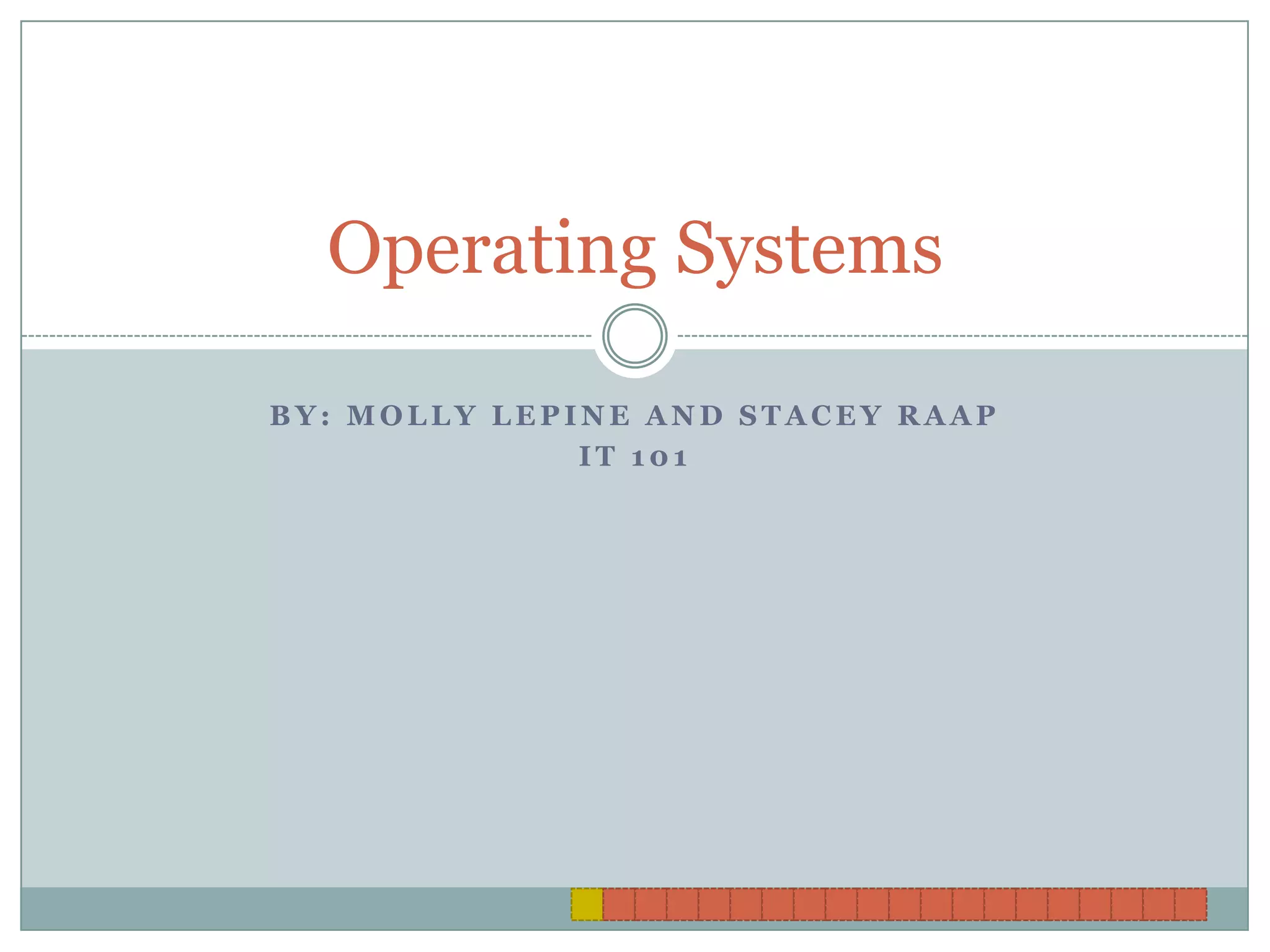
An operating system (OS) controls computer hardware, manages memory and processors, and provides an interface between users and applications. OSes control input/output devices, store and manipulate files, provide networking features, and allow multitasking of multiple programs. Different OSes are designed for specific computer types and applications must be compatible with a particular OS. The OS organizes data storage and allows interaction through a user interface. It communicates with external devices through drivers and controls processing, memory usage, input, and output. Embedded OSes control specialized devices while industrial OSes manage large server systems.