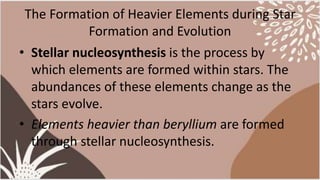
The document discusses the formation of heavier elements through stellar nucleosynthesis. It explains that elements heavier than beryllium are formed through nuclear fusion processes inside stars as they evolve over time. As stars age and burn through lighter elements like hydrogen and helium in their cores, they begin fusing heavier elements like carbon, oxygen, neon, magnesium, and silicon. This process continues until iron is formed, at which point fusion stops releasing energy. When massive stars reach this stage, they explode as supernovae, further fusing elements and scattering them throughout space.