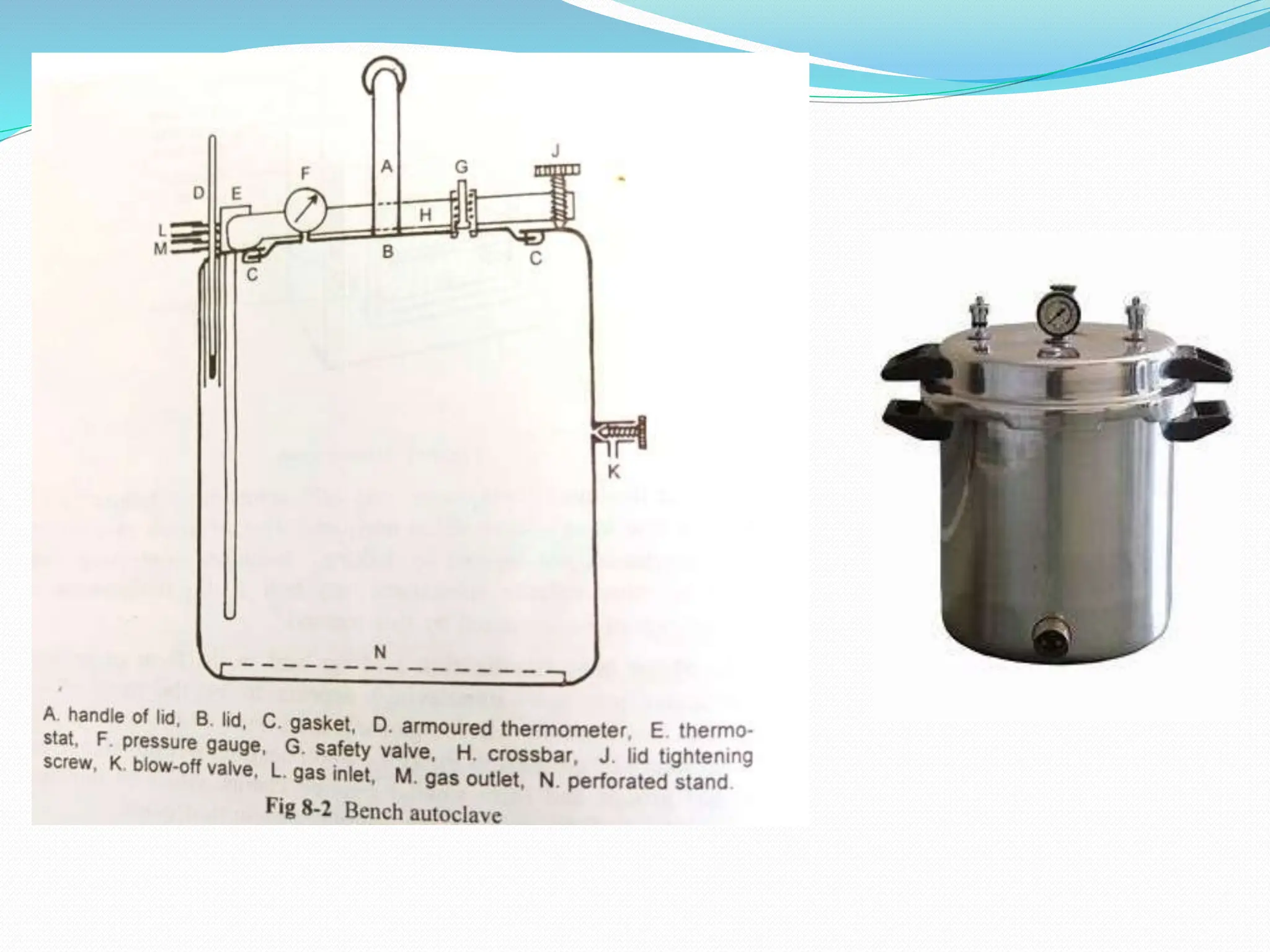
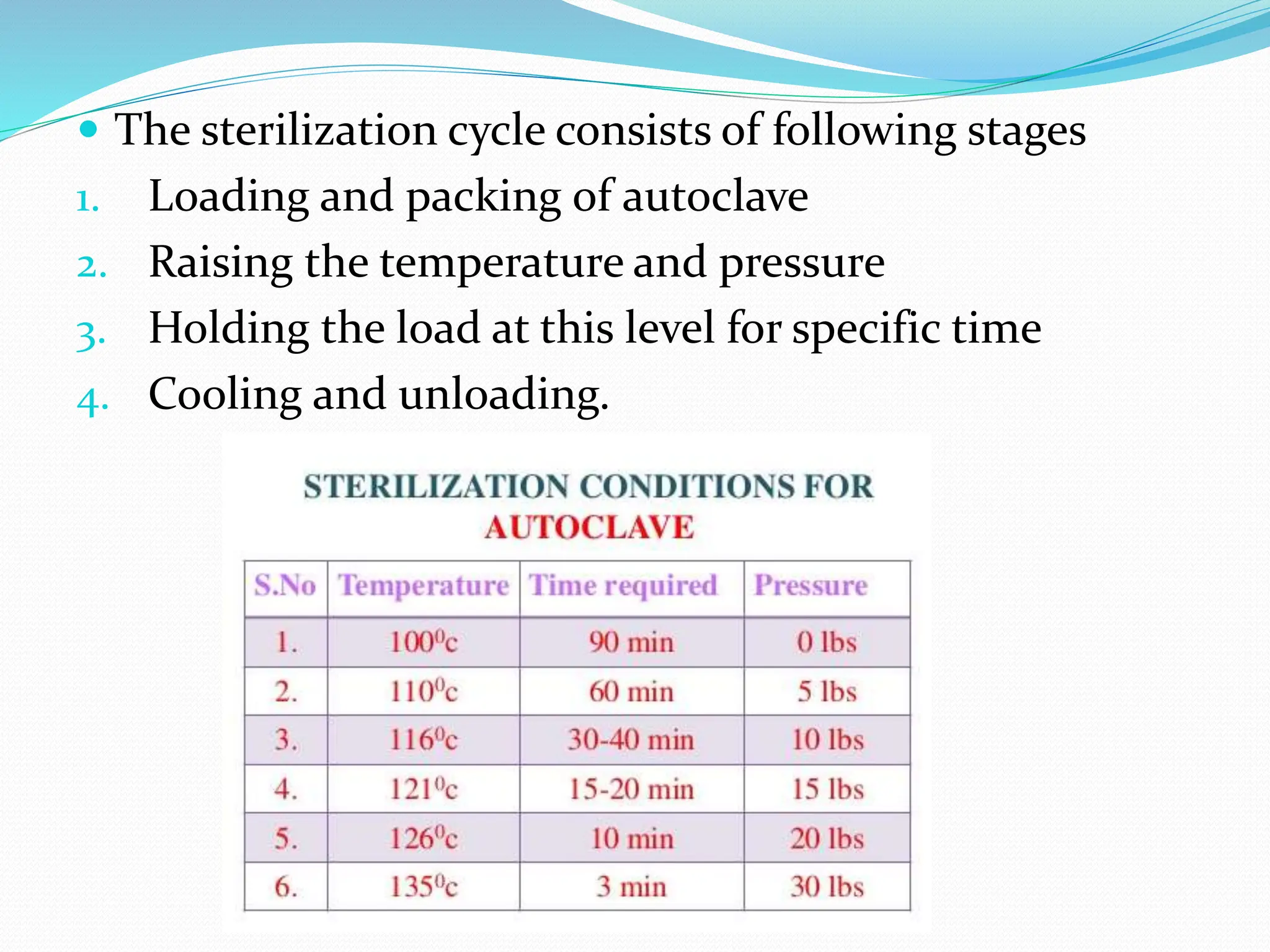
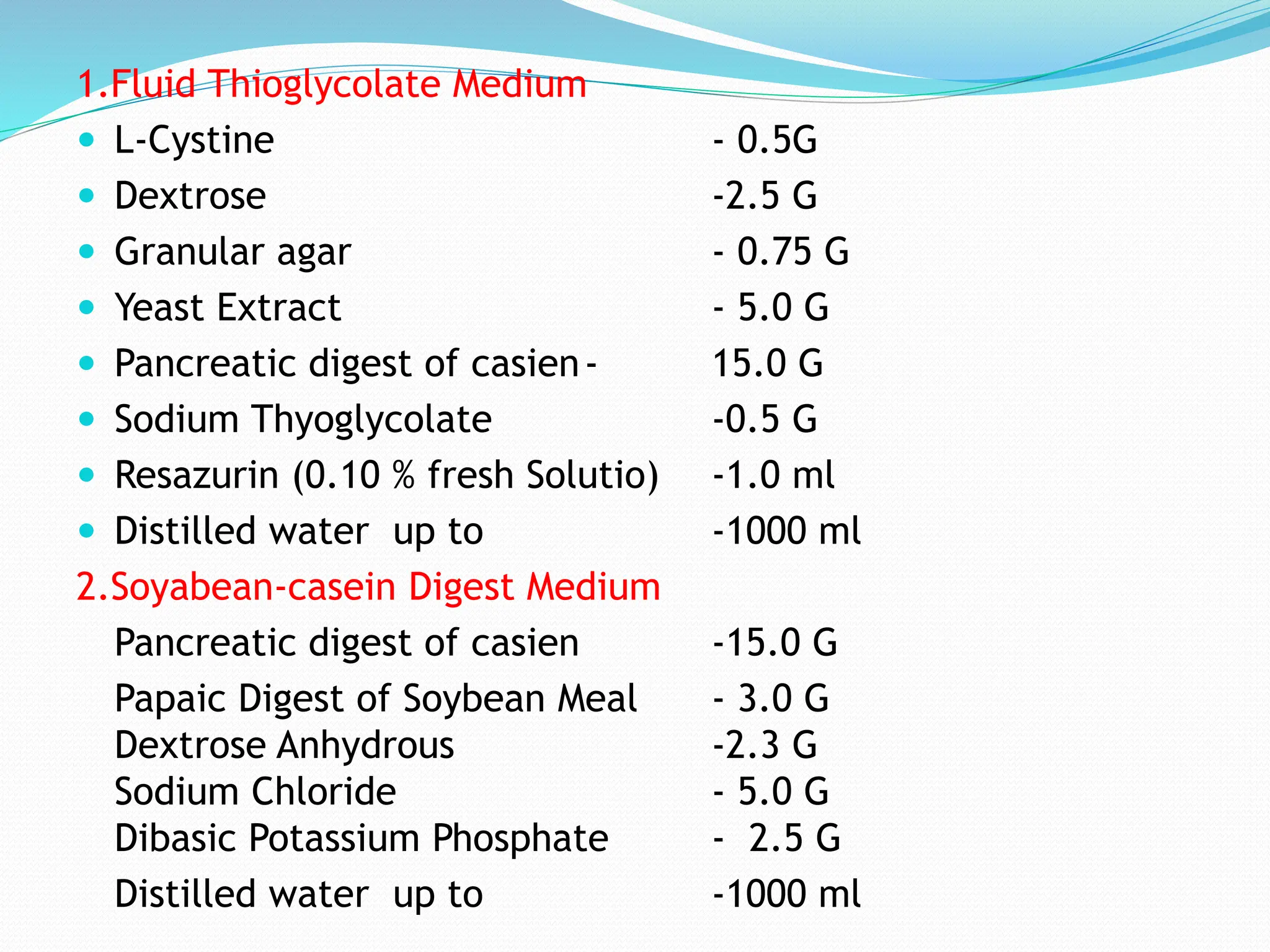
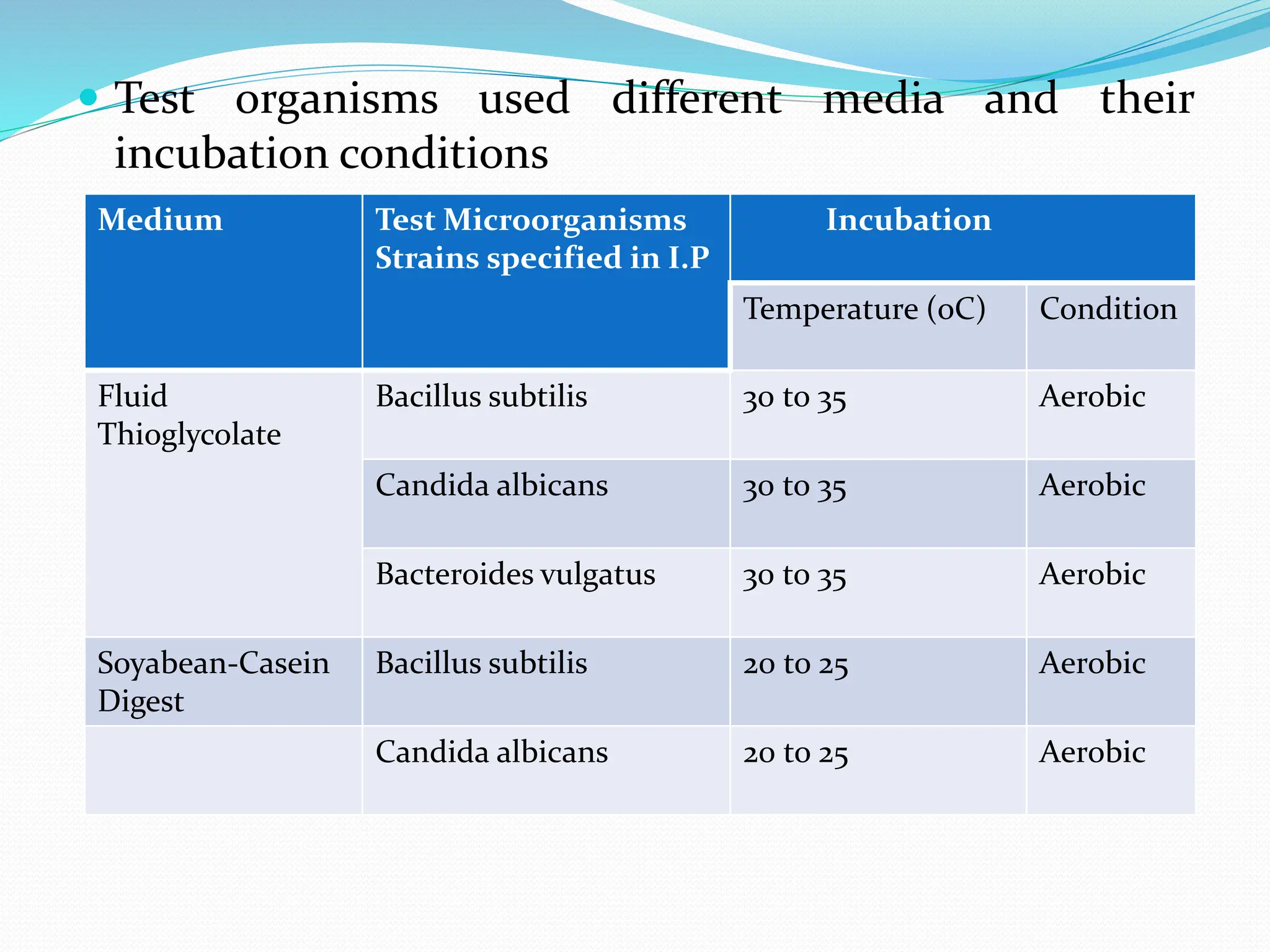
