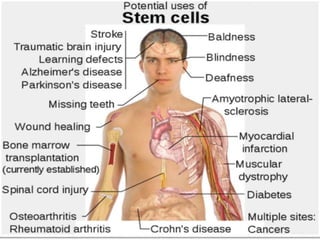
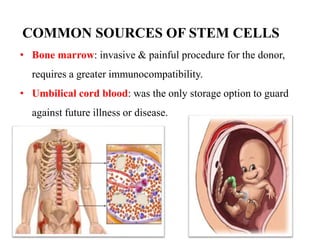
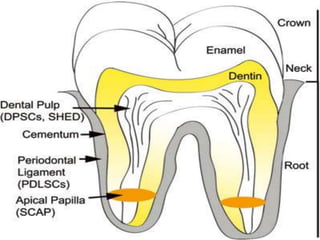
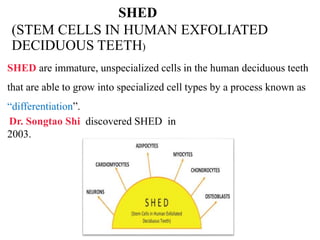
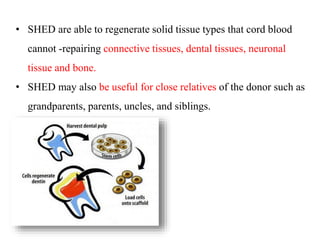
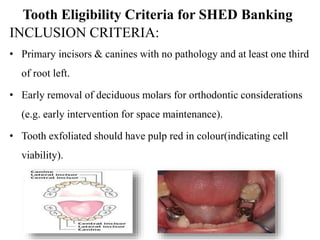
- Recent studies have shown that stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) can develop into more types of body tissue than other stem cell sources.
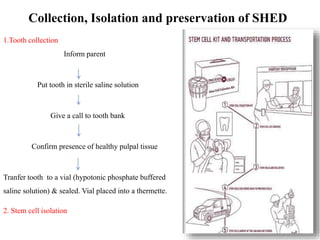
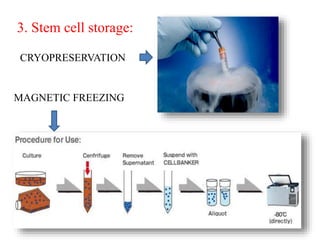
- SHED are a promising source of stem cells because they can be easily collected from discarded baby teeth, have a high proliferation rate, and may be useful for treating a variety of conditions through cell therapy and tissue regeneration.
- It is advantageous for parents to bank their child's SHED now while they are young and healthy to provide a guaranteed stem cell donor source for any future medical needs.