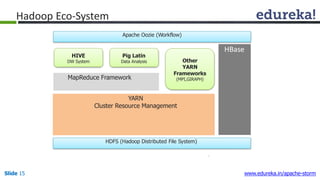
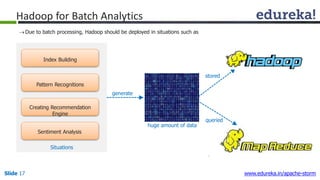
This document provides an introduction to Apache Storm and real-time big data analytics. It discusses how Storm can be used for processing real-time streaming data, as batch processing is not suitable. The three key points are:
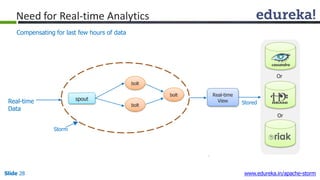
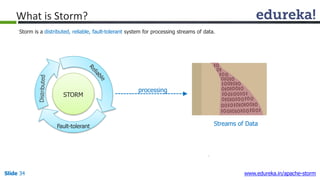
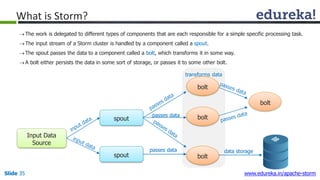
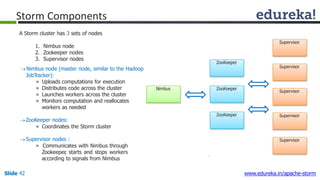
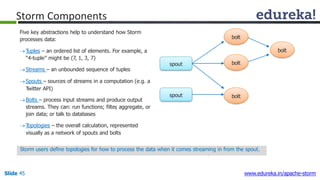
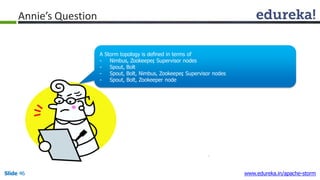
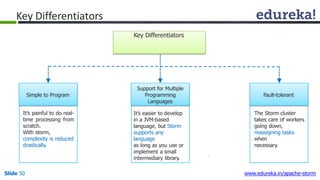
1) Storm is an open source framework for real-time processing of streaming data. It uses spouts and bolts to distribute work across a cluster.
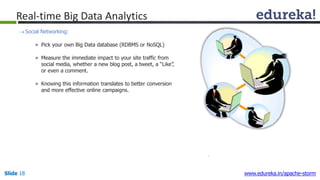
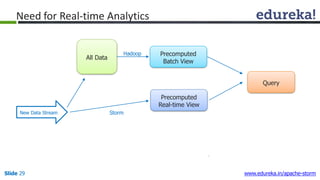
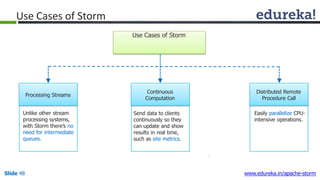
2) Real-time analytics are needed in many domains like social media, SaaS, and financial services to take immediate actions.
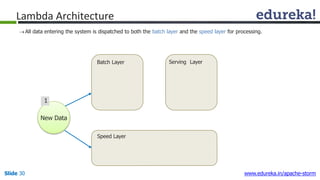
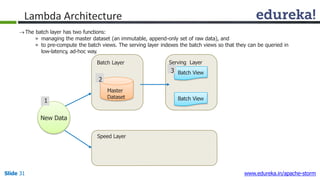
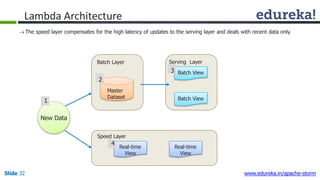
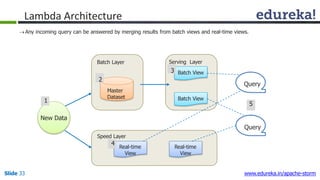
3) The Lambda architecture combines batch and real-time processing to always serve the latest data through merging batch and real-time views.