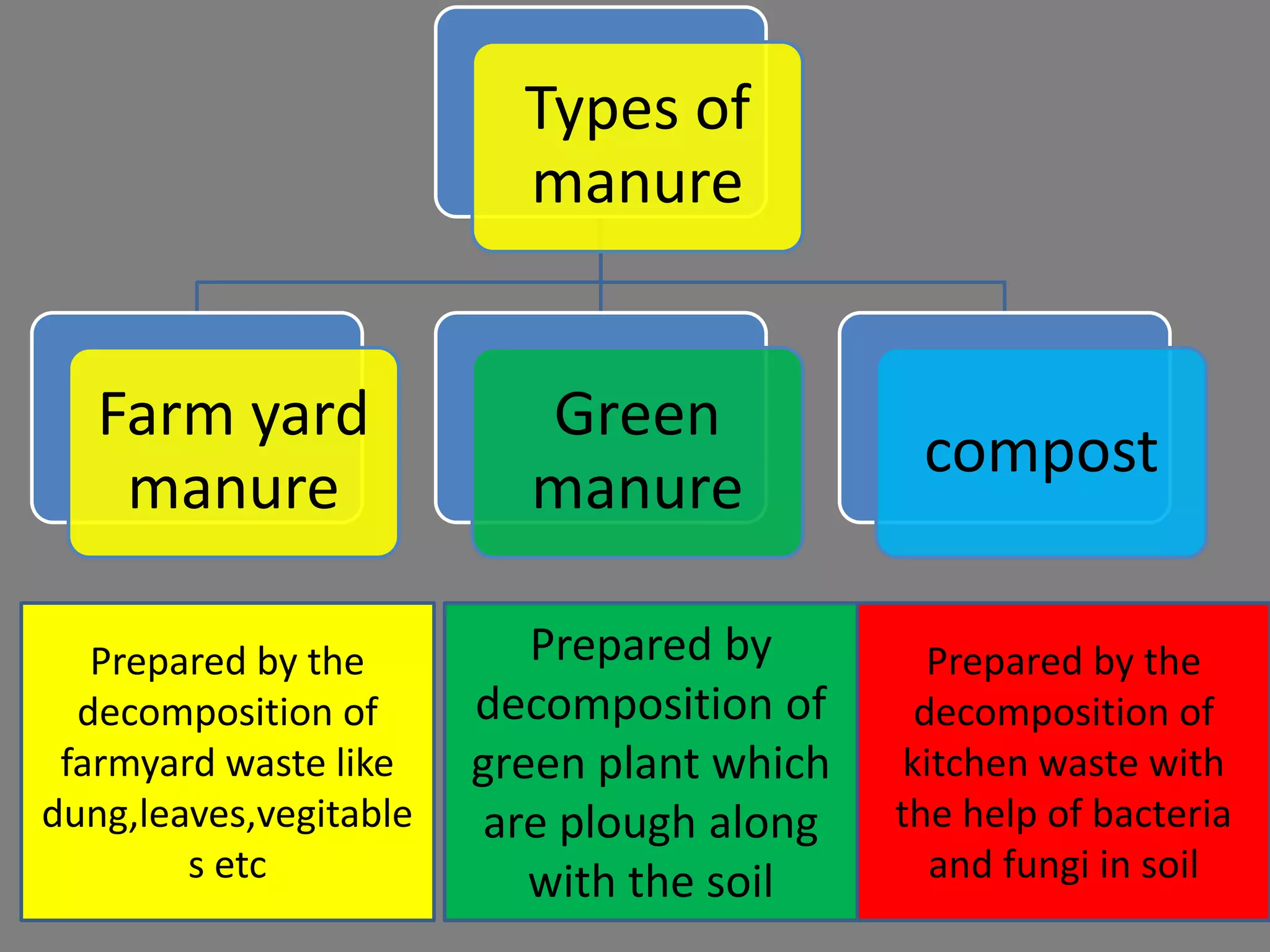
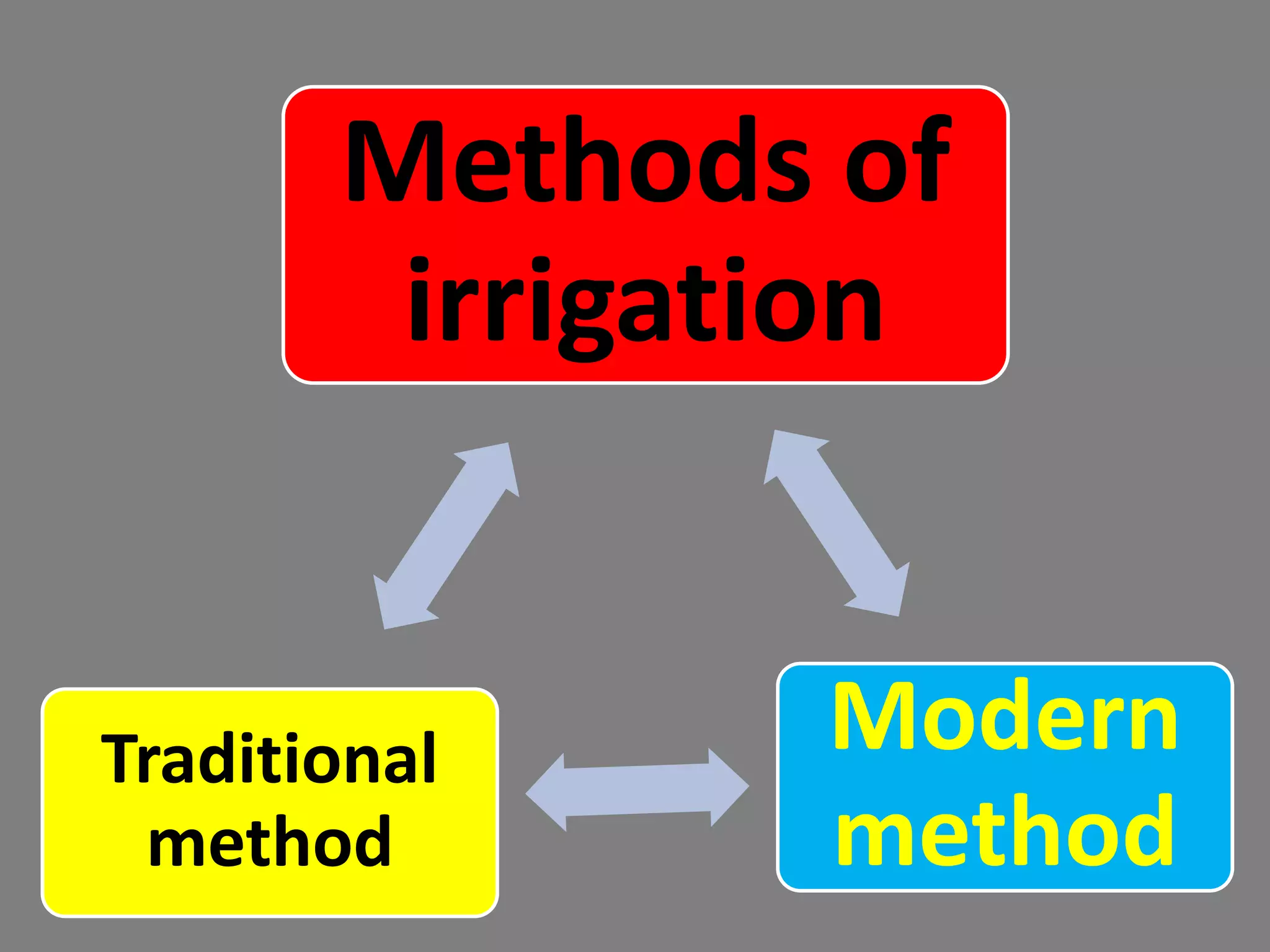
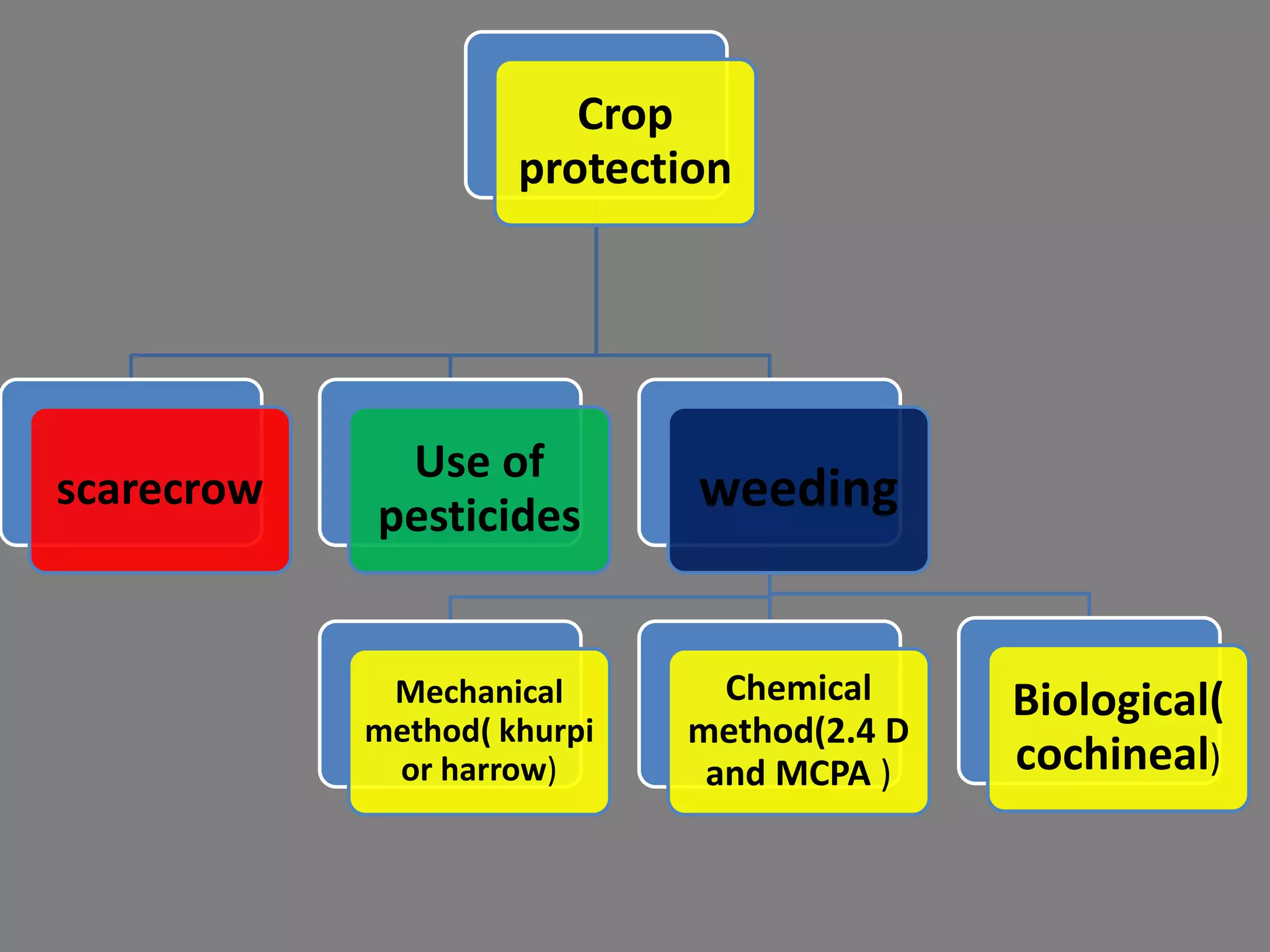
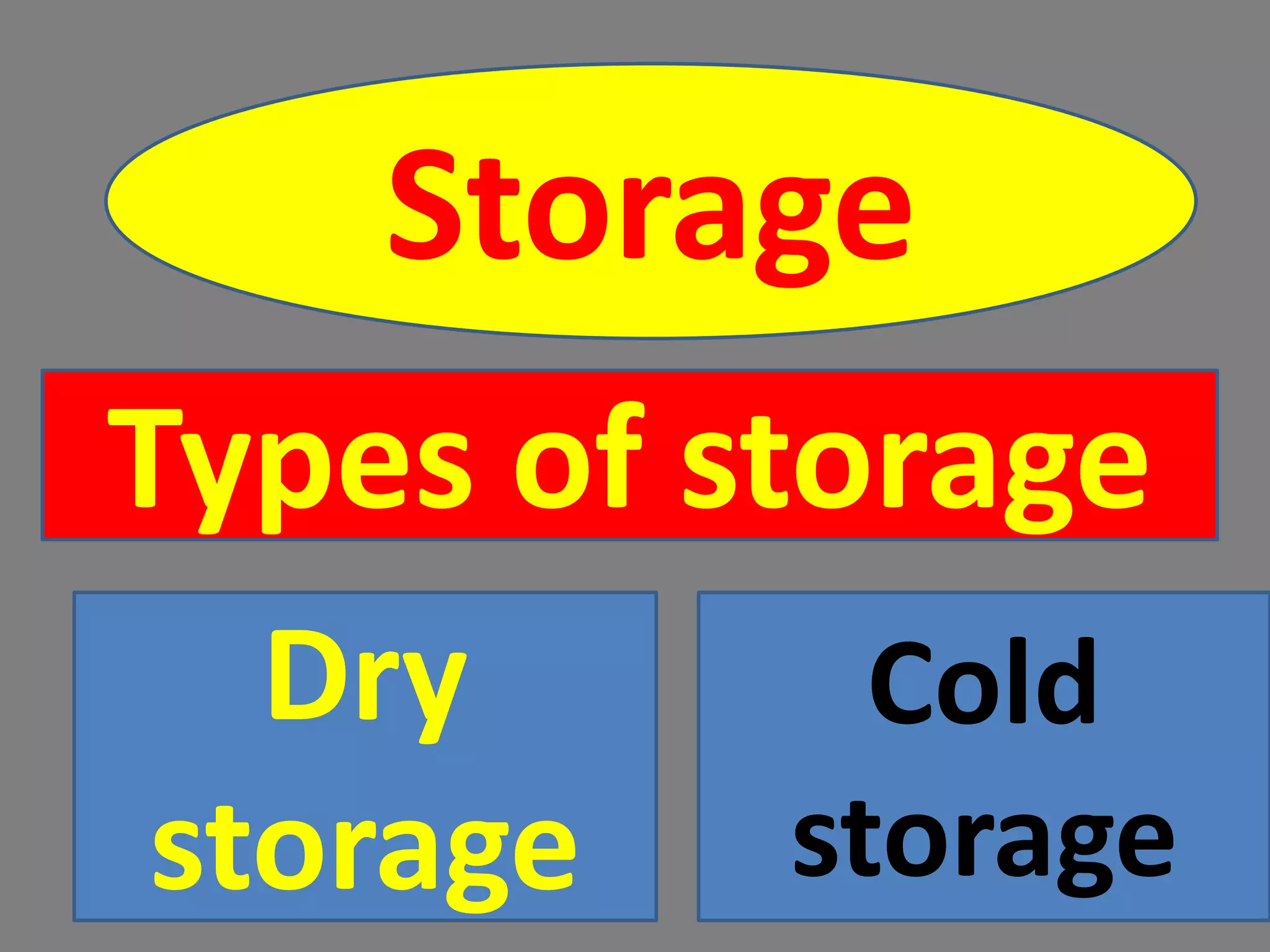
The document provides information on various aspects of crop production and management. It discusses preparing the soil, sowing seeds, manuring, irrigation, crop protection, harvesting, and storage. It describes sowing seeds at the right depth and spacing for proper germination. Crop transplantation involves initially growing seedlings in a nursery and then transplanting them to the main field. Manuring involves adding manure, fertilizers, or compost to soil. Irrigation provides water to crops, while crop protection methods prevent damage from pests. Harvesting is when fully grown crops are cut and gathered, while storage preserves and protects the harvested crops.