Stellar life cycle section 3
•Download as PPT, PDF•
1 like•629 views
Stellar Life Cycle 1. Stars are born from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. 2. Most stars, including our Sun, spend the majority of their lifespan fusing hydrogen into helium as main sequence stars. 3. Towards the end of their life, stars expand into red giants or supergiants and begin fusing heavier elements, before shrinking into white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Life Cycle Of Stars

All stars begin as nebulae of dust and gas that collapse under gravity into protostars. They fuse hydrogen into helium during the main sequence stage, which is the longest phase in a star's life. A star's ultimate fate depends on its mass. Small mass stars become white dwarfs after the main sequence, while medium mass stars become red giants then white dwarfs. Large mass stars over 15 solar masses may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Life Cycle Of A Star

The life cycle of a star consists of 5 main stages:
1. Protostars form from huge clouds of gas that collapse under gravity.
2. Main sequence stars like our Sun fuse hydrogen for billions of years.
3. Red giants expand and their outer layers cool as hydrogen runs out.
4. White dwarfs form as red giants collapse under gravity into dense remnants.
5. Black dwarfs are the final remains that cool for eternity, emitting no light.
Star lifecycles poster

High-mass stars have shorter lifespans of 1 million to tens of millions of years compared to low-mass stars like our Sun which live for tens of millions to trillions of years. During their main sequence phase, stars convert about 1/3 of their hydrogen into helium through nuclear fusion. Massive stars are capable of fusing heavier elements like iron. In their later evolution, stars eject their outer layers and collapse their cores, possibly becoming a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole at the end of their life.
Life cycle of a star

Stars are born from contracting nebulae of gas and dust. They spend most of their lives on the main sequence, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Eventually they run out of fuel in their cores and their outer layers expand, forming red giants or supergiants. From there, smaller stars shed their outer layers to form planetary nebulae and white dwarfs, while larger stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
The life cycle of a star

The document outlines the life cycle of stars from birth in nebulae of gas and dust through their main sequence phase, later evolution into red giants, and final stages as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. It describes how gravity pulls gas together in nebulae to form protostars, which become main sequence stars fueling nuclear fusion for millions of years. As hydrogen runs out in their cores, more massive stars explode as supernovae while lower mass stars expand into red giants then contract into white dwarfs.
Star formation

The document discusses the lifecycle of stars from their formation to death. It begins by defining what stars and constellations are. It then focuses on our sun as a medium-sized, yellow star at the center of our solar system. Stars are classified based on temperature and brightness as young dwarf stars or older, larger supergiant stars. The document outlines the typical stages a star like the sun will progress through over billions of years from birth from clouds of dust and gas, burning hydrogen through nuclear fusion as a main sequence star, and eventual death through expansion and explosion at the end of its life. Various nebulae and supernova remnants are used as examples of star birth and death.
The Life Cycle of a Star PowerPoint

Stars are born from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Over billions of years, stars progress through various stages as they age. Lower mass stars begin as protostars and become main sequence stars fueled by nuclear fusion. As their hydrogen runs out, they become red giants and eventually white dwarfs. Higher mass stars explode as supernovae at the end of their lives, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Planetary nebulae formation

Planetary nebulae form during the late stages of evolution for low-to-medium mass stars. As a star expands into a red giant, it ejects its outer layers through pulsations and stellar winds. The hot core ionizes the ejected gas, causing it to glow brightly. This energized shell of nebulous gas appears as a planetary nebula. Examples are the Helix Nebula and Ring Nebula. More massive stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes, depending on the star's original mass. The document discusses these stages of stellar evolution and death that give rise to different astronomical phenomena like planetary nebulae and neutron stars.
Recommended
Life Cycle Of Stars

All stars begin as nebulae of dust and gas that collapse under gravity into protostars. They fuse hydrogen into helium during the main sequence stage, which is the longest phase in a star's life. A star's ultimate fate depends on its mass. Small mass stars become white dwarfs after the main sequence, while medium mass stars become red giants then white dwarfs. Large mass stars over 15 solar masses may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Life Cycle Of A Star

The life cycle of a star consists of 5 main stages:
1. Protostars form from huge clouds of gas that collapse under gravity.
2. Main sequence stars like our Sun fuse hydrogen for billions of years.
3. Red giants expand and their outer layers cool as hydrogen runs out.
4. White dwarfs form as red giants collapse under gravity into dense remnants.
5. Black dwarfs are the final remains that cool for eternity, emitting no light.
Star lifecycles poster

High-mass stars have shorter lifespans of 1 million to tens of millions of years compared to low-mass stars like our Sun which live for tens of millions to trillions of years. During their main sequence phase, stars convert about 1/3 of their hydrogen into helium through nuclear fusion. Massive stars are capable of fusing heavier elements like iron. In their later evolution, stars eject their outer layers and collapse their cores, possibly becoming a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole at the end of their life.
Life cycle of a star

Stars are born from contracting nebulae of gas and dust. They spend most of their lives on the main sequence, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Eventually they run out of fuel in their cores and their outer layers expand, forming red giants or supergiants. From there, smaller stars shed their outer layers to form planetary nebulae and white dwarfs, while larger stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
The life cycle of a star

The document outlines the life cycle of stars from birth in nebulae of gas and dust through their main sequence phase, later evolution into red giants, and final stages as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. It describes how gravity pulls gas together in nebulae to form protostars, which become main sequence stars fueling nuclear fusion for millions of years. As hydrogen runs out in their cores, more massive stars explode as supernovae while lower mass stars expand into red giants then contract into white dwarfs.
Star formation

