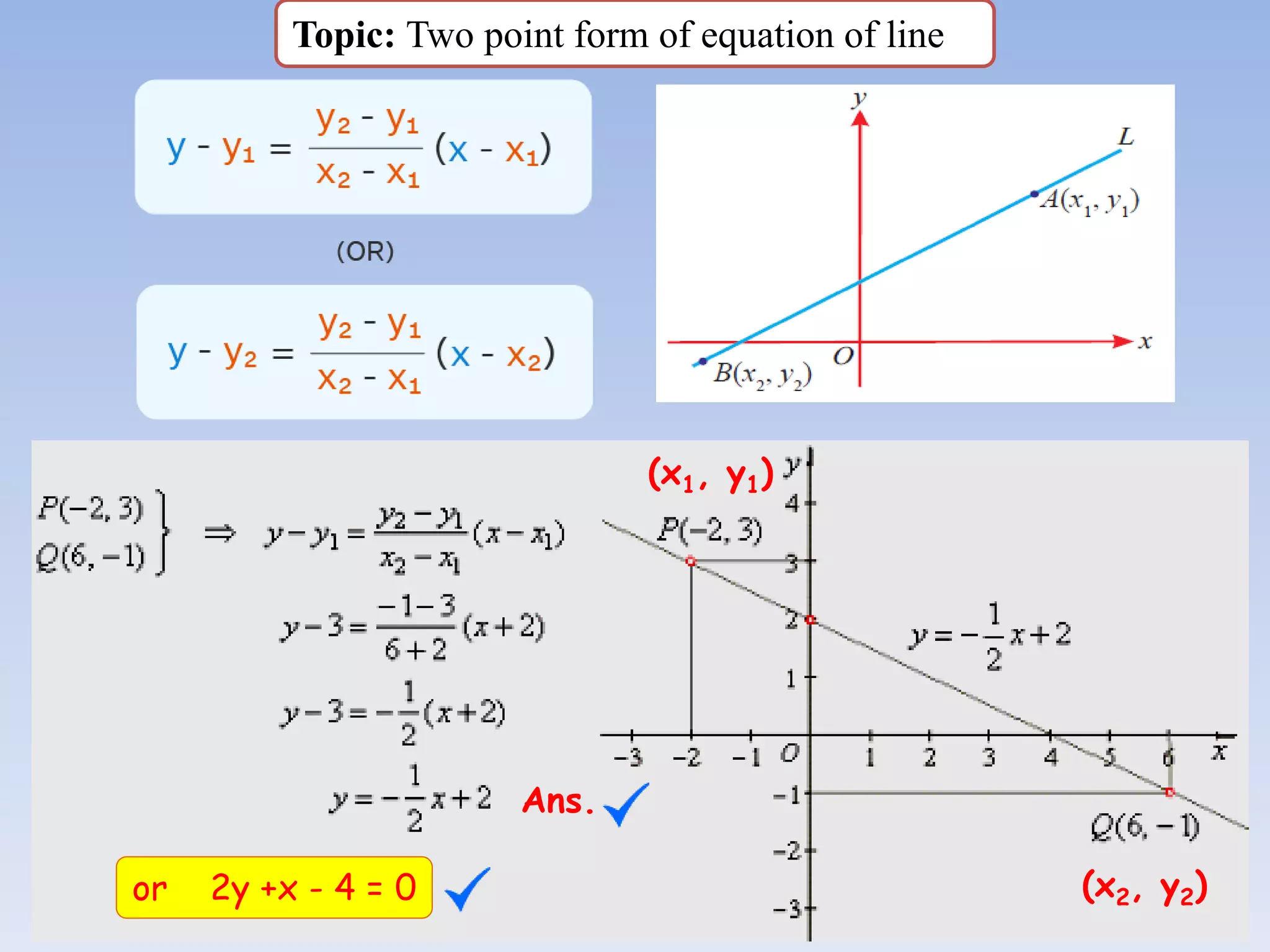
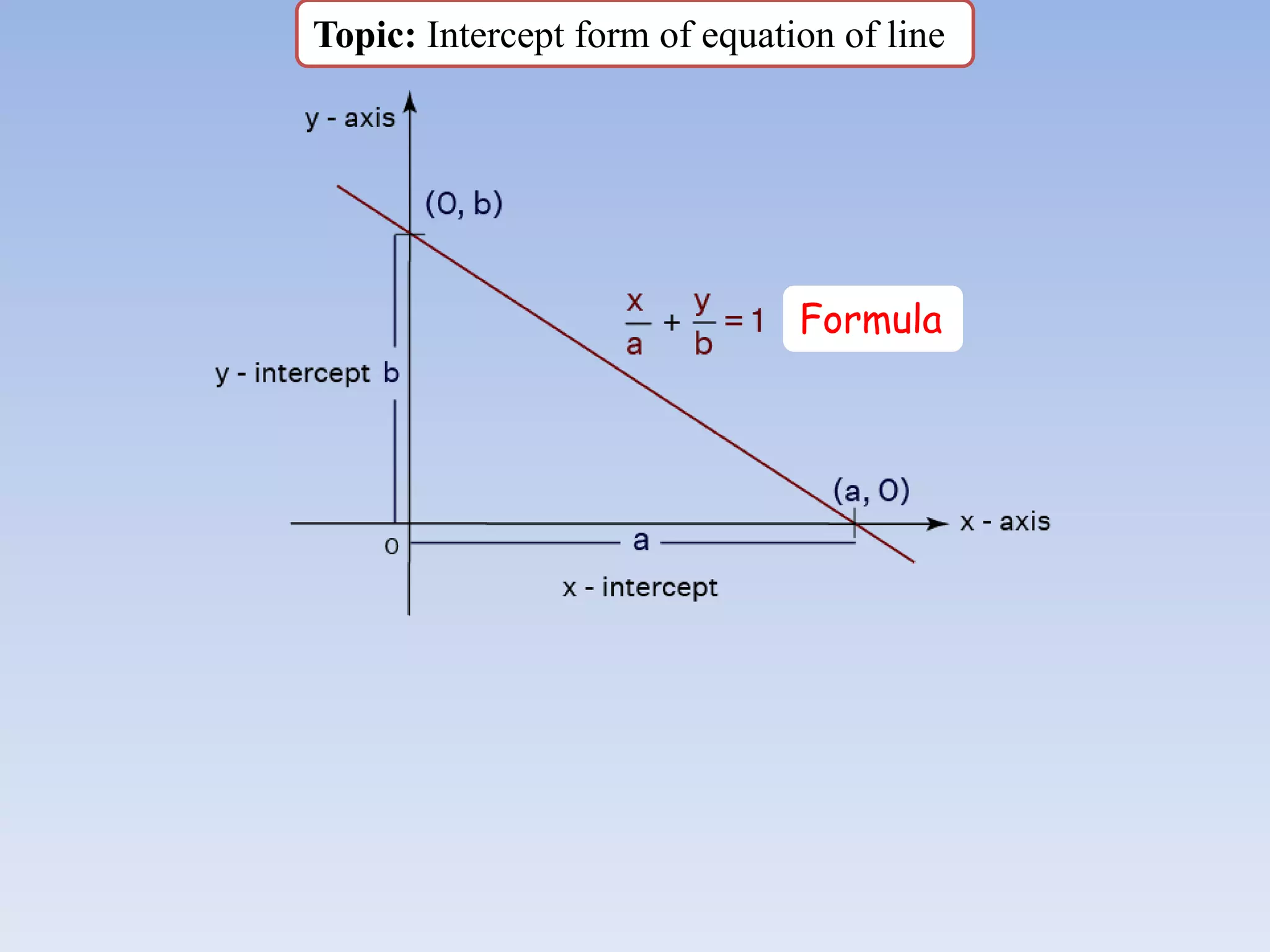
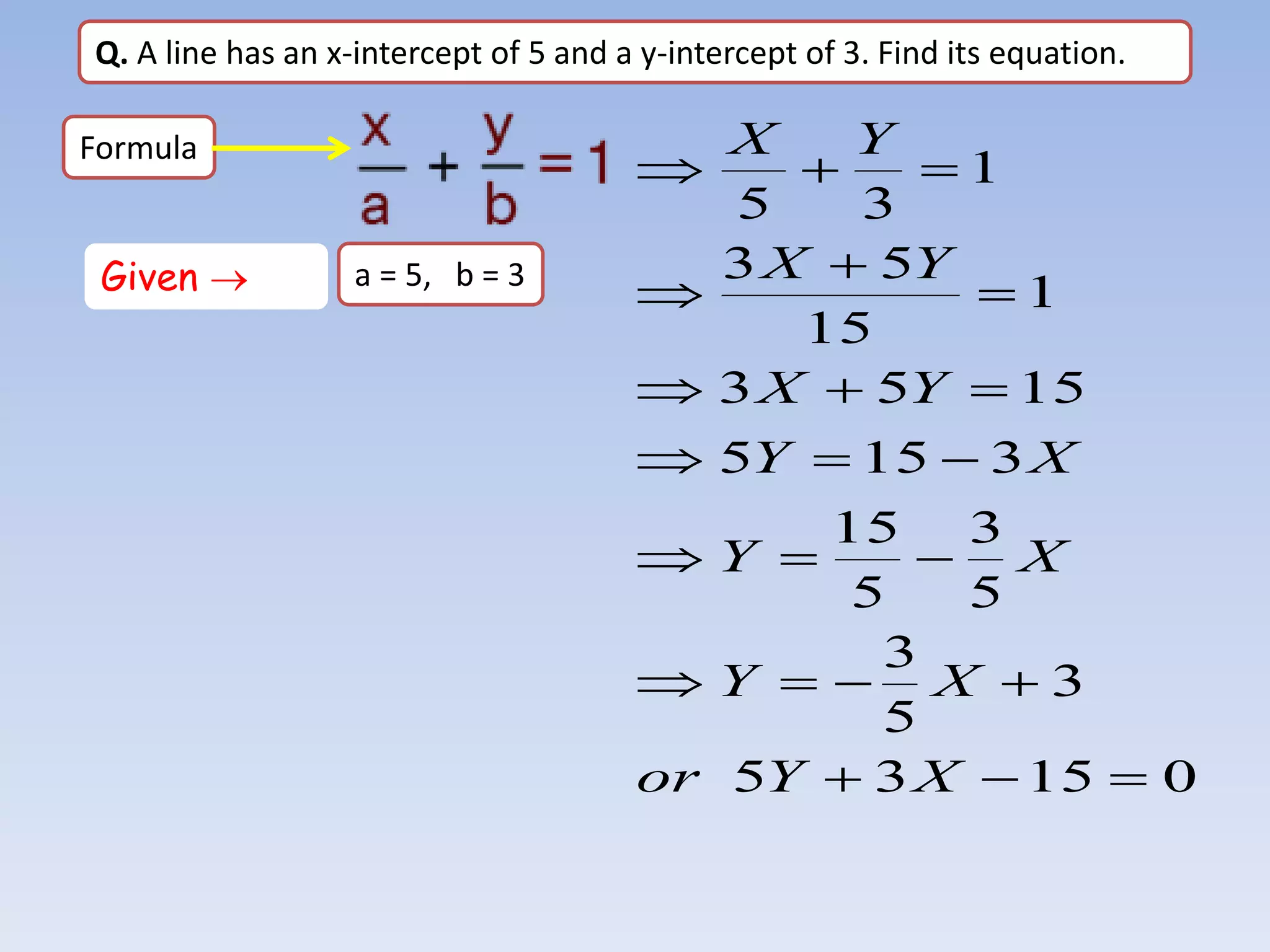
