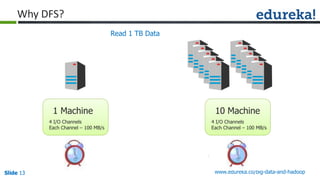
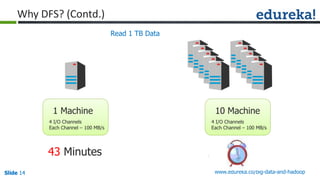
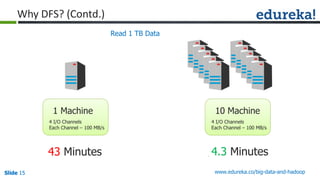
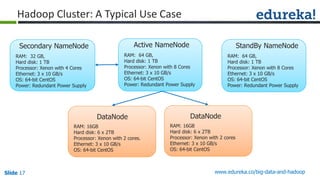
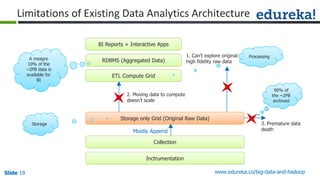
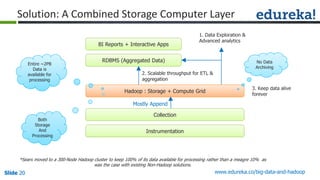
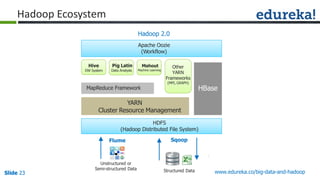
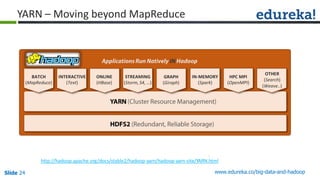
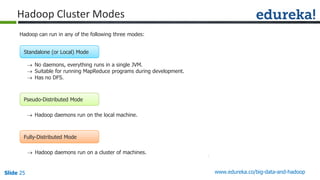
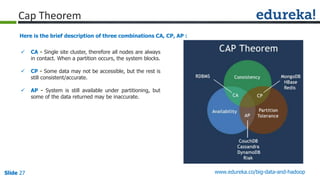
The document provides an introduction to Big Data and Hadoop, outlining key learning paths and objectives, including understanding Hadoop's architecture and ecosystem. It explores the characteristics of Big Data, discusses common use cases across various industries, and highlights the advantages of using Hadoop for processing large datasets. Additionally, it includes information on certification paths, Hadoop cluster modes, and a case study on Sears' transition to a Hadoop cluster for better data processing capabilities.