The document discusses the lifecycle of stars from their formation to death. It begins by defining what stars and constellations are. It then focuses on our sun as a medium-sized, yellow star at the center of our solar system. Stars are classified based on temperature and brightness as young dwarf stars or older, larger supergiant stars. The document outlines the typical stages a star like the sun will progress through over billions of years from birth from clouds of dust and gas, burning hydrogen through nuclear fusion as a main sequence star, and eventual death through expansion and explosion at the end of its life. Various nebulae and supernova remnants are used as examples of star birth and death.
The Life Cycle of a Star PowerPoint

Stars are born from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Over billions of years, stars progress through various stages as they age. Lower mass stars begin as protostars and become main sequence stars fueled by nuclear fusion. As their hydrogen runs out, they become red giants and eventually white dwarfs. Higher mass stars explode as supernovae at the end of their lives, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Planetary nebulae formation

Planetary nebulae form during the late stages of evolution for low-to-medium mass stars. As a star expands into a red giant, it ejects its outer layers through pulsations and stellar winds. The hot core ionizes the ejected gas, causing it to glow brightly. This energized shell of nebulous gas appears as a planetary nebula. Examples are the Helix Nebula and Ring Nebula. More massive stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes, depending on the star's original mass. The document discusses these stages of stellar evolution and death that give rise to different astronomical phenomena like planetary nebulae and neutron stars.
Life Cycle Of A Star

The document discusses the life cycle of stars from their birth in nebulae to their death. Stars are born when gas and dust clouds collapse under gravity and heat up. During their main sequence phase, stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores. Later, larger stars become red giants or supergiants as their cores shrink and outer layers expand. Eventually, stars die and eject their outer layers, leaving behind dense remnants like white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes.
The Life Cycle of a Star

Stars are formed from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. As stars age and evolve, they progress through different stages - from stars to red giants or dwarfs to supernovae. The most massive stars may collapse into neutron stars or black holes. Black holes are objects so dense that not even light can escape their powerful gravitational pull. Material near a black hole forms a swirling accretion disk and is ejected at nearly light speed in powerful jets. Advancing technology is improving our understanding of stellar evolution and black hole formation.
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR!

All stars begin as clouds of dust and gas called nebulae. When gravity causes the nebula to collapse, a protostar forms at the center. The protostar grows in size and temperature through nuclear fusion reactions until it becomes a stable main sequence star. Small stars like our Sun will eventually expand into red giants and shed their outer layers, leaving behind dense white dwarf cores. Larger stars may explode as supernovae, collapsing into neutron stars or black holes. The life cycle of a star depends on its initial mass, with smaller stars ending as white dwarfs and more massive stars ending as black holes or neutron stars.
Stars

A star is a ball of plasma held together by gravity that undergoes nuclear fusion at its core, releasing electromagnetic radiation. Stars exist along a spectrum from hot, blue stars to cooler, red stars and can be classified based on their temperature, luminosity, and color. A star's life cycle begins as a contracting nebula and progresses through stages such as the main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, and white dwarf before ending as a neutron star or black hole.
Types of stars

This document describes different stages and types of stars:
- Main sequence stars like our Sun spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Red giants are large, reddish stars that have exhausted hydrogen fusion and begun fusing helium.
- Planetary nebulae form when average-sized stars eject their outer layers after becoming red giants, leaving behind dense, hot cores called white dwarfs.
- Brown dwarfs are failed stars too small to sustain nuclear fusion.
- Variable stars change in brightness over timescales from seconds to years as they evolve.
- Binary stars are two gravitationally bound stars that orbit a common center of mass.
Star Life Cycle

Stars are born from clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. As the gas spins faster under gravity, it heats up and forms a protostar. Nuclear fusion then occurs, turning the protostar into a main sequence star that shines for millions of years by fusing hydrogen into helium. Eventually the hydrogen runs out, causing the star to expand into a red giant. From there, less massive stars will blow off their outer layers and collapse into white dwarfs, while more massive stars will explode in supernovas and collapse into neutron stars or black holes.
life cycle of a star

The life cycle of stars depends on their mass. Lower mass stars like our Sun will eventually become red giants then white dwarfs. Higher mass stars live shorter lives and end as supernovas, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. All stars begin as nebulae of dust and gas that collapse under gravity into protostars and main sequence stars fueled by nuclear fusion.
Life Cycle Ppt.

Stars are formed from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Over millions of years, the nebula collapses under gravity to form a protostar. Once the protostar's core reaches 10 million K, nuclear fusion begins and the star enters the main sequence stage. During the main sequence, internal pressure balances gravitational forces. Low and medium mass stars end as white dwarfs, then eventually black dwarfs. Massive stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Life cycle of stars

There are different life cycle stages for stars depending on their original mass. Low mass stars progress through the stages of nebula, main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, and black dwarf. High mass stars go through nebula, main sequence, red supergiant, supernova, and either become a neutron star or black hole. The main sequence stage can last billions of years for low mass stars but only millions for high mass stars.
NEUTRON STARS AND WHITE DWARFS

