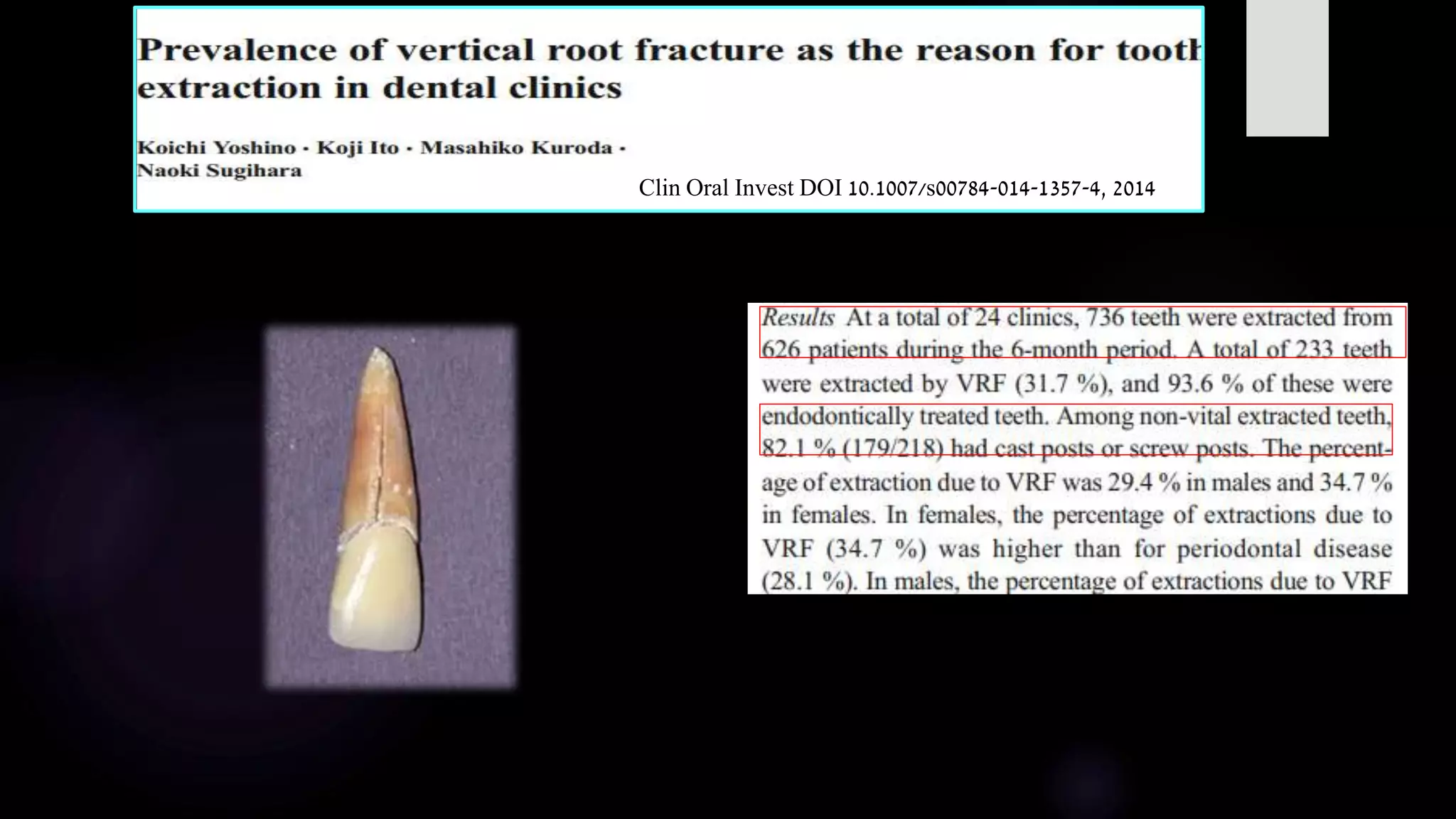
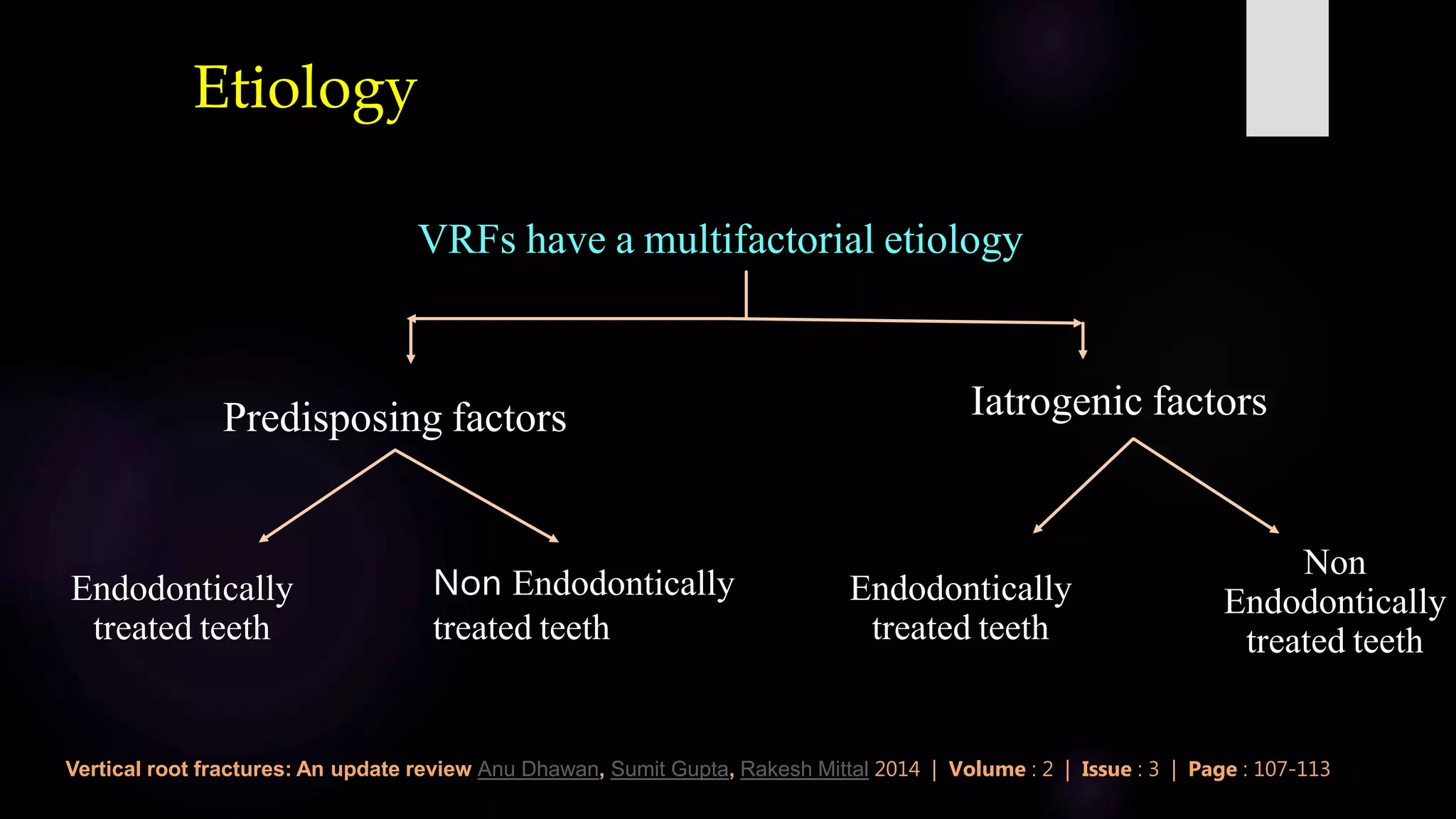
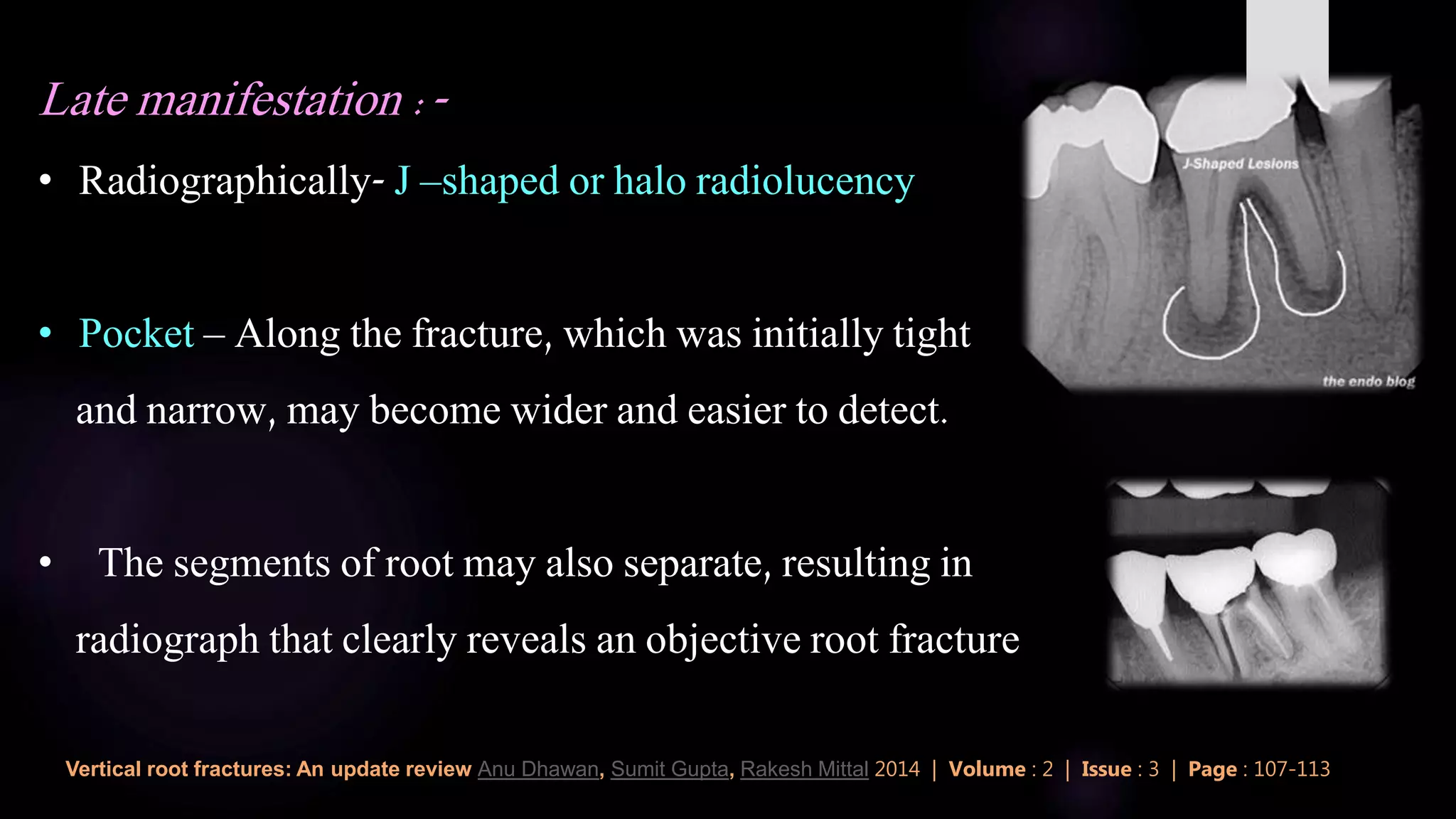
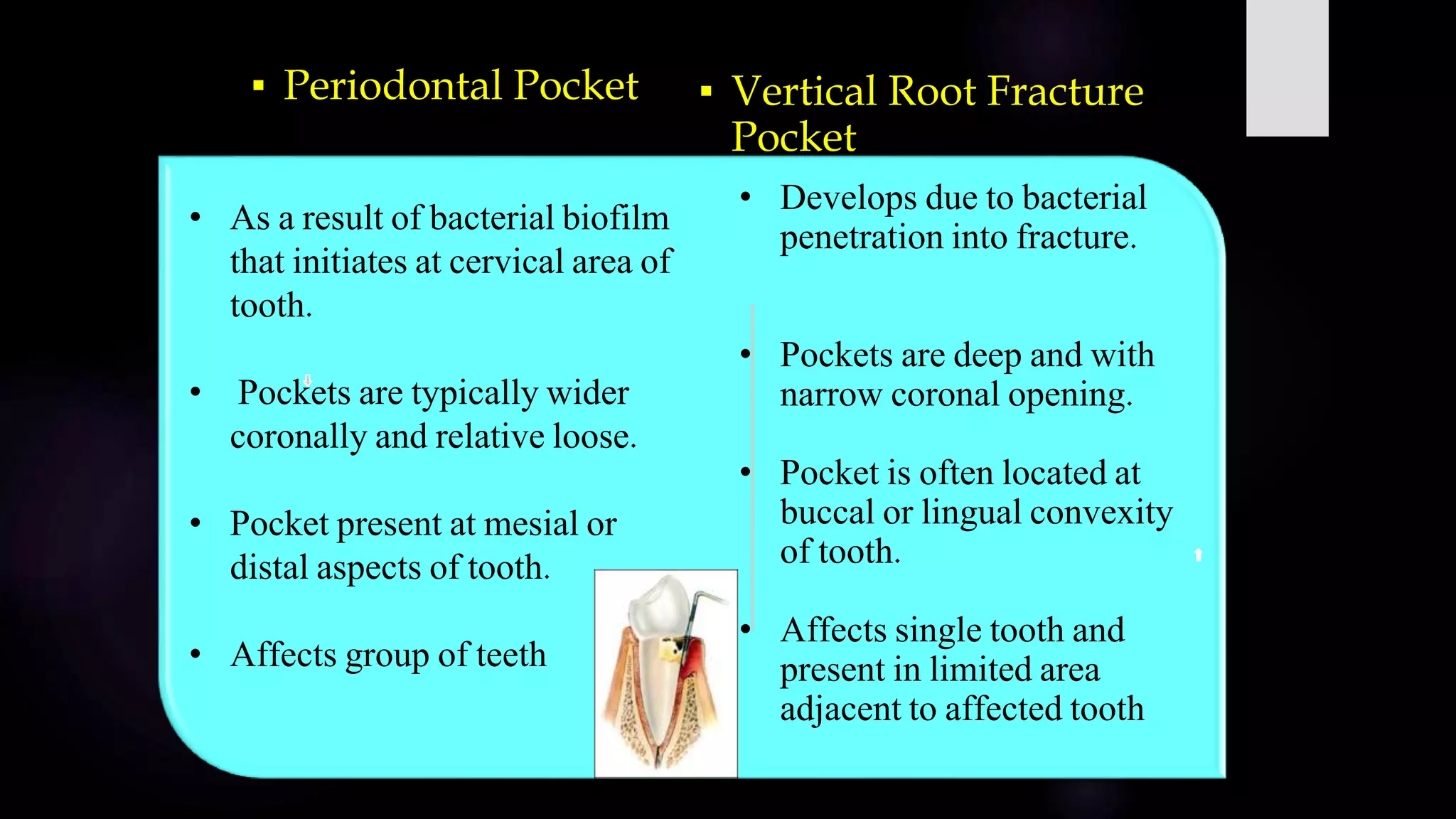
