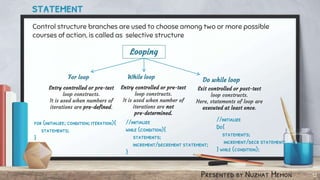
Chapter 7 of the document covers Java operators, including arithmetic, comparison, logical, conditional, and assignment operators, detailing their functions and examples. It also explains control structures such as loops (for, while, do-while) and selective structures (if statements, switch statements). The content is presented by Nuzhat Memon and includes practical examples and syntax.








![Presented by Nuzhat Memon
Brain Stroming Session
Which of the following is compiled error free?
(A)for(;;){int i=7}; (B) while (1) { int i=7};
(C) while (true){int i=7} (D) All of these
What will be output of following program?
class abc{
public static void main(string[] S){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
SYSTEM.out.println(i);
}
}
}
(A) error (B) i (C) Display 1 to 10 (D) 1,2,3,…….10
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/std12computerjavabasicspart2-210510072813/85/Std-12-Computer-Chapter-7-Java-Basics-Part-2-10-320.jpg)