White dwarfs are the burned-out cores of stars that have collapsed into an extremely dense state with no empty space between atoms. They have a mass similar to the sun's but are very small, around the size of Earth. Neutron stars are created during supernova explosions from the central core of a star that collapsed under gravity. They are an extremely compact ball of neutrons that are very hot, small, dense, and have masses higher than the sun's. Both white dwarfs and neutron stars achieve extreme density through electron or quantum degeneracy pressure preventing further gravitational collapse.
4.2 Stars have Life Cycles

Stars change over their life cycles depending on their mass. Low-mass stars like our Sun remain on the main sequence for billions of years, slowly fusing hydrogen into helium. Eventually they expand into red giants and later cool into white dwarfs. High-mass stars burn through their fuel quickly and explode as supernovae after millions of years, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. All stars form from contracting nebulae of gas and dust.
Stellar Evolution Powerpoint

This document discusses stellar evolution and how we observe stars across the universe. It notes that we can view stars forming, burning, and exploding using satellites and telescopes. The document also discusses the speed of light being 300,000 km/s and how we can observe stars millions or billions of light years away, seeing light from stars up to 10-15 billion light years away. Finally, it mentions that the Sun will gradually increase in radius and luminosity for another 5 billion years as hydrogen fusion provides its energy.
Galaxies nebulae stars notes

Within galaxies, star forming regions called nebulae contain clouds of dust, hydrogen and helium gases. Stars sometimes form within these nebulae as the gases and dust collapse under their own gravity. A nebula with protostars, or young stars that are still forming, is shown in the diagram. The document then goes on to describe the life cycle of stars like our Sun and the changes it will undergo as it evolves and eventually dies in approximately 5 billion years.
The Star

This document provides an overview of the characteristics, classifications, motions, and significance of stars. It discusses their sizes, colors, temperatures, compositions, and magnitudes. Stars are classified based on their spectral types, which relate to their surface temperatures. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram plots stars' luminosities and temperatures. Stars exhibit both apparent and actual motions, including proper motion across the sky. Studying stars helps us understand how elements are formed, how our solar system evolved, and the dynamics influencing galaxies.
Birth of the star

Stars are formed in nebulae, clouds of dust and gas found in spiral galaxies. Dense parts of these clouds undergo gravitational collapse, compressing to form a rotating gas globule. As the globule collapses over thousands to millions of years due to gravity and pressure, the increasing temperature and rotation cause it to form a central core and surrounding protoplanetary disk. Once the core reaches temperatures over 27 million degrees and nuclear fusion begins, it becomes a stable main sequence star.
Stars

Stars can be classified by their temperature as hot blue stars around 30,000 degrees, cool red stars around 2,500 degrees, or yellow stars like our sun around 6,000 degrees. Constellations like Orion can be identified by patterns of brighter stars. The brightness of stars is measured by their apparent and absolute magnitudes, with lower numbers indicating brighter stars. A nebula is a cloud where stars are born, and the Eagle Nebula is an example. Stellar evolution progresses from protostars to main sequence stars like our sun fusing hydrogen, then to giants and supergiants fusing helium, eventually leaving behind planetary nebulae and forming white dwarfs, or in massive stars, supernovae leading to neutron stars or
Star's Life Cycle

Stars go through life cycles like humans, being born from collapsing gas clouds, burning hydrogen through nuclear fusion on the main sequence, and eventually dying. Medium and low mass stars end as white dwarfs after shedding their outer layers, while high mass stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. Neutron stars are incredibly dense, rotating rapidly, while black holes have event horizons beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape.
Ch 19 -life and death of stars

1. Stars are born through nuclear fusion and spend most of their life fusing hydrogen into helium as a main sequence star.
2. When stars exhaust their hydrogen fuel, low mass stars become red giants and high mass stars explode as supernovae.
3. The remnants of dead stars are white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes depending on the original star's mass.
Star life cycle

Stars form from collapsing clouds of gas and dust found in nebulae. A star's life cycle depends on its mass - smaller stars less than 3 times the Sun's mass will spend most of their existence on the main sequence fusing hydrogen. Larger stars evolve more quickly, becoming red giants and eventually exploding as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Neutron stars liu jia

This document discusses neutron stars and explores them as natural laboratories for studying extremely dense matter. It provides background on stellar evolution and supernovae that form neutron stars. Neutron stars are incredibly small yet dense, with masses of around 1.35-2 times the sun's mass compressed into the size of Manhattan. They also spin incredibly fast due to conservation of angular momentum. The document examines using neutron stars to study how matter behaves under extreme density and discusses challenges in measuring their precise masses and radii from Earth. It outlines the author's research simulating neutron star atmospheres to help answer fundamental physics questions about their properties.
Birth & death of stars (teach)

A short description, at the elementary school level, describing stars and telling how they are created and how they end.
Stars

Stars form from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Nuclear fusion in the core of stars produces heat and light. Small, low-mass stars like our Sun will live for billions of years on the main sequence before becoming red giants then white dwarfs. Massive stars burn quickly and end their lives in supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. A star's life cycle depends on its initial mass, with smaller stars living longer.
More Related Content
What's hot
Life Cycle Of A Star

The document discusses the life cycle of stars from their birth in nebulae to their death. Stars are born when gas and dust clouds collapse under gravity and heat up. During their main sequence phase, stars fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores. Later, larger stars become red giants or supergiants as their cores shrink and outer layers expand. Eventually, stars die and eject their outer layers, leaving behind dense remnants like white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes.
The Life Cycle of a Star

Stars are formed from clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. As stars age and evolve, they progress through different stages - from stars to red giants or dwarfs to supernovae. The most massive stars may collapse into neutron stars or black holes. Black holes are objects so dense that not even light can escape their powerful gravitational pull. Material near a black hole forms a swirling accretion disk and is ejected at nearly light speed in powerful jets. Advancing technology is improving our understanding of stellar evolution and black hole formation.
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR!

