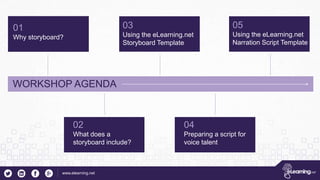
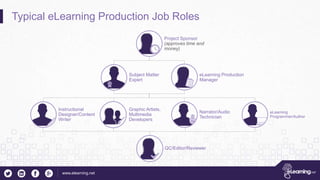
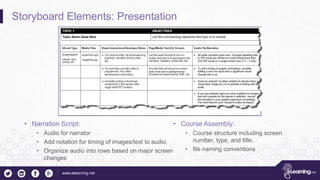
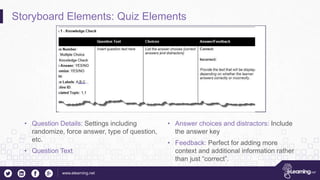
This document outlines the importance of storyboarding for eLearning production, detailing its role as a blueprint for various job functions including instructional design and content writing. It emphasizes the need for project sign-offs to prevent changes during production, and provides guidelines for preparing scripts for voice talent. Additionally, it describes essential storyboard elements, roles, and rules to ensure efficient and effective eLearning project management.