The document outlines the Stacki server provisioning system led by David Peterson, detailing hardware requirements, ZFS integration, and customization capabilities. It emphasizes the ease of managing large server arrays, configuration specifics, and the integration of Chef for server provisioning. The vendor provides guidelines for handling SAN setups and detecting provisioning issues through various monitoring techniques.







![Stacki Configuration
Concurrent kickstart limitation
▪ /export/stack/sbin/kickstart.cgi:L154
# Use a semaphore to restrict the number of concurrent kickstart
# file generators. The first time through we set the semaphore
# to the number of CPUs (not a great guess, but reasonable).
▪ semaphore = stack.lock.Semaphore('/var/tmp/kickstart.semaphore')
[root@stacki]# echo 200 > /var/tmp/kickstart.semaphore](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-12-2048.jpg)

![/export/stack/site-profiles/prod/2.0/nodes/replace-storage-controller-client.xml
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<kickstart>
<pre>
if [ "&nukecontroller;" == "true" ]
then
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 delete forced override
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2,1I:1:3,1I:1:4 raid=1+0 size=200000
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2,1I:1:3,1I:1:4 raid=1+0
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=2I:0:5,2I:0:6 raid=0
fi
</pre>
<!-- now reset the nukecontroller attribute to false -->
<pre>
<eval>
/opt/stack/bin/stack set host attr &hostname; attr=nukecontroller value=false
</eval>
</pre>
</kickstart>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-14-2048.jpg)
![/export/stack/site-profiles/prod/2.0/nodes/replace-storage-controller-client.xml
<pre cond="appliance in [’rabbitmq']">
if [ "&nukecontroller;" == "true" ]
then
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 delete forced override
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2,1I:1:3,1I:1:4 raid=1+0 size=500000