All stars begin as clouds of dust and gas called nebulae. When gravity causes the nebula to collapse, a protostar forms at the center. The protostar grows in size and temperature through nuclear fusion reactions until it becomes a stable main sequence star. Small stars like our Sun will eventually expand into red giants and shed their outer layers, leaving behind dense white dwarf cores. Larger stars may explode as supernovae, collapsing into neutron stars or black holes. The life cycle of a star depends on its initial mass, with smaller stars ending as white dwarfs and more massive stars ending as black holes or neutron stars.
Stars

A star is a ball of plasma held together by gravity that undergoes nuclear fusion at its core, releasing electromagnetic radiation. Stars exist along a spectrum from hot, blue stars to cooler, red stars and can be classified based on their temperature, luminosity, and color. A star's life cycle begins as a contracting nebula and progresses through stages such as the main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, and white dwarf before ending as a neutron star or black hole.
Types of stars

This document describes different stages and types of stars:
- Main sequence stars like our Sun spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores.
- Red giants are large, reddish stars that have exhausted hydrogen fusion and begun fusing helium.
- Planetary nebulae form when average-sized stars eject their outer layers after becoming red giants, leaving behind dense, hot cores called white dwarfs.
- Brown dwarfs are failed stars too small to sustain nuclear fusion.
- Variable stars change in brightness over timescales from seconds to years as they evolve.
- Binary stars are two gravitationally bound stars that orbit a common center of mass.
Star Life Cycle

Stars are born from clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. As the gas spins faster under gravity, it heats up and forms a protostar. Nuclear fusion then occurs, turning the protostar into a main sequence star that shines for millions of years by fusing hydrogen into helium. Eventually the hydrogen runs out, causing the star to expand into a red giant. From there, less massive stars will blow off their outer layers and collapse into white dwarfs, while more massive stars will explode in supernovas and collapse into neutron stars or black holes.
life cycle of a star

The life cycle of stars depends on their mass. Lower mass stars like our Sun will eventually become red giants then white dwarfs. Higher mass stars live shorter lives and end as supernovas, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. All stars begin as nebulae of dust and gas that collapse under gravity into protostars and main sequence stars fueled by nuclear fusion.
Life Cycle Ppt.

Stars are formed from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulas. Over millions of years, the nebula collapses under gravity to form a protostar. Once the protostar's core reaches 10 million K, nuclear fusion begins and the star enters the main sequence stage. During the main sequence, internal pressure balances gravitational forces. Low and medium mass stars end as white dwarfs, then eventually black dwarfs. Massive stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Life cycle of stars

There are different life cycle stages for stars depending on their original mass. Low mass stars progress through the stages of nebula, main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, and black dwarf. High mass stars go through nebula, main sequence, red supergiant, supernova, and either become a neutron star or black hole. The main sequence stage can last billions of years for low mass stars but only millions for high mass stars.
NEUTRON STARS AND WHITE DWARFS

White dwarfs are the burned-out cores of stars that have collapsed into an extremely dense state with no empty space between atoms. They have a mass similar to the sun's but are very small, around the size of Earth. Neutron stars are created during supernova explosions from the central core of a star that collapsed under gravity. They are an extremely compact ball of neutrons that are very hot, small, dense, and have masses higher than the sun's. Both white dwarfs and neutron stars achieve extreme density through electron or quantum degeneracy pressure preventing further gravitational collapse.
4.2 Stars have Life Cycles

Stars change over their life cycles depending on their mass. Low-mass stars like our Sun remain on the main sequence for billions of years, slowly fusing hydrogen into helium. Eventually they expand into red giants and later cool into white dwarfs. High-mass stars burn through their fuel quickly and explode as supernovae after millions of years, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. All stars form from contracting nebulae of gas and dust.
Stellar Evolution Powerpoint

This document discusses stellar evolution and how we observe stars across the universe. It notes that we can view stars forming, burning, and exploding using satellites and telescopes. The document also discusses the speed of light being 300,000 km/s and how we can observe stars millions or billions of light years away, seeing light from stars up to 10-15 billion light years away. Finally, it mentions that the Sun will gradually increase in radius and luminosity for another 5 billion years as hydrogen fusion provides its energy.
Galaxies nebulae stars notes

Within galaxies, star forming regions called nebulae contain clouds of dust, hydrogen and helium gases. Stars sometimes form within these nebulae as the gases and dust collapse under their own gravity. A nebula with protostars, or young stars that are still forming, is shown in the diagram. The document then goes on to describe the life cycle of stars like our Sun and the changes it will undergo as it evolves and eventually dies in approximately 5 billion years.
The Star

This document provides an overview of the characteristics, classifications, motions, and significance of stars. It discusses their sizes, colors, temperatures, compositions, and magnitudes. Stars are classified based on their spectral types, which relate to their surface temperatures. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram plots stars' luminosities and temperatures. Stars exhibit both apparent and actual motions, including proper motion across the sky. Studying stars helps us understand how elements are formed, how our solar system evolved, and the dynamics influencing galaxies.
Birth of the star

