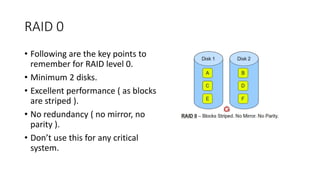
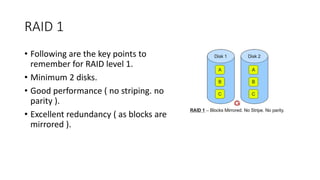
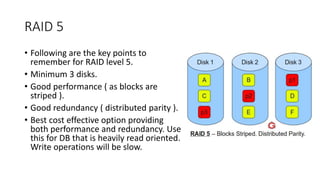
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), detailing its functions, storage solutions, and the importance of digital data management in medical imaging. It discusses both short-term and long-term storage options including Direct Attached Storage, Network Attached Servers, Storage Area Networks, and cloud-based systems, highlighting their performance, redundancy, and data backup capabilities. Additionally, the document addresses the challenges and benefits associated with adopting cloud-based PACS solutions within healthcare institutions.