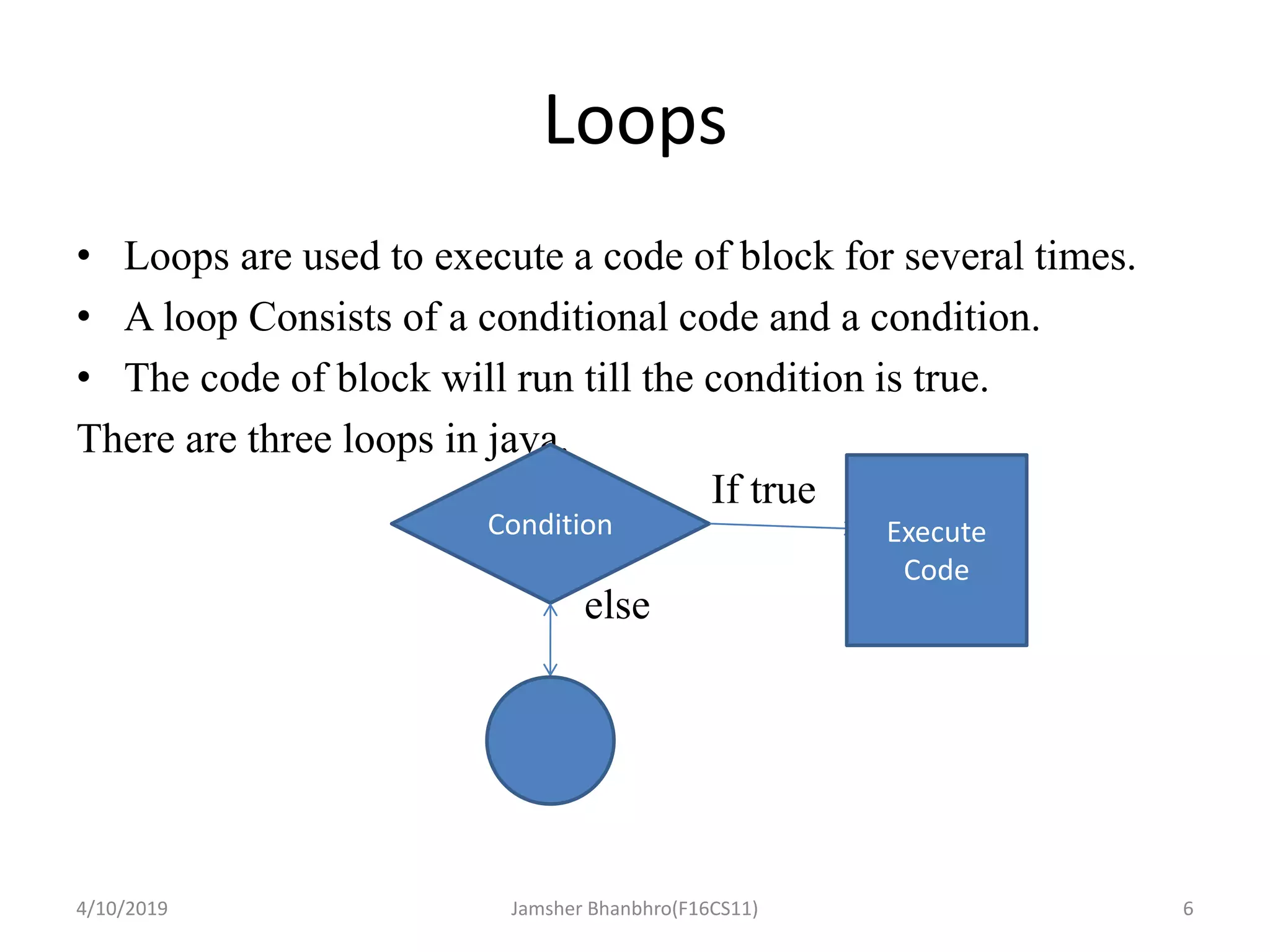
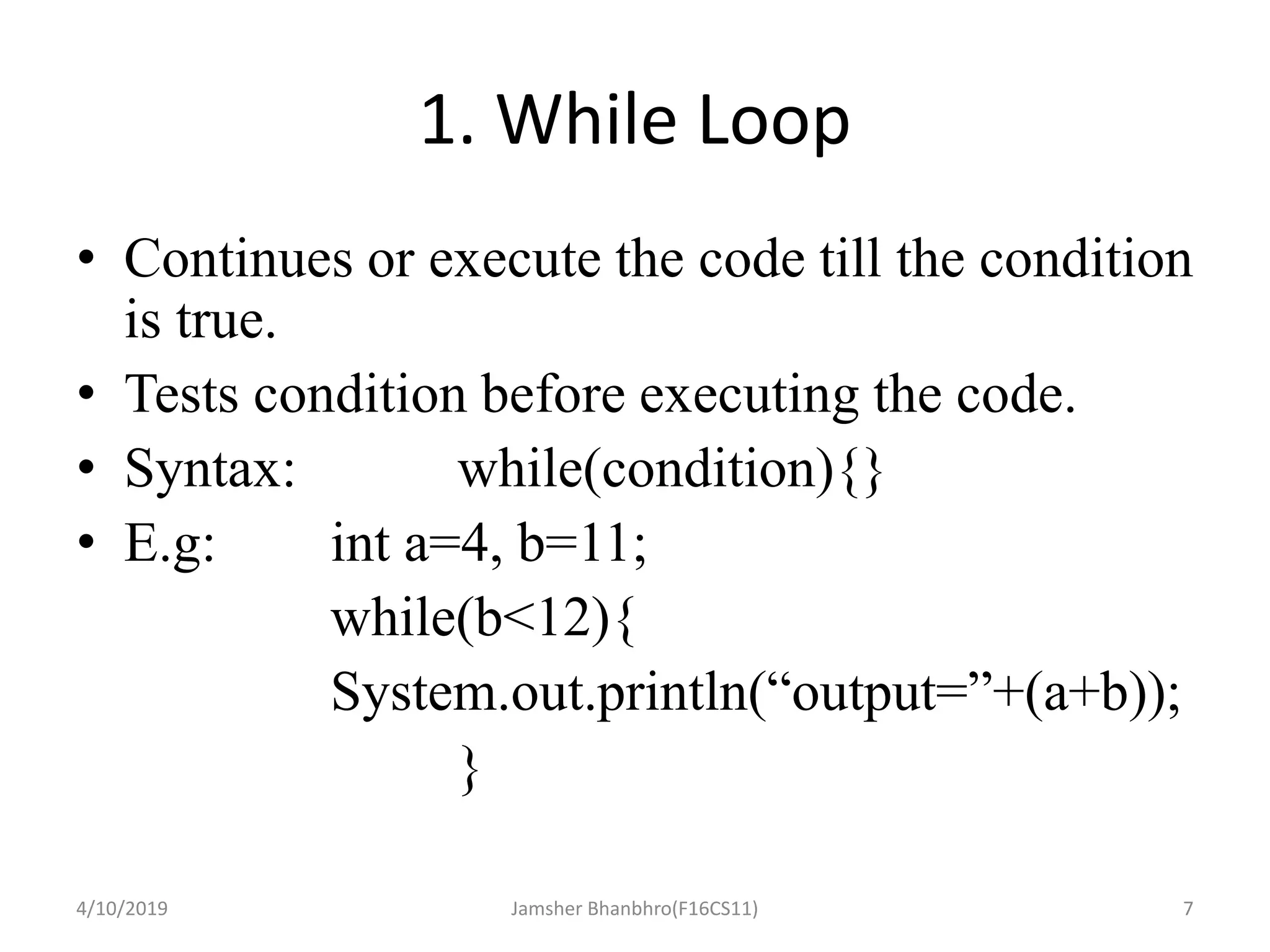
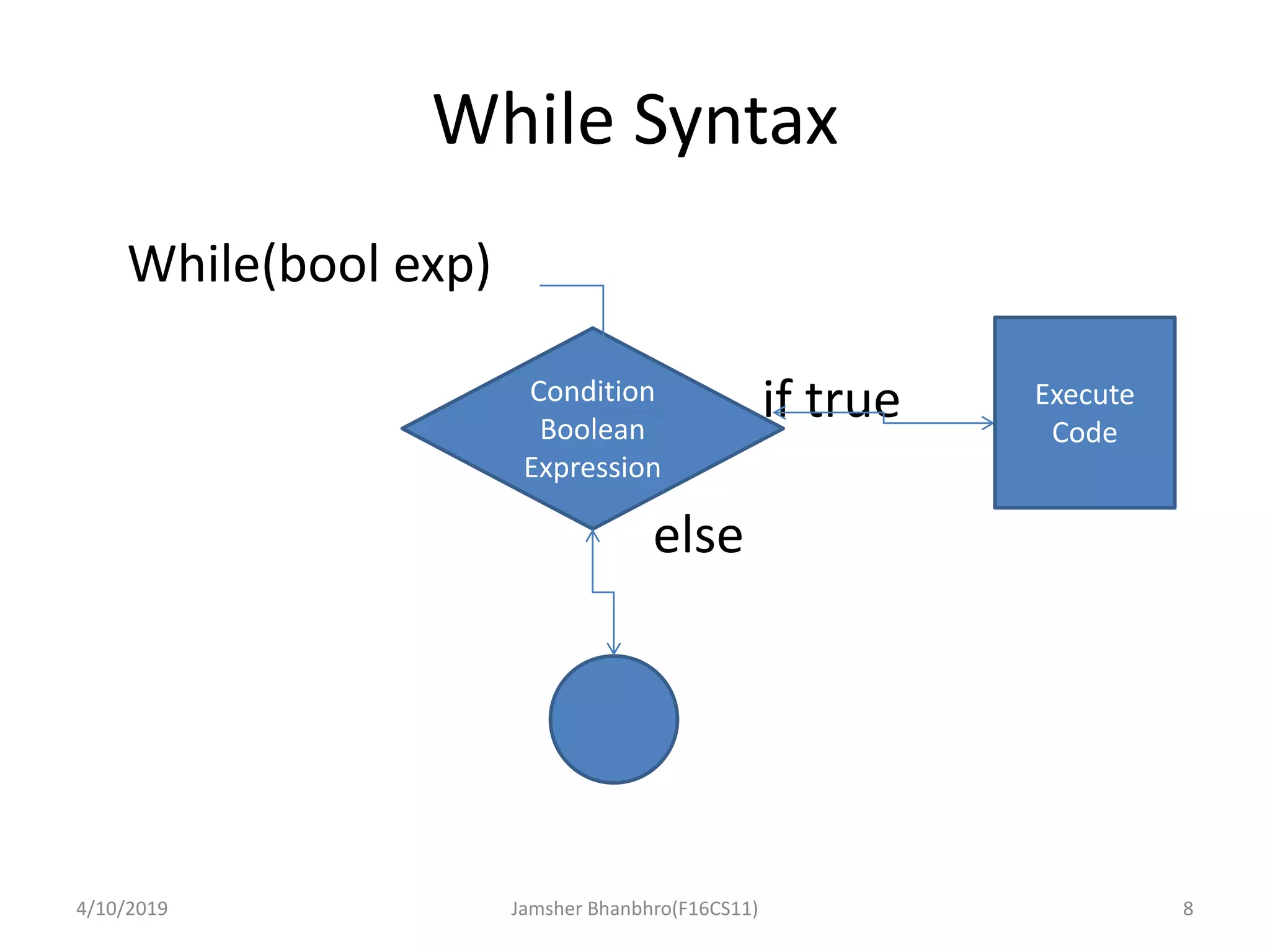