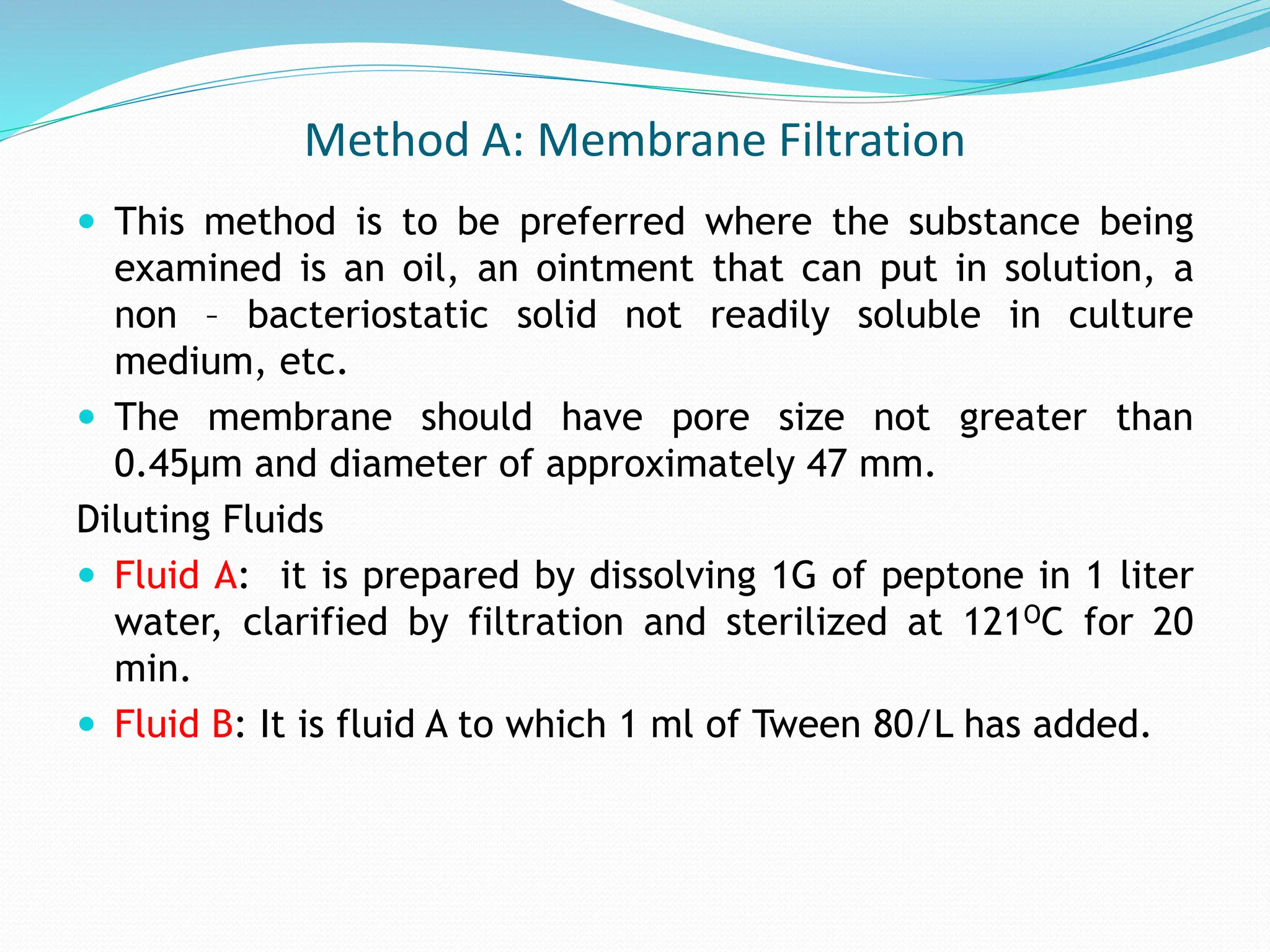
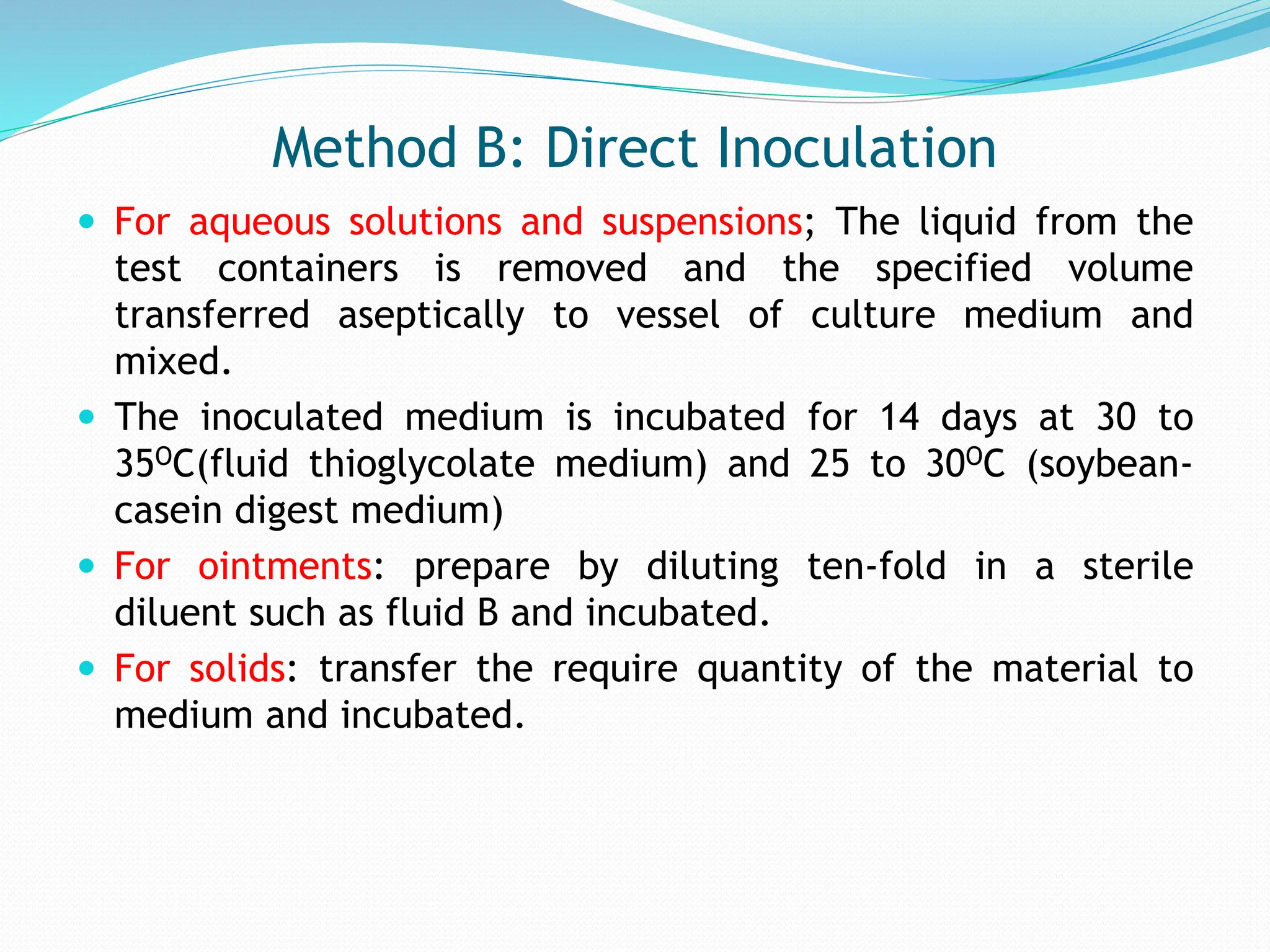
Sterilization refers to any process that eliminates transmissible agents like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. There are several methods of sterilization, including heat, radiation, filtration, and chemicals. Heat sterilization is the most common method and involves the use of dry heat or moist heat to kill microorganisms. Moist heat in the form of steam under pressure, as used in an autoclave, is effective at penetrating materials and achieving sterilization. Other methods include radiation like UV light or gamma rays, filtration through fine filters to physically remove microbes, and chemicals like ethylene oxide gas that sterilize without heat.