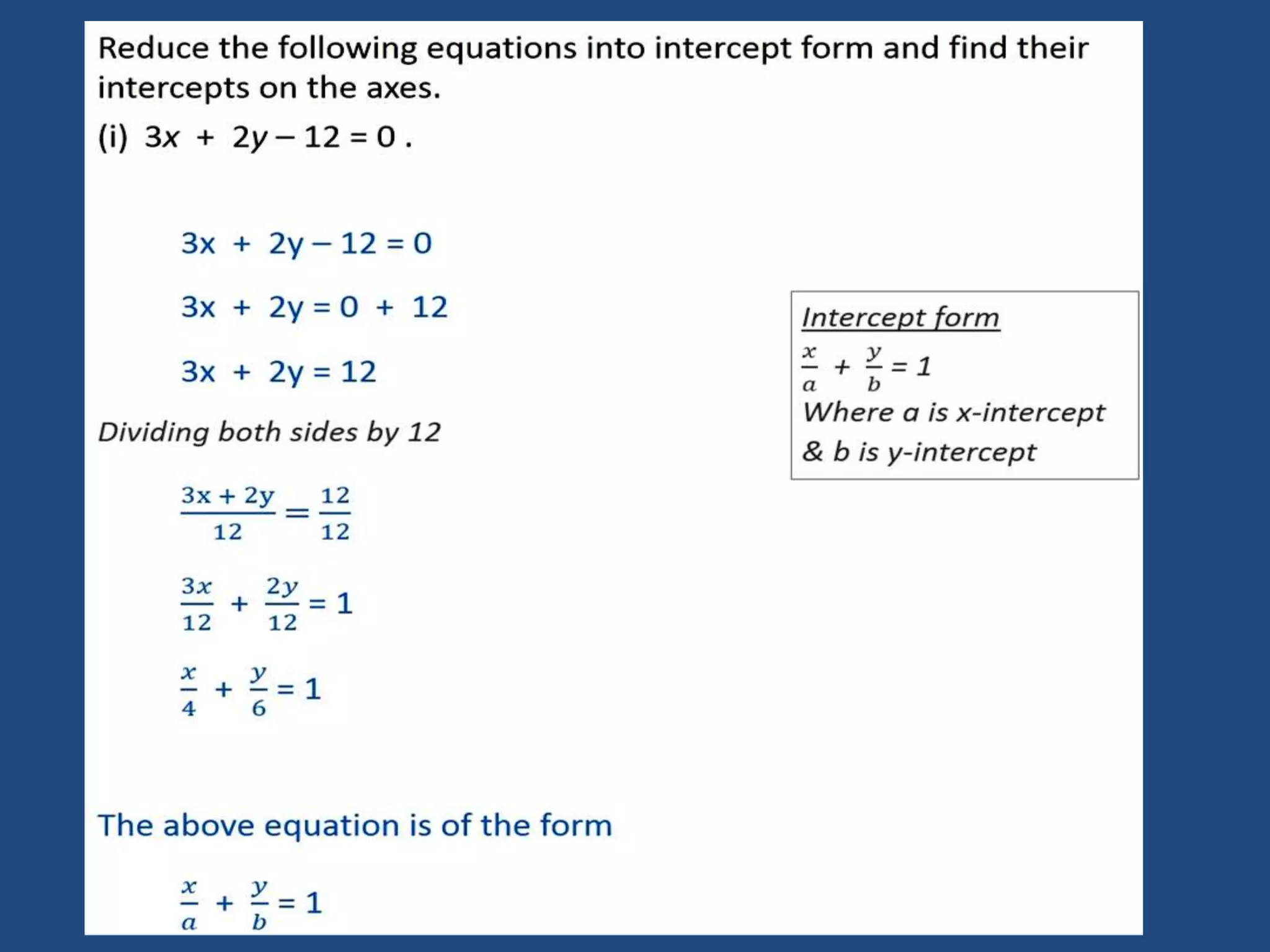
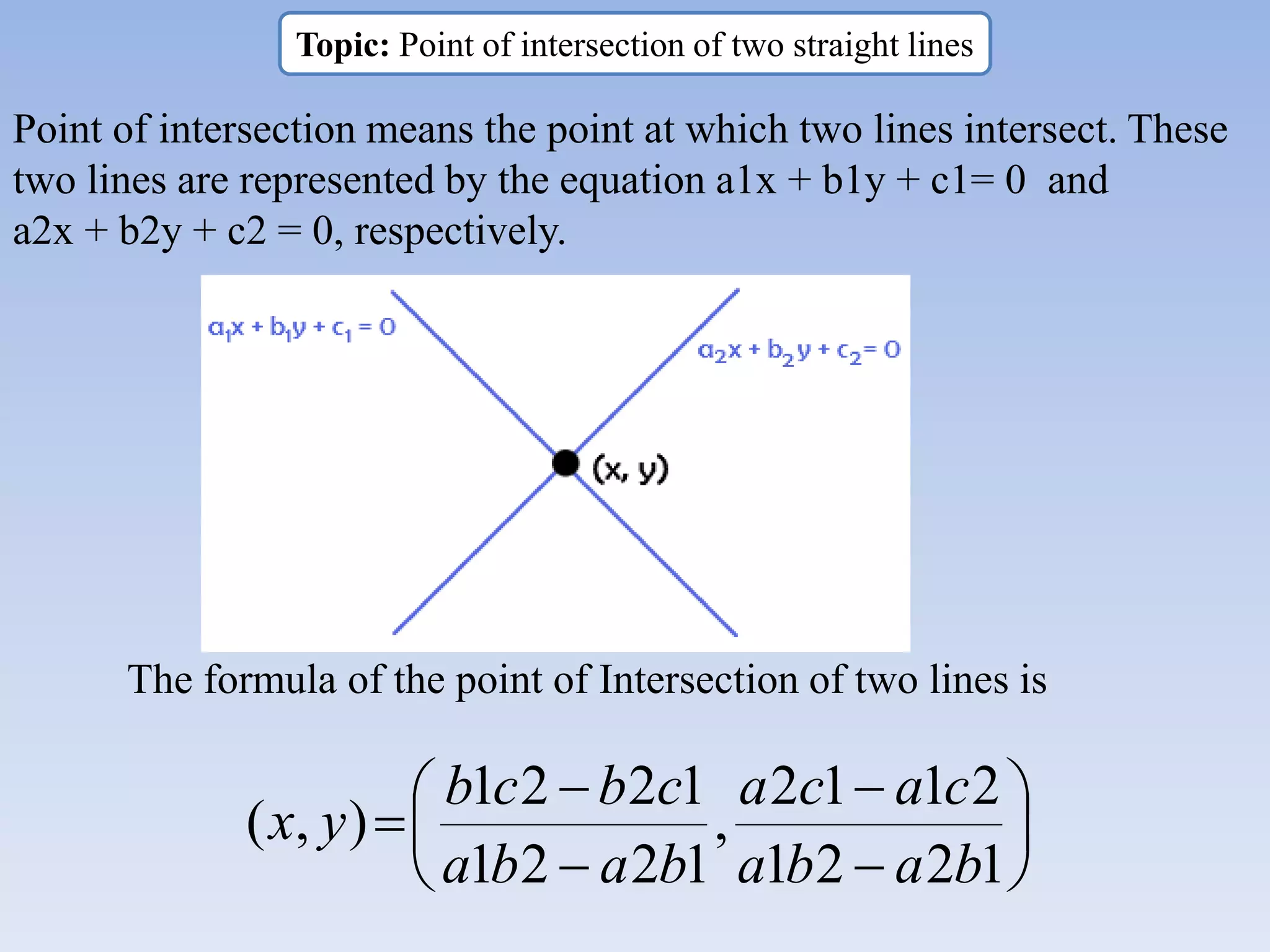
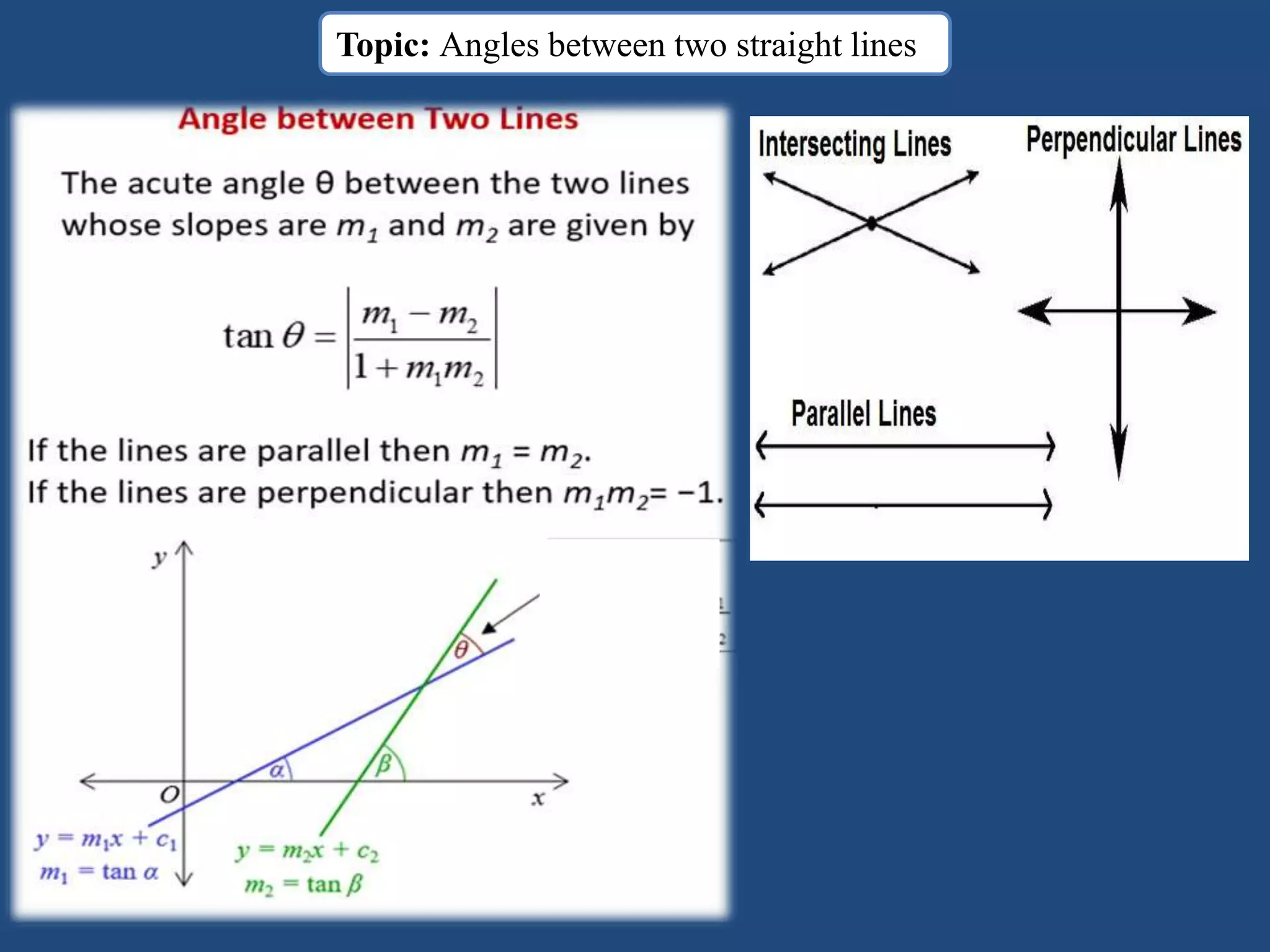