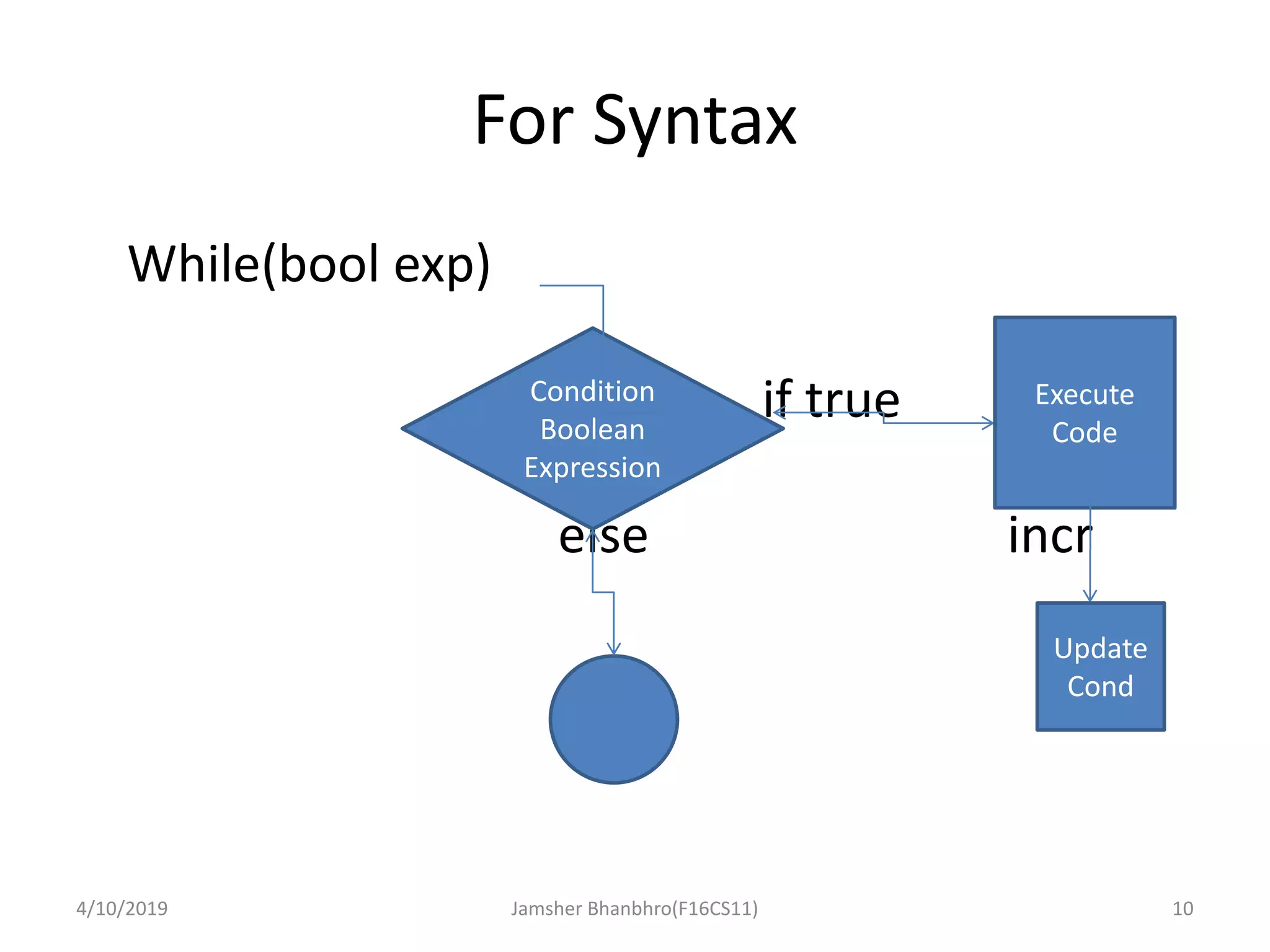
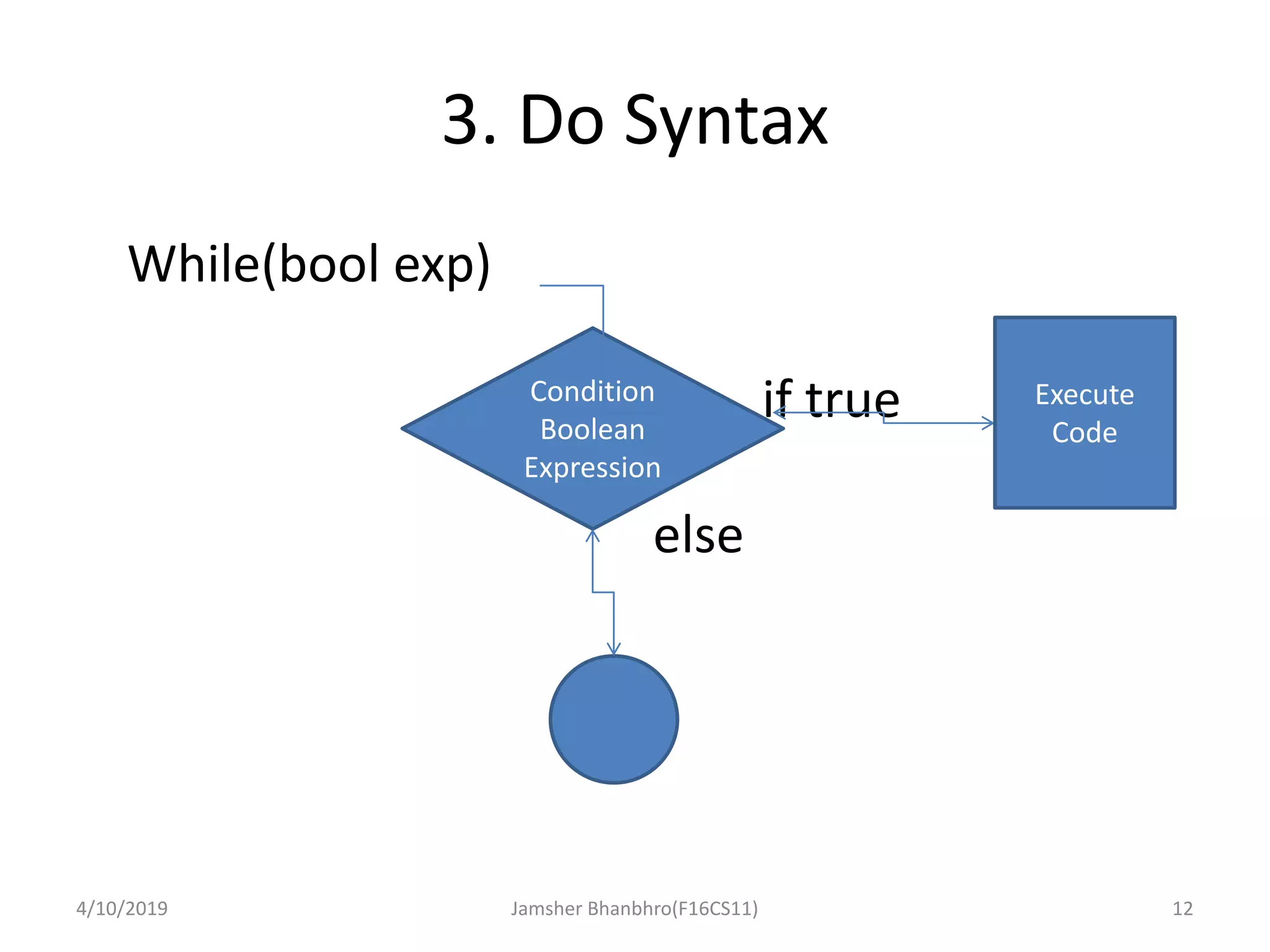
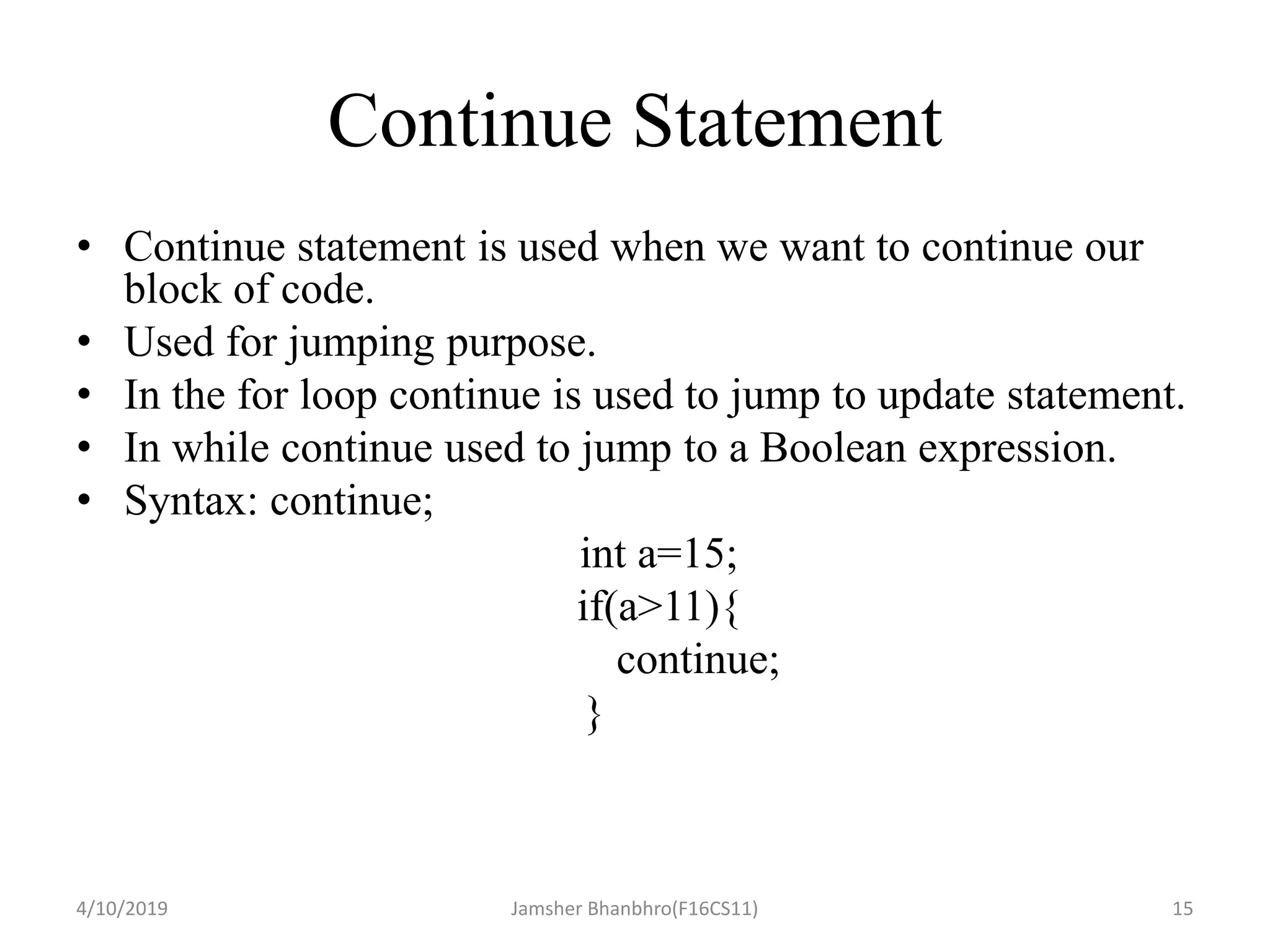
The document discusses basic operators, loops, and control statements in Java. It covers arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, and assignment operators. The core loops covered are for, while, and do-while loops, including their syntax and usage. Break and continue statements are also discussed, explaining how break exits the current block/loop and continue skips to the next iteration. The document provides examples of each concept and proposes programming tasks to demonstrate understanding.