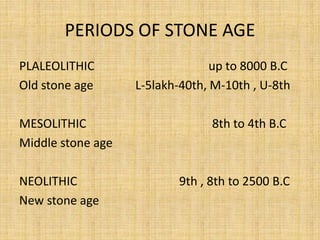
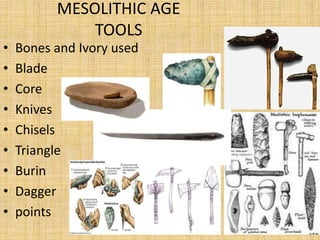
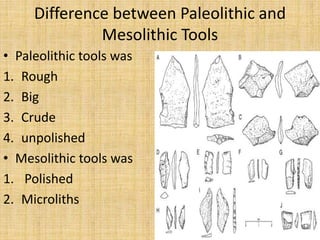
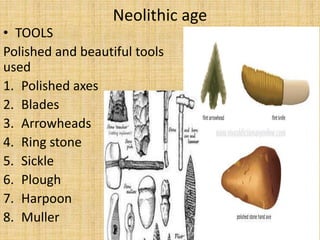
The document summarizes the three periods of the Stone Age - Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic. It describes tools, dwellings, food sources, and religious practices in each period. The Paleolithic period saw the earliest stone tools used by hunter-gatherers living in caves. The Mesolithic period introduced smaller polished stone tools and early domestication of animals. The Neolithic period marked the emergence of permanent settlements, polished stone tools for farming, and early social organization and religious practices like burial and ancestor worship.