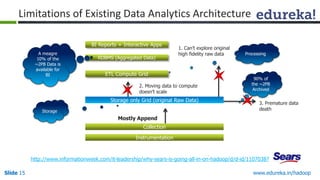
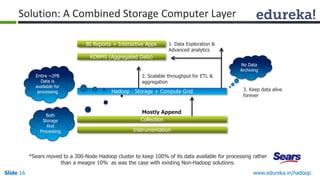
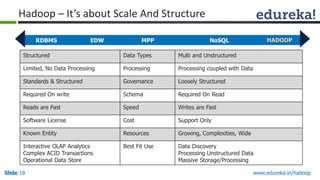
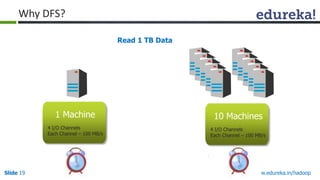
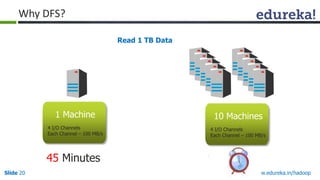
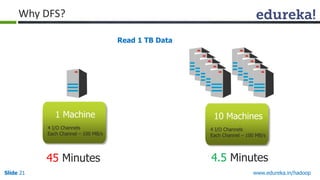
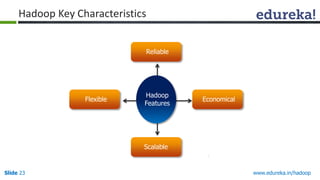
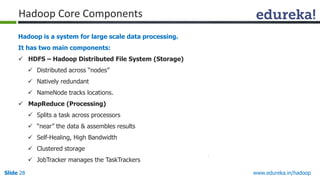
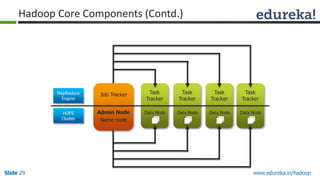
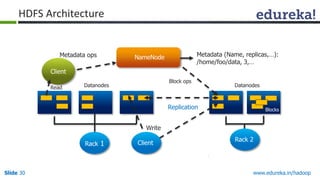
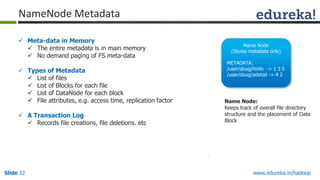
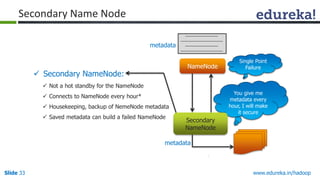
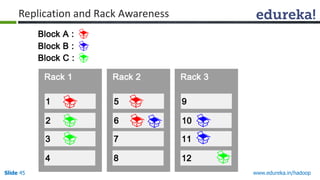
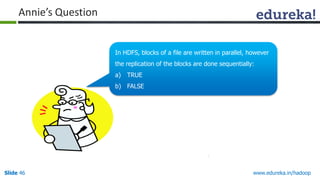
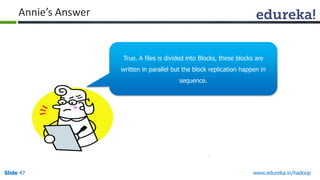
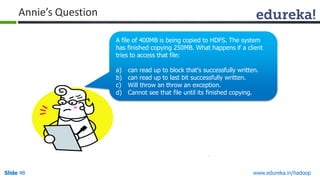
This document outlines the modules and topics covered in an Edureka course on Hadoop. The 10 modules cover understanding Big Data and Hadoop architecture, Hadoop cluster configuration, MapReduce framework, Pig, Hive, HBase, Hadoop 2.0 features, and Apache Oozie. Interactive questions are also included to test understanding of concepts like Hadoop core components, HDFS architecture, and MapReduce job execution.