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=1I:1:1,1I:1:2,1I:1:3,1I:1:4 raid=1+0
/opt/stack/sbin/hpssacli ctrl slot=0 create type=ld
drives=2I:0:5,2I:0:6 raid=1
fi
</pre>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-15-2048.jpg)

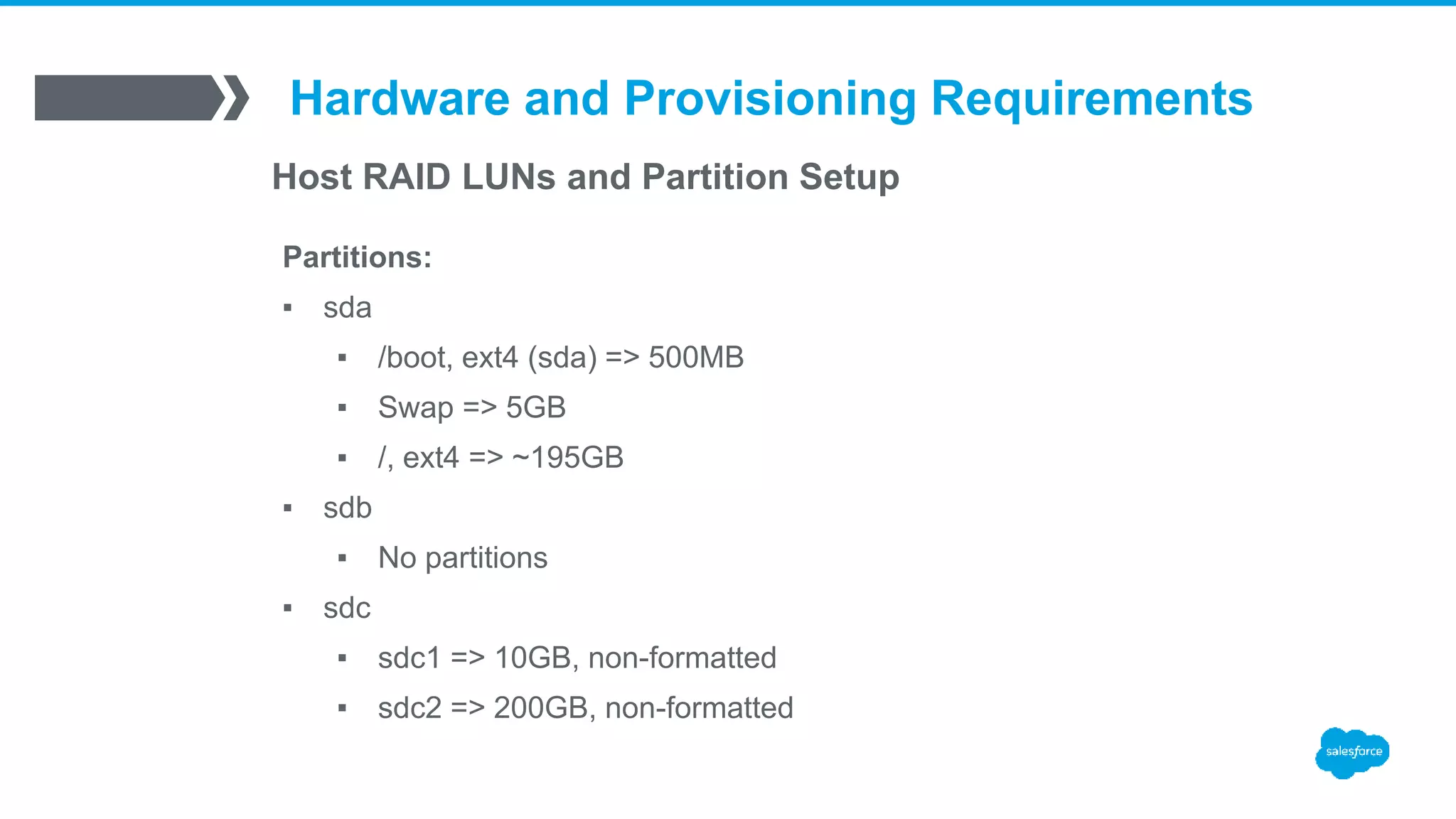
![/export/stack/site-profiles/prod/2.0/nodes/extend-partition.xml
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<kickstart>
<post>
<![CDATA[
/sbin/fdisk /dev/sdc << EOF
d
w
EOF
/sbin/fdisk /dev/sdc << EOF
n
p
1
1
+10G
w
EOF
/sbin/fdisk /dev/sdc << EOF
n
p
2
+200G
w
EOF
]]>
</post>
</kickstart>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-18-2048.jpg)
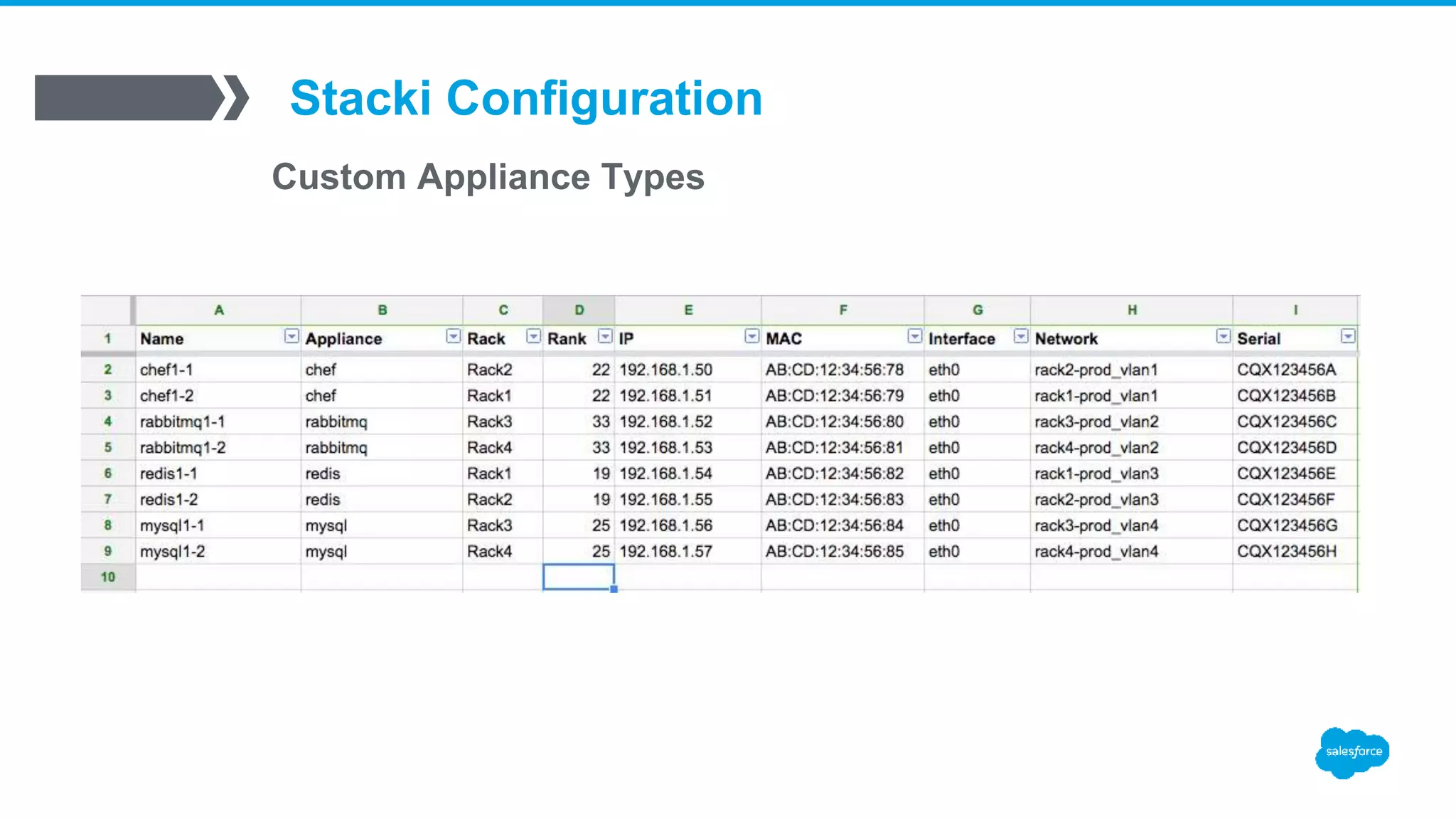
![Stacki Configuration
Custom Appliance Types
▪ /export/stack/site-profiles/prod/2.0/nodes/extend-backend.xml
[root@stacki]# stack list appliance
APPLIANCE MEMBERSHIP PUBLIC
frontend: Frontend no
backend: Backend yes
rabbitmq: Rabbitmq yes
redis: Redis yes
mysql: Mysql yes
[root@stacki]# stack add appliance loadbalancer
