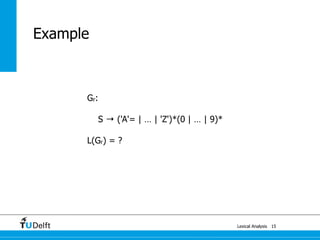
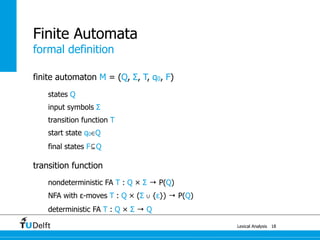
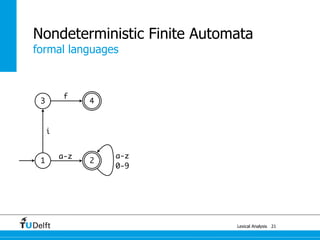
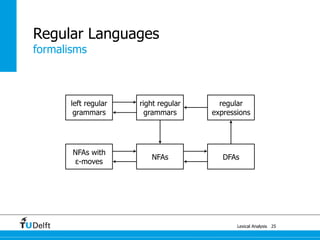
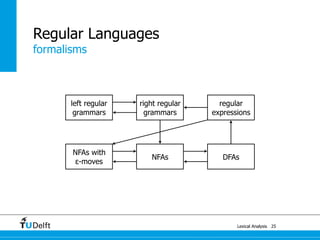
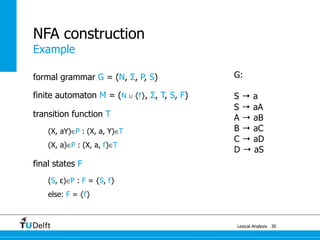
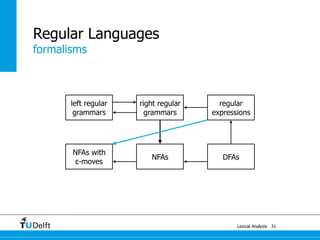
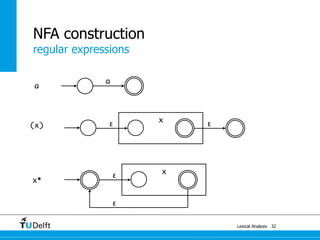
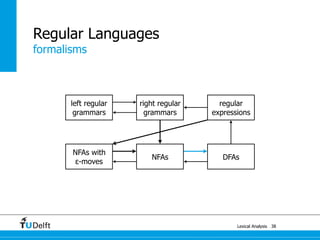
The document discusses lexical analysis and regular languages. It begins with an overview of lexical analysis and its components, including regular languages defined via regular grammars, regular expressions, and finite state automata. It then covers the equivalence between these formalisms for describing regular languages and how to construct a nondeterministic finite automaton from a regular expression.