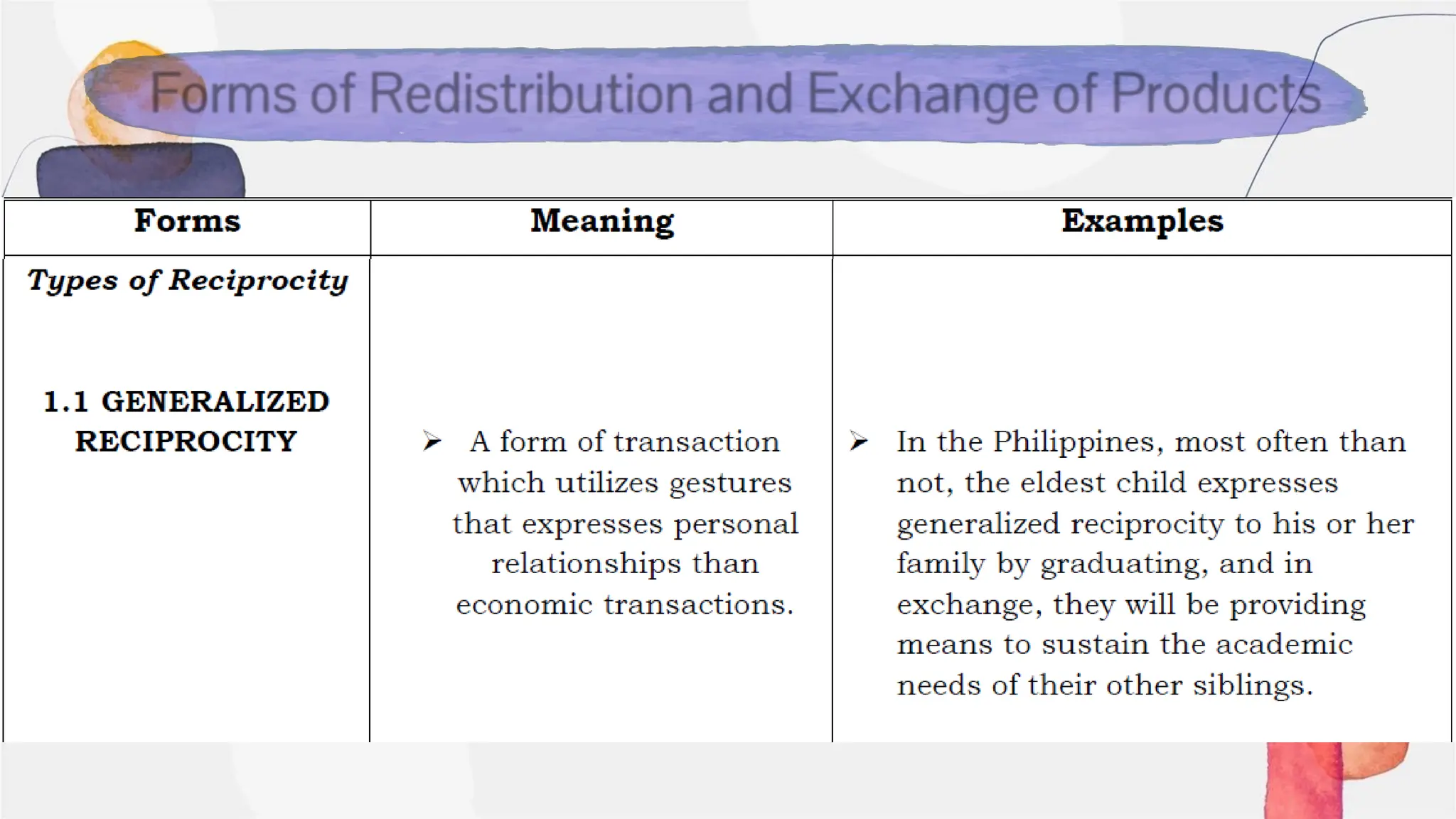
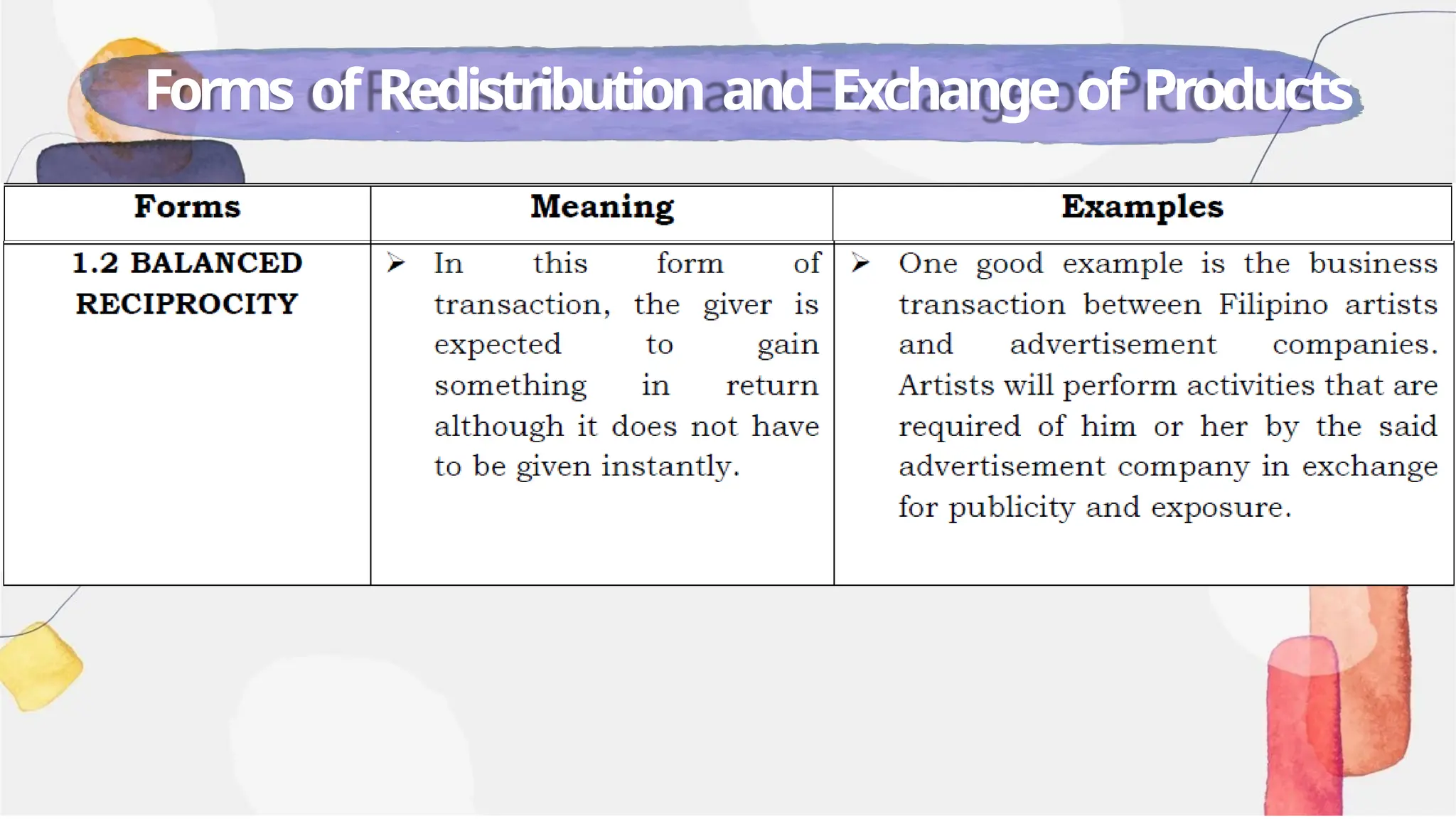
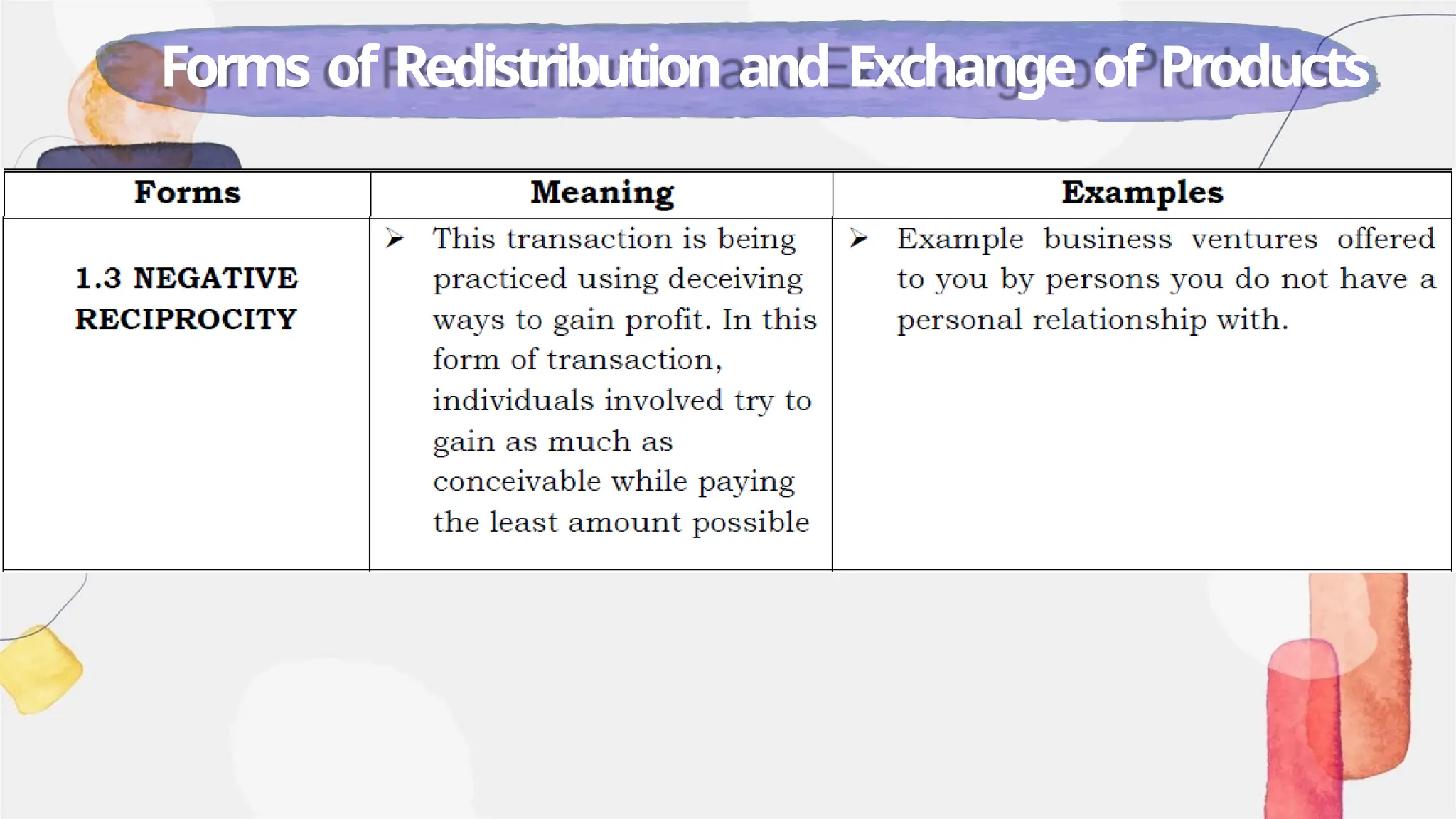
The document is an educational module for the 2024-2025 academic year that focuses on understanding state and non-state institutions, including their forms, functions, and roles in society. It outlines objectives such as identifying and describing different institutions and their functions, alongside discussing the significance of sovereignty, government, and types of non-state entities like NGOs and cooperatives. Additionally, the module emphasizes the importance of these institutions in maintaining social order and supporting the welfare of populations.