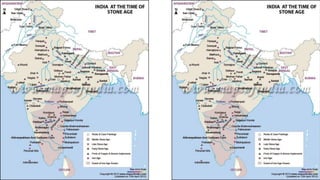
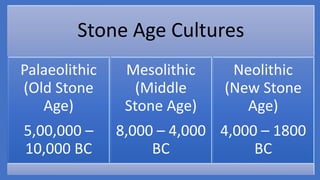
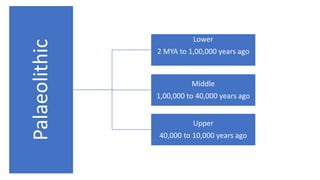
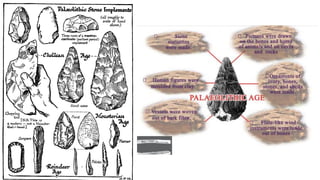
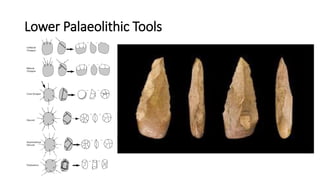
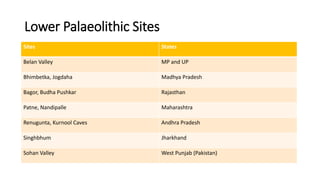
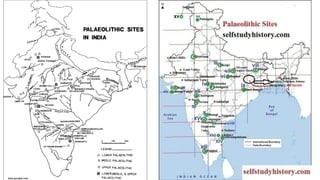
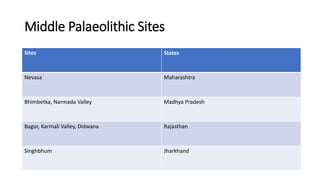
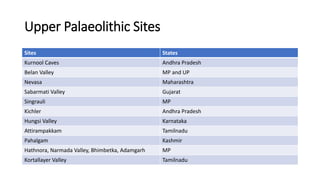
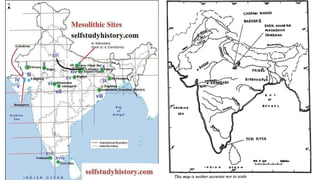
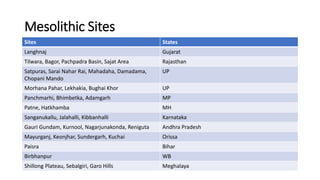
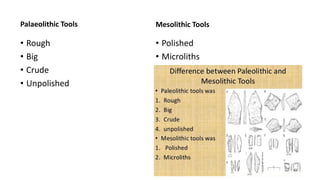
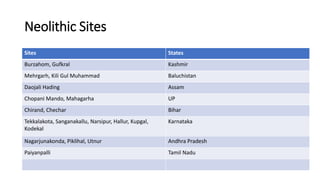
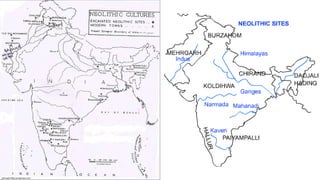
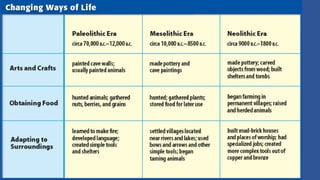
The document summarizes Stone Age cultures from the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods. It discusses the evolution of tool technology over time from crude stone tools to polished tools. It provides details on tool types, sites discovered, changes in subsistence patterns from hunting/gathering to agriculture, and developments in arts, religion, and settlements. The Stone Age spans from around 2-2.5 million years ago to 1800 BC and saw significant cultural and technological developments among prehistoric humans.