Stars are formed in nebulae, clouds of dust and gas found in spiral galaxies. Dense parts of these clouds undergo gravitational collapse, compressing to form a rotating gas globule. As the globule collapses over thousands to millions of years due to gravity and pressure, the increasing temperature and rotation cause it to form a central core and surrounding protoplanetary disk. Once the core reaches temperatures over 27 million degrees and nuclear fusion begins, it becomes a stable main sequence star.
Stars

Stars can be classified by their temperature as hot blue stars around 30,000 degrees, cool red stars around 2,500 degrees, or yellow stars like our sun around 6,000 degrees. Constellations like Orion can be identified by patterns of brighter stars. The brightness of stars is measured by their apparent and absolute magnitudes, with lower numbers indicating brighter stars. A nebula is a cloud where stars are born, and the Eagle Nebula is an example. Stellar evolution progresses from protostars to main sequence stars like our sun fusing hydrogen, then to giants and supergiants fusing helium, eventually leaving behind planetary nebulae and forming white dwarfs, or in massive stars, supernovae leading to neutron stars or
Star's Life Cycle

Stars go through life cycles like humans, being born from collapsing gas clouds, burning hydrogen through nuclear fusion on the main sequence, and eventually dying. Medium and low mass stars end as white dwarfs after shedding their outer layers, while high mass stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. Neutron stars are incredibly dense, rotating rapidly, while black holes have event horizons beyond which nothing, not even light, can escape.
Ch 19 -life and death of stars

1. Stars are born through nuclear fusion and spend most of their life fusing hydrogen into helium as a main sequence star.
2. When stars exhaust their hydrogen fuel, low mass stars become red giants and high mass stars explode as supernovae.
3. The remnants of dead stars are white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes depending on the original star's mass.
Star life cycle

Stars form from collapsing clouds of gas and dust found in nebulae. A star's life cycle depends on its mass - smaller stars less than 3 times the Sun's mass will spend most of their existence on the main sequence fusing hydrogen. Larger stars evolve more quickly, becoming red giants and eventually exploding as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Neutron stars liu jia

This document discusses neutron stars and explores them as natural laboratories for studying extremely dense matter. It provides background on stellar evolution and supernovae that form neutron stars. Neutron stars are incredibly small yet dense, with masses of around 1.35-2 times the sun's mass compressed into the size of Manhattan. They also spin incredibly fast due to conservation of angular momentum. The document examines using neutron stars to study how matter behaves under extreme density and discusses challenges in measuring their precise masses and radii from Earth. It outlines the author's research simulating neutron star atmospheres to help answer fundamental physics questions about their properties.
What's hot (20)
Similar to Stellar life cycle section 3
Birth & death of stars (teach)

A short description, at the elementary school level, describing stars and telling how they are created and how they end.
Stars

Stars form from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Nuclear fusion in the core of stars produces heat and light. Small, low-mass stars like our Sun will live for billions of years on the main sequence before becoming red giants then white dwarfs. Massive stars burn quickly and end their lives in supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. A star's life cycle depends on its initial mass, with smaller stars living longer.
Adolfo

1) The document discusses the lifecycle of stars, from their birth in nebulae made of hydrogen and helium gas, to their evolution through different stages as they fuse hydrogen and helium into heavier elements.
2) It describes how massive stars may end as red supergiants or supernovae, and how the material from dying stars can form nebulae and be incorporated into new stars and planets.
3) It also discusses the formation of planets from protoplanetary disks around new stars, and the different classes of objects in our solar system like planets, asteroids, comets, and meteorites.
Space science ( stars and galaxy)

The document summarizes key concepts in space science, including the life cycles of stars and galaxies. It describes how stars are formed from contracting gas clouds, progressing through steady state burning of hydrogen to helium, then expanding as red giants before ending as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes depending on their mass. It also explains that galaxies are groups of millions of stars held together by gravity, and summarizes the types of galaxies including spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Finally, it provides an overview of the leading cosmological model of the Big Bang theory which proposes the expansion of the universe from an initial hot, dense state approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
HPU NCS2200 Universe formation Lecture II

THis is the second part of the Universe formation lecture for the HPU NCS2200 earth science for elementary education majors summer online course
Ch14 stellar evolution

This document provides an overview of stellar evolution, beginning with the formation of stars from collapsing gas clouds. It describes the main stages that stars pass through, including the main sequence, red giant phase, and death of low-mass versus high-mass stars. Key concepts discussed include how a star's mass determines its core temperature and fusion processes, and how gravity and nuclear fusion power stellar evolution over millions to billions of years until the star dies, seeding new elements into space.
Ns1 origin of universe

The document discusses the origin and evolution of the universe, Earth, and life over billions of years according to scientific theories. It describes how the universe began with the Big Bang around 14 billion years ago, then galaxies, stars, and planetary systems formed. Around 4.5 billion years ago, Earth formed from accretion in our solar system. Early life emerged around 3.8 billion years ago, evolving into complex organisms over time. The document provides timelines of these cosmic and biological events from the birth of the universe to the present.
Life cycle of a star

Stars are born from contracting nebulae of gas and dust. They spend most of their lives on the main sequence, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Eventually they run out of fuel in their cores and their outer layers expand, forming red giants or supergiants. From there, smaller stars shed their outer layers to form planetary nebulae and white dwarfs, while larger stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Stars.ppt

Stars are balls of plasma held together by gravity. Nuclear fusion in their cores releases electromagnetic radiation, providing heat and light. Stars exist on the main sequence for most of their lives but eventually exhaust their fuel. Small stars will become white dwarfs, while larger stars may explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
David y carlos s.

