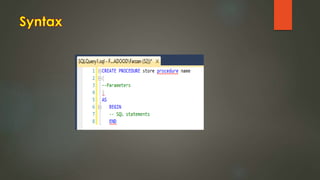
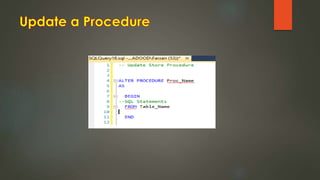
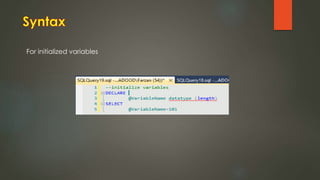
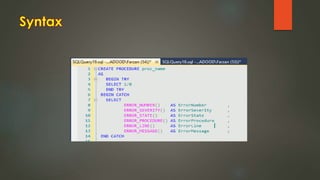
This document discusses stored procedures in SQL Server. It covers creating, updating, and deleting stored procedures, as well as using parameters, variables, and error handling within stored procedures. Several key benefits of stored procedures are that they reduce network traffic, can be optimized by the database compiler, and allow centralized management of logic and security. The document also provides examples of creating parameterized and non-parameterized stored procedures.