[root@stacki]# stack set appliance attr loadbalancer attr=managed value=true
[root@stacki]# stack set appliance attr loadbalancer attr=kickstartable value=true
[root@stacki]# stack set appliance attr loadbalancer attr=node value=backend](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-19-2048.jpg)
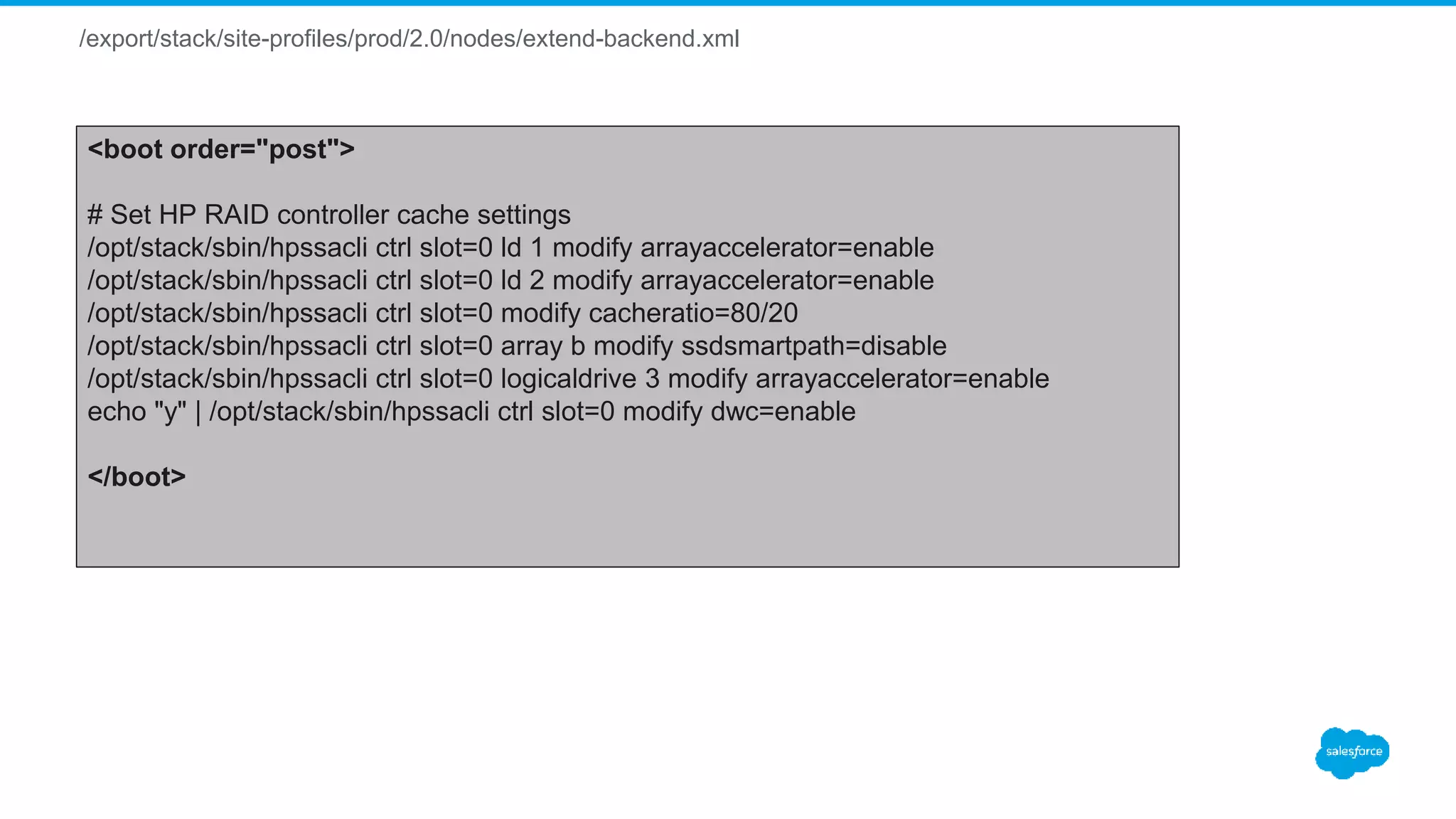
![/export/stack/site-profiles/prod/2.0/nodes/extend-backend.xml
<boot order="post" cond="appliance == ’rabbitmq' and (nukecontroller or nukedisks)">
/sbin/zfs create data/rabbitmq
/sbin/zfs set mountpoint=/var/lib/rabbitmq data/rabbitmq
</boot>
<boot order="post" cond="appliance == ’redis' and (nukecontroller or nukedisks)">
/sbin/zfs create data/redis
/sbin/zfs set mountpoint=/var/lib/redis data/redis
adduser -r redis -U
chown redis:redis /var/lib/redis
</boot>
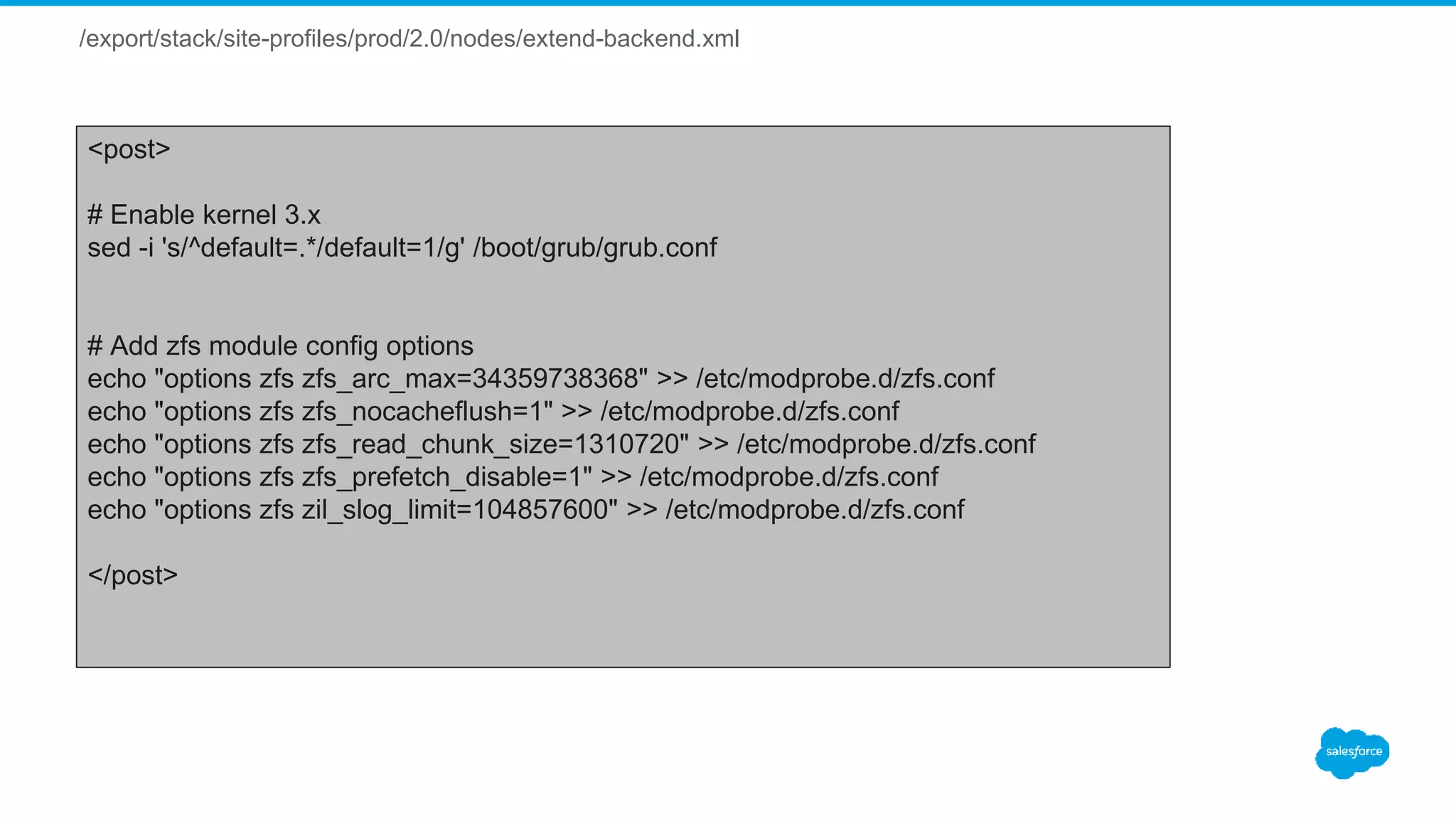
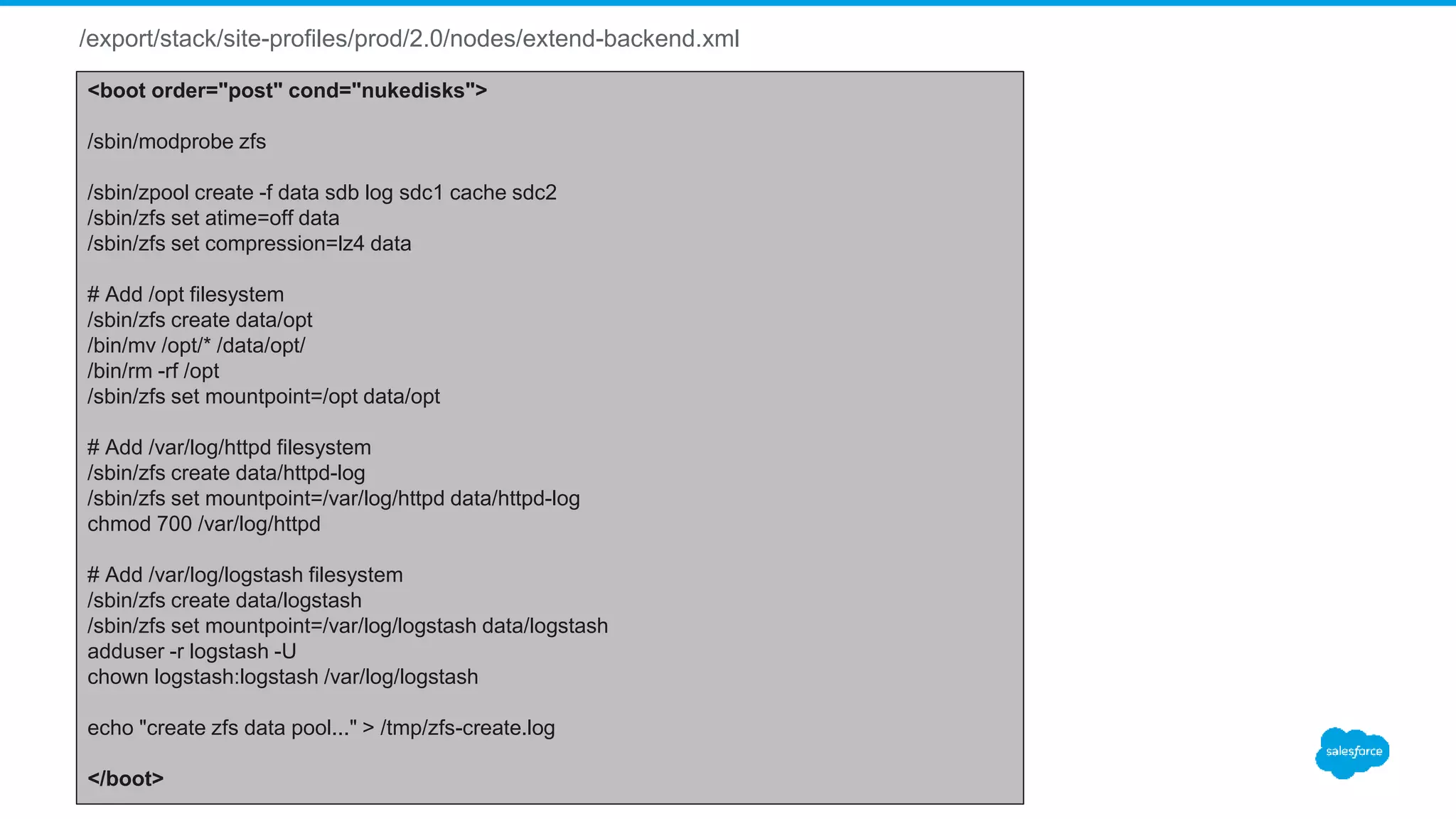
<boot order="post" cond="appliance == 'mysql' and (nukecontroller or nukedisks)">
# Disabling THP
<![CDATA[
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag
