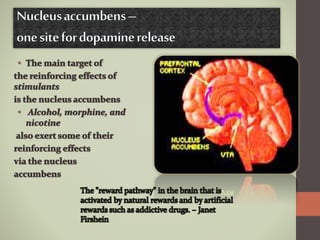
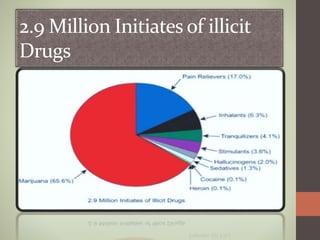
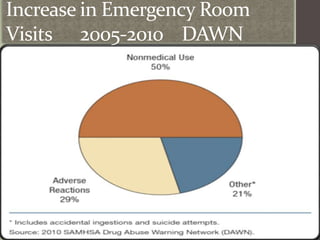
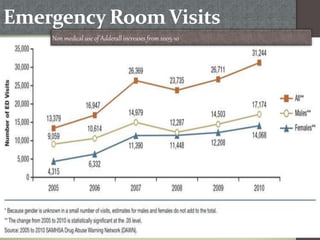
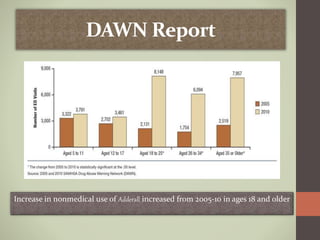
Prescription drug abuse, especially of stimulants used to treat conditions like ADHD, has been rising in recent years according to national surveys. Stimulants work by increasing levels of dopamine in the brain, which can produce feelings of pleasure and reward. Dopamine plays a key role in functions like cognition, motivation, and mood. Commonly abused prescription stimulants include Adderall and Ritalin, which are normally prescribed to treat ADHD. While they can improve focus and energy when taken properly, abusing these drugs by crushing them and snorting or injecting can have serious unwanted side effects and lead to addiction. Emergency room visits and deaths related to prescription drug overdoses have been increasing from 2005 to