The document summarizes information about the universe and the formation of planets. It describes early models of the universe centered around Earth and later recognizing other galaxies. The Big Bang theory established that the universe rapidly expanded from an initial hot, dense state. Dark matter and an accelerating expansion suggest unknown forces at work. Space exploration helps observe the universe by overcoming Earth's atmosphere. Galaxies, nebulae, and stars are described along with the stages of star formation. Planets form from disks around new stars, and our solar system contains rocky inner and gaseous outer planets along with satellites, asteroids, comets, and planetary debris.
09 uni 07

Stars form from dense clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. As gravity pulls the particles together, nuclear fusion begins in the core, converting hydrogen to helium and releasing energy. Over billions of years, a star will burn through its hydrogen fuel. Less massive stars will expand into red giants then shed their outer layers, leaving behind a dense white dwarf core. More massive stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes depending on their original mass.
Unit vi chapter 24 (stars, space and galaxies)

1) Stars originate from nebulae of dust and gas. They spend most of their life fusing hydrogen into helium through nuclear fusion in their cores as main sequence stars.
2) When stars have exhausted their hydrogen, their cores collapse and outer layers expand, forming red giants. More massive stars explode as supernovae, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
3) The sun is classified as a yellow dwarf star. Its atmosphere consists of the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. Nuclear fusion in its core provides its energy.
Physical Science Lesson 1day1.pptx

The document discusses the formation of heavier elements through stellar nucleosynthesis. It explains that elements heavier than beryllium are formed through nuclear fusion processes inside stars as they evolve over time. As stars age and burn through lighter elements like hydrogen and helium in their cores, they begin fusing heavier elements like carbon, oxygen, neon, magnesium, and silicon. This process continues until iron is formed, at which point fusion stops releasing energy. When massive stars reach this stage, they explode as supernovae, further fusing elements and scattering them throughout space.
Notes 7.4 life cyle of stars

Looking at the Life Cycle of Stars including protostars, nebula, red giant, super red giants, white dwarfs and black hole.
lecture16

1) Stars form from dense fragments within interstellar clouds that collapse under gravity over millions of years.
2) Protostars form within the collapsing fragments and grow in mass through accretion until their cores reach temperatures high enough for nuclear fusion.
3) After 10 million years, the protostar becomes a true star on the main sequence, where nuclear fusion powers the star for its lifetime.
Conley cis100 ppt_assignment

This document provides an overview of star formation, evolution, and death. It discusses how stars form from clouds of hydrogen and helium in nebulas. Once stars accumulate enough mass, nuclear fusion begins in their cores. The document outlines the life cycles of stars of different masses, from red giants to supernovae and the formation of neutron stars or black holes. Key stages in a massive star's death are described, such as the core collapse that causes type II supernovae and the ejection of heavier elements into space.
Formation of Heavier Elements.pptx

The document discusses the synthesis of new elements, beginning with the earliest elements of hydrogen and helium formed in the Big Bang. It then explains how elements up to iron are formed through nuclear fusion in stars, and how heavier elements are created through neutron capture processes during supernovae or in the cores of massive stars. The text also outlines several key discoveries in the development of the periodic table and synthesis of both naturally occurring and man-made transuranic elements.
life cycle of stars

- Stars form inside dense clouds of gas and dust known as molecular clouds. As the cloud contracts, it forms a protostar that continues to gather mass and become denser.
- Once a protostar gains enough mass, nuclear fusion of hydrogen can ignite in its core, turning it into a main-sequence star. Stars with insufficient mass become brown dwarfs.
- More massive stars have shorter lifespans than lower mass stars and end their lives in supernova explosions, while lower mass stars evolve more gradually over billions of years.
Formation of stars

Stars are formed from clouds of dust and gas that collapse under gravity. Most stars spend around 90% of their life fusing hydrogen into helium through nuclear reactions. When stars run out of fuel, their cores collapse and they expel their outer layers, forming planetary nebulae. This leaves behind dense, hot cores known as white dwarfs. More massive stars may explode as supernovae when nuclear fusion can no longer counter gravity, or collapse entirely into black holes.
Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 6

This document summarizes key components and concepts about the structure of the solar system:
- The solar system consists of the Sun, eight planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and other small bodies. The Sun contains over 99% of the solar system's mass.
- The inner terrestrial planets are rocky, while the outer gas giants are large planets composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. An asteroid belt exists between Mars and Jupiter.
- Factors like a planet's mass, distance from the Sun, composition, and atmospheric properties help determine its environment and surface conditions. Larger planets retain heat and atmospheres better than smaller ones.
- Techniques like radioactive dating indicate the solar system formed
Similar to Stellar life cycle section 3 (20)
Recently uploaded
The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx

