The document discusses statutory requirements for contract labour and the Employees' Provident Fund Act.
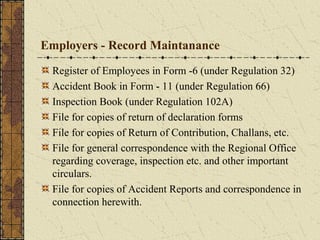
It outlines the applicability and registration/licensing process for the Contract Labour Act, obligations of principal employers and contractors, and welfare facilities that must be provided.
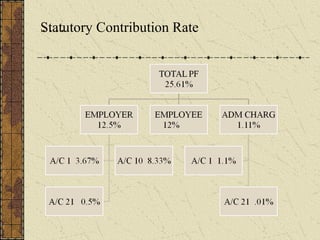
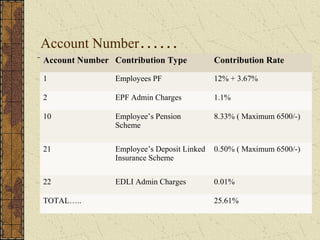
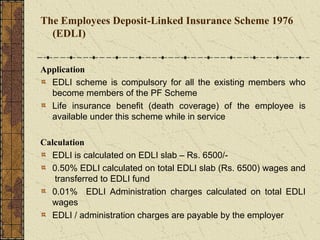
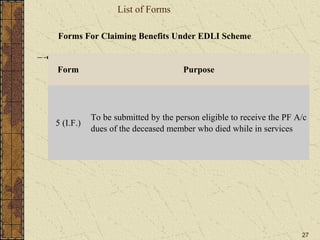
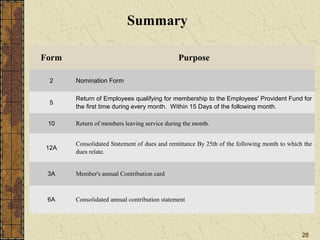
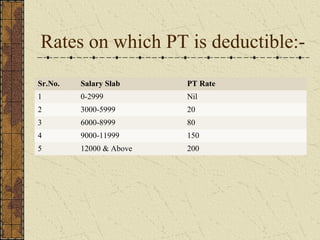
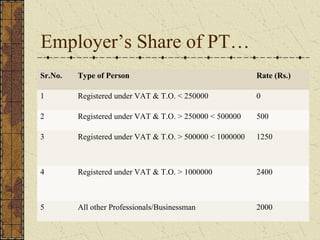
It also summarizes key aspects of the Employees' Provident Fund Act including contribution rates, roles of employers and employees, benefits like pension and insurance schemes, and required forms and monthly/annual returns.