sed -i 's/kernel.* console=ttyS0,19200n8$/& transparent_hugepage=never/' /boot/grub/grub.conf
sed -i 's/kernel.* crashkernel=auto$/& transparent_hugepage=never/' /boot/grub/grub.conf
]]>
/sbin/zfs create data/mysql
/sbin/zfs create data/mysql-log
/sbin/zfs create data/mysql-tmp
/sbin/zfs set recordsize=16K data/mysql
/sbin/zfs set mountpoint=/var/lib/mysql data/mysql
/sbin/zfs set mountpoint=/var/log/mysql data/mysql-log
/sbin/zfs set mountpoint=/var/lib/mysql/tmp data/mysql-tmp
adduser -r mysql -U
chown mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql /var/log/mysql /var/lib/mysql/tmp
</boot>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-20-2048.jpg)
![/export/stack/carts/chef/nodes/cart-chef-backend.xml
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<kickstart>
<description>
chef cart backend appliance extensions
</description>
<package>chef</package>
<!-- shell code for post RPM installation -->
<post>
mkdir -p /etc/chef /var/log/chef /var/run/chef
</post>
<post cond="not ‘proxy’ in hostname">
<file name="/etc/chef/client.rb">
<![CDATA[
#
# Chef Client Config File
#
# Dynamically generated by Stacki
#
log_level :info
log_location STDOUT
chef_server_url "#CHEF_SERVER#"
validation_client_name ”chef-validator"
validation_key "/etc/chef/validation.pem"
client_key "/etc/chef/client.pem"
ssl_verify_mode :verify_none
http_proxy 'http://proxy1:3128'
https_proxy 'http://proxy2:3128'
no_proxy ’test1,localhost,127.0.0.1'
environment 'production'
# Using default node name (fqdn)
node_name "#HOSTNAME#”
Ohai::Config[:plugin_path] << '/etc/chef/ohai'
]]>
</file>
# Need to add the chef server and client hostname to the client.rb file
sed -i 's,#CHEF_SERVER#,&chef_server;,g' /etc/chef/client.rb
sed -i 's/#HOSTNAME#/&hostname;.&domainname;/g' /etc/chef/client.rb
</post>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-23-2048.jpg)
![/export/stack/carts/chef/nodes/cart-chef-backend.xml
<post>
<file name="/etc/chef/first-boot.json">
{
"run_list": [
"role[base_role]",
"role[dc_sfo]"
]