Although Artemia has been known to man for centuries, its use as a food for the culture of larval organisms apparently began only in the 1930s, when several investigators found that it made an excellent food for newly hatched fish larvae (Litvinenko et al., 2023). As aquaculture developed in the 1960s and ‘70s, the use of Artemia also became more widespread, due both to its convenience and to its nutritional value for larval organisms (Arenas-Pardo et al., 2024). The fact that Artemia dormant cysts can be stored for long periods in cans, and then used as an off-the-shelf food requiring only 24 h of incubation makes them the most convenient, least labor-intensive, live food available for aquaculture (Sorgeloos & Roubach, 2021). The nutritional value of Artemia, especially for marine organisms, is not constant, but varies both geographically and temporally. During the last decade, however, both the causes of Artemia nutritional variability and methods to improve poorquality Artemia have been identified (Loufi et al., 2024).
Brine shrimp (Artemia spp.) are used in marine aquaculture worldwide. Annually, more than 2,000 metric tons of dry cysts are used for cultivation of fish, crustacean, and shellfish larva. Brine shrimp are important to aquaculture because newly hatched brine shrimp nauplii (larvae) provide a food source for many fish fry (Mozanzadeh et al., 2021). Culture and harvesting of brine shrimp eggs represents another aspect of the aquaculture industry. Nauplii and metanauplii of Artemia, commonly known as brine shrimp, play a crucial role in aquaculture due to their nutritional value and suitability as live feed for many aquatic species, particularly in larval stages (Sorgeloos & Roubach, 2021).
Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility

Deep Software Variability and Frictionless ReproducibilityUniversity of Rennes, INSA Rennes, Inria/IRISA, CNRS
The ability to recreate computational results with minimal effort and actionable metrics provides a solid foundation for scientific research and software development. When people can replicate an analysis at the touch of a button using open-source software, open data, and methods to assess and compare proposals, it significantly eases verification of results, engagement with a diverse range of contributors, and progress. However, we have yet to fully achieve this; there are still many sociotechnical frictions.
Inspired by David Donoho's vision, this talk aims to revisit the three crucial pillars of frictionless reproducibility (data sharing, code sharing, and competitive challenges) with the perspective of deep software variability.
Our observation is that multiple layers — hardware, operating systems, third-party libraries, software versions, input data, compile-time options, and parameters — are subject to variability that exacerbates frictions but is also essential for achieving robust, generalizable results and fostering innovation. I will first review the literature, providing evidence of how the complex variability interactions across these layers affect qualitative and quantitative software properties, thereby complicating the reproduction and replication of scientific studies in various fields.
I will then present some software engineering and AI techniques that can support the strategic exploration of variability spaces. These include the use of abstractions and models (e.g., feature models), sampling strategies (e.g., uniform, random), cost-effective measurements (e.g., incremental build of software configurations), and dimensionality reduction methods (e.g., transfer learning, feature selection, software debloating).
I will finally argue that deep variability is both the problem and solution of frictionless reproducibility, calling the software science community to develop new methods and tools to manage variability and foster reproducibility in software systems.
Exposé invité Journées Nationales du GDR GPL 2024
Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.

This presentation explores a brief idea about the structural and functional attributes of nucleotides, the structure and function of genetic materials along with the impact of UV rays and pH upon them.
原版制作(carleton毕业证书)卡尔顿大学毕业证硕士文凭原版一模一样

原版纸张【微信:741003700 】【(carleton毕业证书)卡尔顿大学毕业证】【微信:741003700 】学位证,留信认证(真实可查,永久存档)offer、雅思、外壳等材料/诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本,帮您解决无法毕业带来的各种难题!外壳,原版制作,诚信可靠,可直接看成品样本。行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备。十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,包您满意。
本公司拥有海外各大学样板无数,能完美还原海外各大学 Bachelor Diploma degree, Master Degree Diploma
1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问Q/微741003700
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
BREEDING METHODS FOR DISEASE RESISTANCE.pptx

Plant breeding for disease resistance is a strategy to reduce crop losses caused by disease. Plants have an innate immune system that allows them to recognize pathogens and provide resistance. However, breeding for long-lasting resistance often involves combining multiple resistance genes
Equivariant neural networks and representation theory

Or: Beyond linear.
Abstract: Equivariant neural networks are neural networks that incorporate symmetries. The nonlinear activation functions in these networks result in interesting nonlinear equivariant maps between simple representations, and motivate the key player of this talk: piecewise linear representation theory.
Disclaimer: No one is perfect, so please mind that there might be mistakes and typos.
dtubbenhauer@gmail.com
Corrected slides: dtubbenhauer.com/talks.html
ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx

With increasing population, people need to rely on packaged food stuffs. Packaging of food materials requires the preservation of food. There are various methods for the treatment of food to preserve them and irradiation treatment of food is one of them. It is the most common and the most harmless method for the food preservation as it does not alter the necessary micronutrients of food materials. Although irradiated food doesn’t cause any harm to the human health but still the quality assessment of food is required to provide consumers with necessary information about the food. ESR spectroscopy is the most sophisticated way to investigate the quality of the food and the free radicals induced during the processing of the food. ESR spin trapping technique is useful for the detection of highly unstable radicals in the food. The antioxidant capability of liquid food and beverages in mainly performed by spin trapping technique.
bordetella pertussis.................................ppt

Bordettela is a gram negative cocobacilli spread by air born drop let
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

Isolation of pure culture, its various method.
The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects

Assuming spherical symmetry and weak field, it is shown that if one solves the Poisson equation or the Einstein field
equations sourced by a topological defect, i.e. a singularity of a very specific form, the result is a localized gravitational
field capable of driving flat rotation (i.e. Keplerian circular orbits at a constant speed for all radii) of test masses on a thin
spherical shell without any underlying mass. Moreover, a large-scale structure which exploits this solution by assembling
concentrically a number of such topological defects can establish a flat stellar or galactic rotation curve, and can also deflect
light in the same manner as an equipotential (isothermal) sphere. Thus, the need for dark matter or modified gravity theory is
mitigated, at least in part.
Bob Reedy - Nitrate in Texas Groundwater.pdf