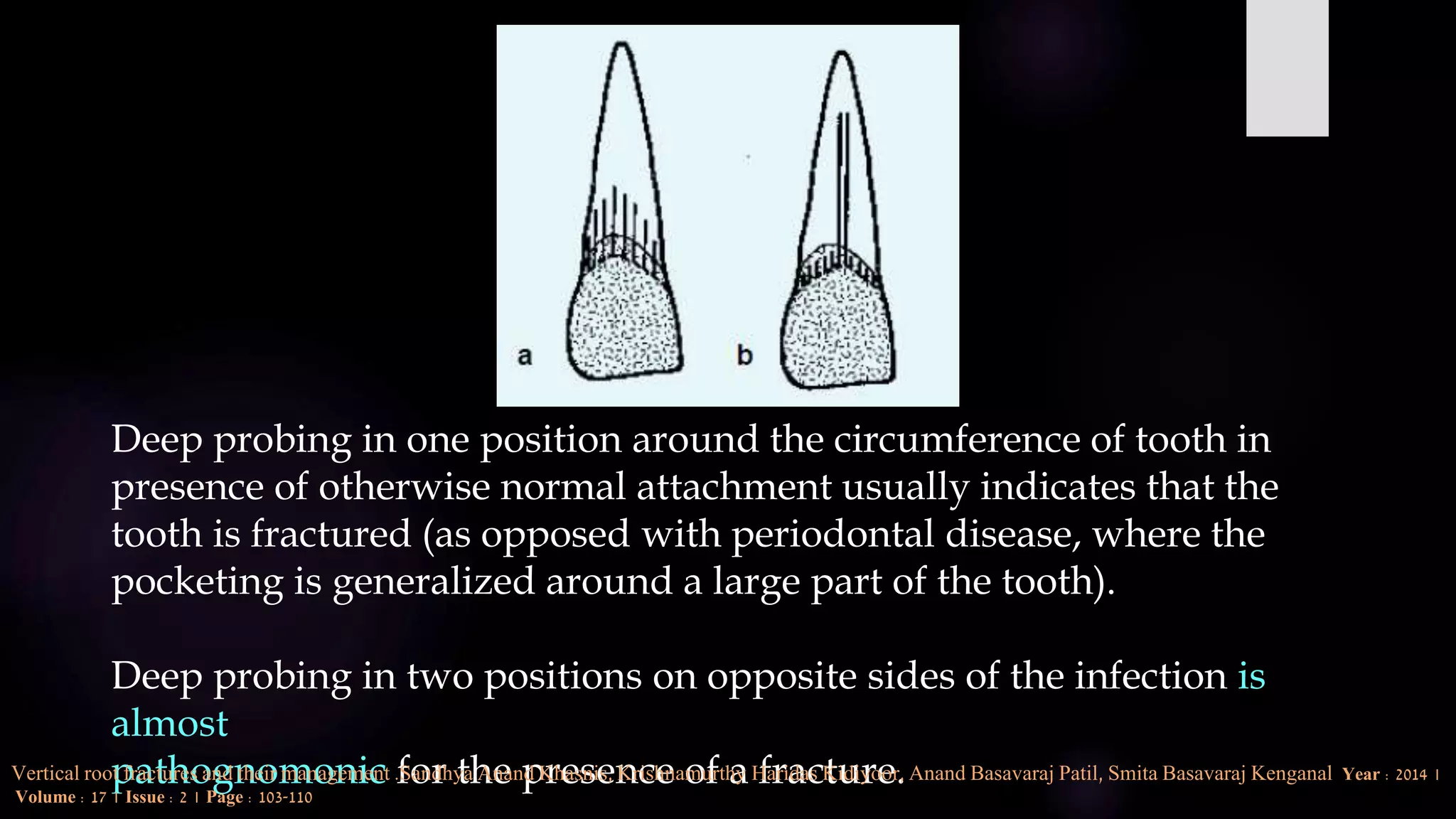
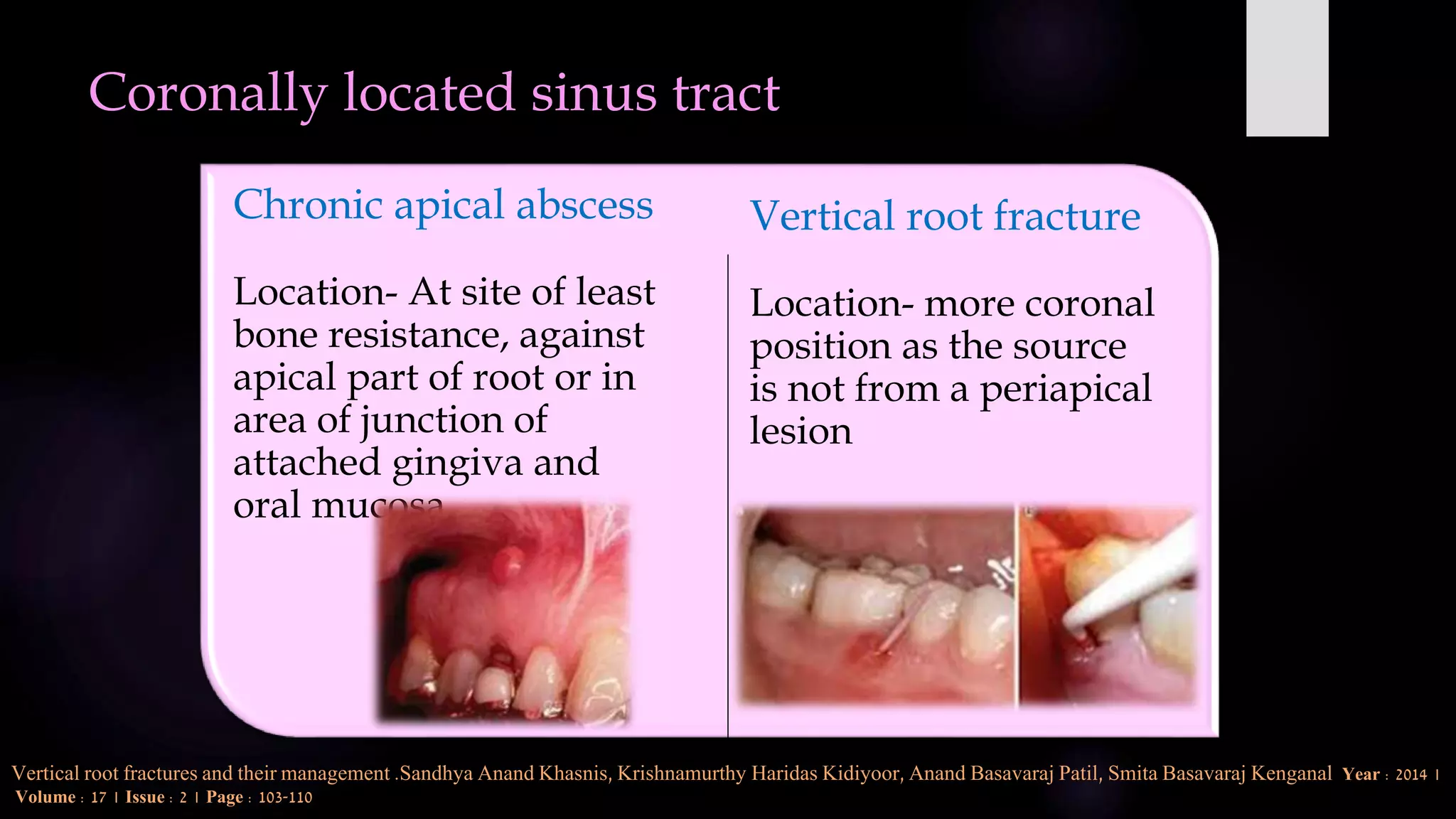
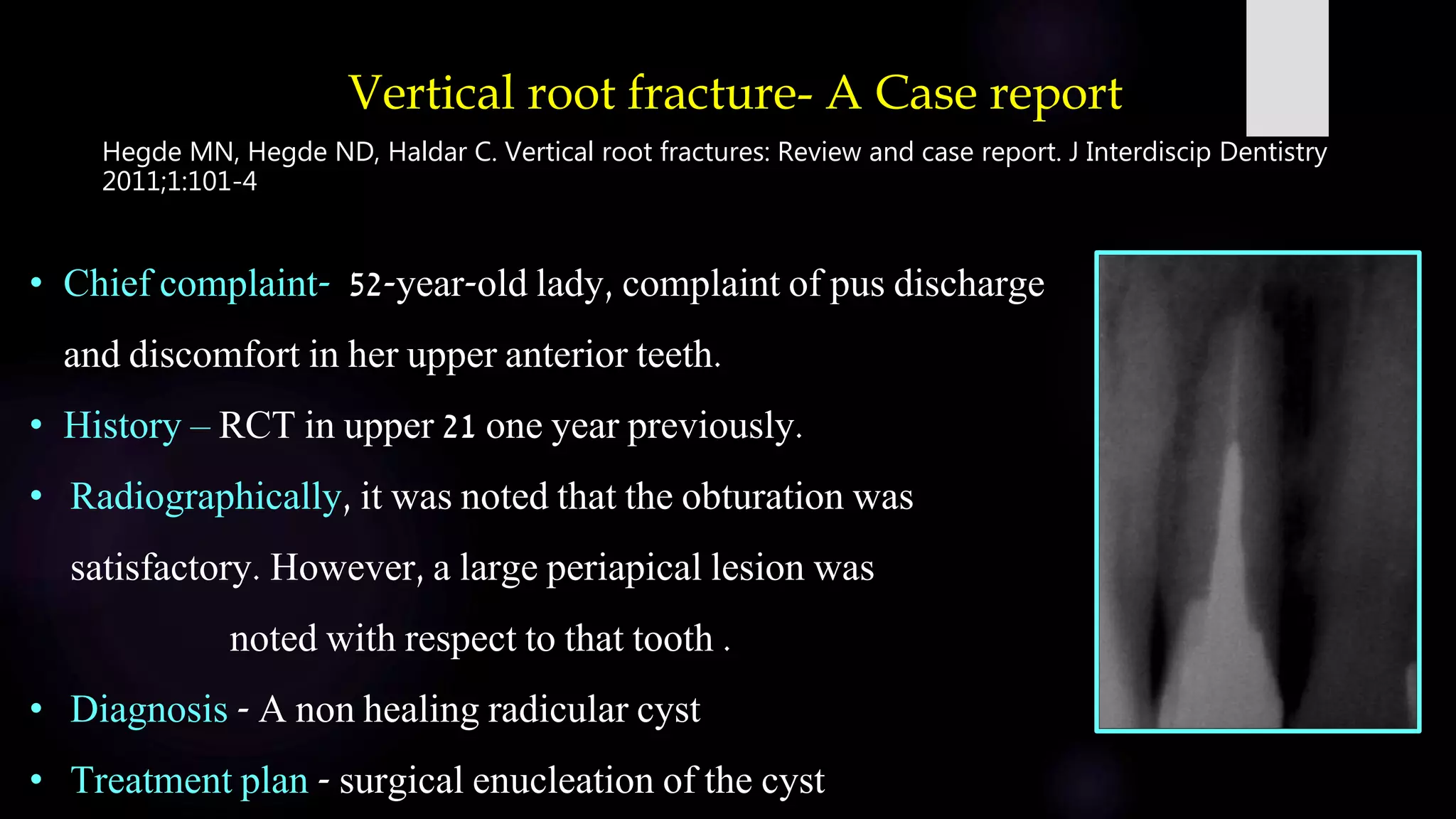
This document discusses vertical root fractures, including their definition, classification, etiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and prevalence. A vertical root fracture is a longitudinally oriented complete or incomplete fracture that originates in the root. Premolars are the most susceptible teeth. Risk factors include endodontic treatment, posts, and excessive forces from trauma or heavy chewing. Clinically, a vertical root fracture may cause vague pain, a sinus tract, or a narrow isolated periodontal pocket. Radiographs may reveal a J-shaped radiolucency or separated root segments. Diagnosis is based on clinical history and examination, as well as radiographic findings. Vertical root fractures account for 3-20% of extracted teeth.