}
</file>
</post>
# If we are nuking disks we are assuming this is a new server
# or the chef client/node has been deleted out of the chef server if it existed.
<boot order="post" cond="nukedisks">
# Run chef-client for the first time
/usr/bin/chef-client -j /etc/chef/first-boot.json -L /var/log/chef/chef.log
# Make a backup of the chef private key in case we need to re-provision/upgrade a server
mkdir -p /data/chef-backup
chown root:root /data/chef-backup
chmod 700 /data/chef-backup
cp -a /etc/chef/* /data/chef-backup
</boot>
# If we are not nuking the disks we are assuming we are re-loading or upgrading
# the OS and need to keep the client.pem chef key so chef-client can run properly
<boot order="post" cond="not nukedisks">
cp /data/chef-backup/client.pem /etc/chef/
/usr/bin/chef-client -L /var/log/chef/chef.log
</boot>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-24-2048.jpg)
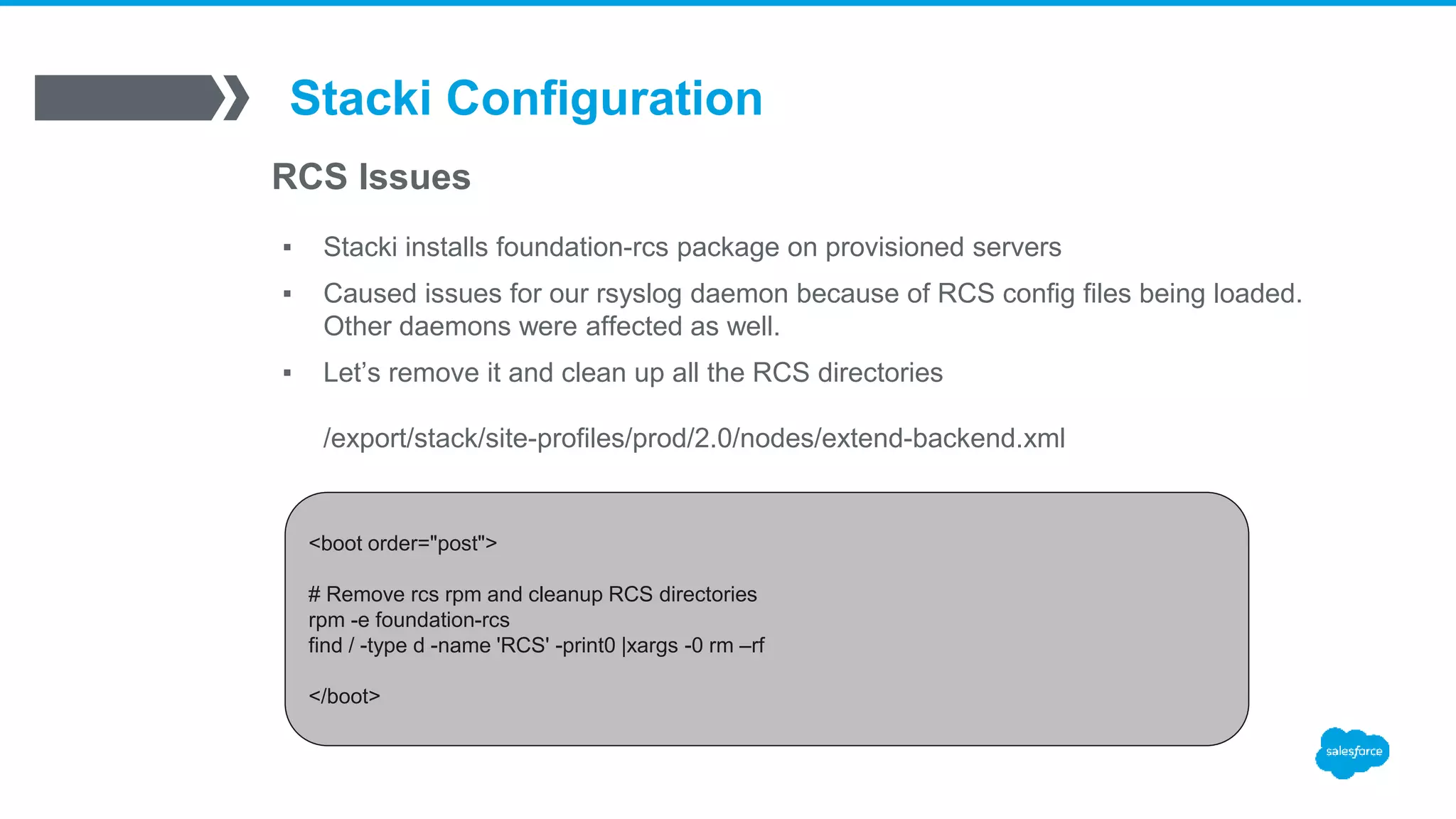






![Detecting Issues and AdHoc Reporting
What? We have Issues?