Presented at June 6-7 Texas Alliance of Groundwater Districts Business Meeting
ANAMOLOUS SECONDARY GROWTH IN DICOT ROOTS.pptx

Abnormal or anomalous secondary growth in plants. It defines secondary growth as an increase in plant girth due to vascular cambium or cork cambium. Anomalous secondary growth does not follow the normal pattern of a single vascular cambium producing xylem internally and phloem externally.
Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water

Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero WaterTexas Alliance of Groundwater Districts
Presented at June 6-7 Texas Alliance of Groundwater Districts Business Meeting20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

Evaporation step counter work. I have done a physical experiment.
(Work in progress.)
Thornton ESPP slides UK WW Network 4_6_24.pdf

ESPP presentation to EU Waste Water Network, 4th June 2024 “EU policies driving nutrient removal and recycling
and the revised UWWTD (Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive)”
Recently uploaded (20)
The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx

The use of Nauplii and metanauplii artemia in aquaculture (brine shrimp).pptx
Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility

Deep Software Variability and Frictionless Reproducibility
Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.

Nucleic Acid-its structural and functional complexity.
aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel

aziz sancar nobel prize winner: from mardin to nobel
Equivariant neural networks and representation theory

Equivariant neural networks and representation theory
ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx

ESR spectroscopy in liquid food and beverages.pptx
bordetella pertussis.................................ppt

bordetella pertussis.................................ppt
8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf

8.Isolation of pure cultures and preservation of cultures.pdf
The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects

The binding of cosmological structures by massless topological defects
Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water

Sharlene Leurig - Enabling Onsite Water Use with Net Zero Water
20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx

20240520 Planning a Circuit Simulator in JavaScript.pptx
Stellar life cycle section 3
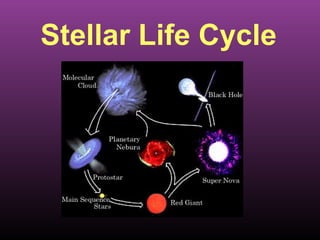
- 2. Bell Ringer – match term with definition 1. Large cloud of gas and dust 2. Longest stage 3. Hydrogen is depleted and outer layers expand and cool 4. Extremely dense 5. Light cannot escape A. Black hole B. Giant C. Main sequence D. Nebula E. Neutron star
- 3. Bell Ringer 1. Describe how stars release energy. 2. Outline the past and future of our Sun.
- 5. Nebula • Cloud of gas and dust • 70% hydrogen, 28% helium, 2% other elements • Weak gravitational attraction
- 6. Nebula – cloud of gas and dust. Birthplace of stars.
- 7. NGC 604 – one of the largest regions of star birth currently known. Contains massive stars, about 120 times larger than our sun.
- 8. Orion Nebula – Closest region of star formation to earth
- 9. Eagle Nebula – pillars of star- forming gas
- 10. Nebula to a star • Force (i.e. explosion from nearby star) compresses particles • Nebula begins to contract • Particles come closer together • Temperatures increase • At 10 million K, nuclear fusion begins • Star is born
- 12. Main sequence star • Energy is generated in the core of the star • Hydrogen atoms fuse to helium atoms • Longest stage in life of a star • Balances pressure from fusion heat with gravity
- 13. Our closest star
- 14. Giants and Supergiants • Hydrogen fuel is used up • The core of the star contracts, increasing the temperature • Outer shell of star expands and cools • Helium fuses to form carbon • Giants are 10 times bigger than the sun. • Supergiants are 100 times bigger than the sun.
- 16. Red giant at the center, illuminating a cloud of gas
- 17. Betelgeuse – Red Supergiant
- 18. Planetary Nebula • Helium fusion ends • Star loses its outer gases • The core heats and illuminates the ring of gas
- 19. Planetary Nebula – glowing shell of gas and plasma formed by some stars when they die
- 20. Planetary Nebula
- 21. White Dwarfs • Gravity pulls the last matter of the star inward • Hot, dense core of matter • Shine for billions of years before they cool completely into a black dwarf.
- 22. Nova • During process of white dwarf cooling, explosions may occur • Release energy, gas, and dust into space • Star becomes much brighter and then fades back to its normal brightness • May occur several times
- 23. Nova – large explosion of a white dwarf star. Energy, gas, and dust are released into space.
- 24. Supernova • Occur in very large stars • Large stars contract producing very high pressures and temperatures • Carbon fuses into magnesium which then fuses into iron • The iron core absorbs huge amounts of energy and collapses, causing the outer part of the star to explode
- 25. Supernova – large star explosion
- 26. Neutron Stars • The core of a supernova contracts into a very small, dense ball of neutrons • Rotate very rapidly • Some emit beams of radiation and are called pulsars
- 27. Pulsar - highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars that emit beams of electromagnetic radiation Crab
- 29. Black Holes • After a supernova, some large stars contract with even greater force • The force crushes the core of the star, leaving a hole in space • The gravity is so great that not even light can escape from it
- 30. Recycling • Matter emitted by a star over its life time is recycled and can become part of a new nebula
- 31. Supernova remnant – ejected material expanding from the star explosion