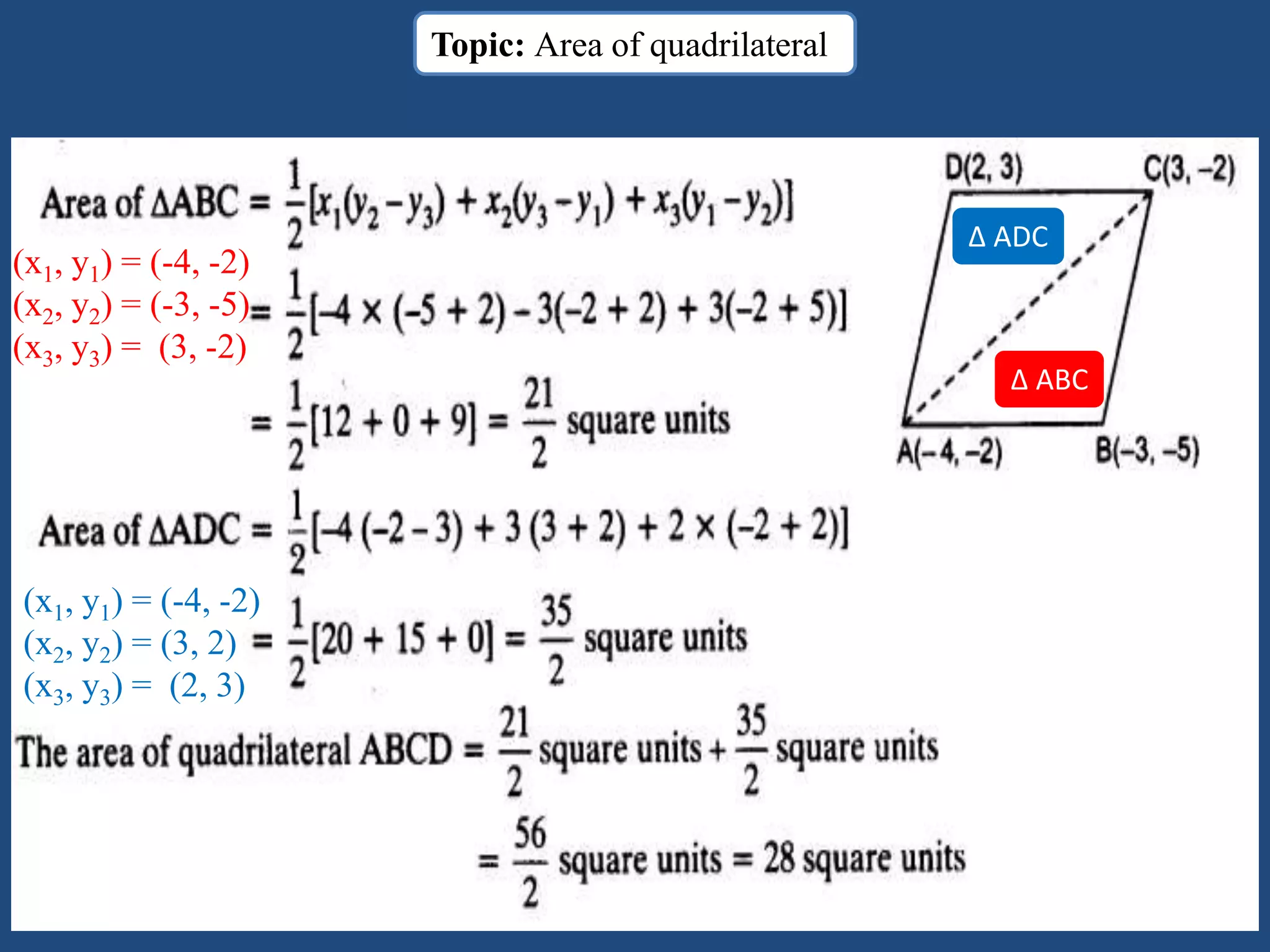
The document provides information about a mathematics course titled "Elementary Mathematics" for first year students. It includes details about the teacher, contact information, and topics that will be covered such as straight lines, coordinate systems, distance and section formulas, forms of equations of lines, and calculating areas of triangles and quadrilaterals. Formulas and examples are provided for finding slopes, intercepts, points of intersection, angles between lines, and applying formulas to find distances, ratios, and areas.