▪ Watching the nukecontroller and nukedisks attributes
[root@stacki]# stack list host attr chef1-1 |grep nuke
chef1-1: -------------------- nukecontroller true H
chef1-1: -------------------- nukedisks true H
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:20:39:52 -0700] "GET /install/sbin/public/setDbPartitions.cgi HTTP/1.1" 200 1
/var/log/httpd/ssl_access_log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-34-2048.jpg)
![Detecting Issues and AdHoc Reporting
What? We have Issues?
▪ Tailing /var/log/httpd/access_log for rpm downloads
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:32 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/gtk2-2.24.23-6.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 3339880 "-" "-"
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:31 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/hdparm-9.43-4.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 83060 "-" "-”
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:32 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/libXext-1.3.2-2.1.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 35644 "-" "-"
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:32 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/filesystem-2.4.30-3.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 1057228 "-" "-"
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:32 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/NetworkManager-0.8.1-99.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 1185212 "-" "-"
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:17:09:32 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/RedHat/RPMS/libstoragemgmt-1.2.3-1.el6.x86_64.rpm HTTP/1.1" 200 211068 "-" "-"
tail –f /var/log/httpd/access_log | grep –E “192.168.10.50|192.168.10.51”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-35-2048.jpg)
![Detecting Issues and AdHoc Reporting
What? We have Issues?
▪ Watching the boot action flag
[root@stacki]# stack list host boot chef1-*
HOST ACTION
chef1-2: install
chef1-1: os
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:20:39:52 -0700] "GET /install/sbin/public/setPxeboot.cgi?params={"action":"os"} HTTP/1.1" 200 1
/var/log/httpd/ssl_access_log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-36-2048.jpg)


![Host: test1
Checking for IP: 192.168.10.50
Feb 9 19:32:12 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPOFFER on 192.168.10.50 to ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
Feb 9 19:32:12 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPOFFER on 192.168.10.50 to ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
Feb 9 19:32:16 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPREQUEST for 192.168.10.50 (192.168.10.5) from ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
Feb 9 19:32:16 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPACK on 192.168.10.50to ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
Feb 9 19:32:16 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPREQUEST for 192.168.10.50 (192.168.10.5) from ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
Feb 9 19:32:16 stacki-host dhcpd: DHCPACK on 192.168.10.50 to ba:c2:3d:c3:ab:13 via 192.168.10.1
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:19:32:54 -0700] "GET /install/sbin/kickstart.cgi?arch=x86_64&np=40 HTTP/1.1" 200 96101
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:19:33:13 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/images/updates.img HTTP/1.1" 404 329 "-" "-”
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:19:33:33 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/images/product.img HTTP/1.1" 200 782336 "-" "-"
192.168.10.50 - - [09/Feb/2016:19:33:35 -0700] "GET /install/distributions/prod/x86_64/images/install.img HTTP/1.1" 200 236163072 "-" "-"
Host: test2
Checking for IP: 192.168.10.51
Host: test3
Checking for IP: 192.168.10.52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-39-2048.jpg)
![Detecting Issues and AdHoc Reporting
AdHoc Reporting
▪ Find the top racks with the most un-provisioned hosts. Helps us
identify racks with potential ACL issues.
[root@stacki]# stack list network|awk '{print $1}’
NETWORK
rack1-prod_vlan1:
rack2-prod_vlan2:
rack3-prod_vlan1:
rack4-prod_vlan2:
rack5-prod_vlan2:
[root@stacki]# for h in `stack list host boot |grep -w install|awk '{print $1}'|sed s/://`; do stack list host interface $h; done
|grep eth0|awk '{print $3}'|cut -d- -f 1|sort|uniq -c|sort -rn|head
40 rack2
9 rack3
7 rack5
6 rack1
6 rack4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stacki-1600serverjourney-170111212812/75/Stacki-The1600-Server-Journey-40-2048.jpg)

