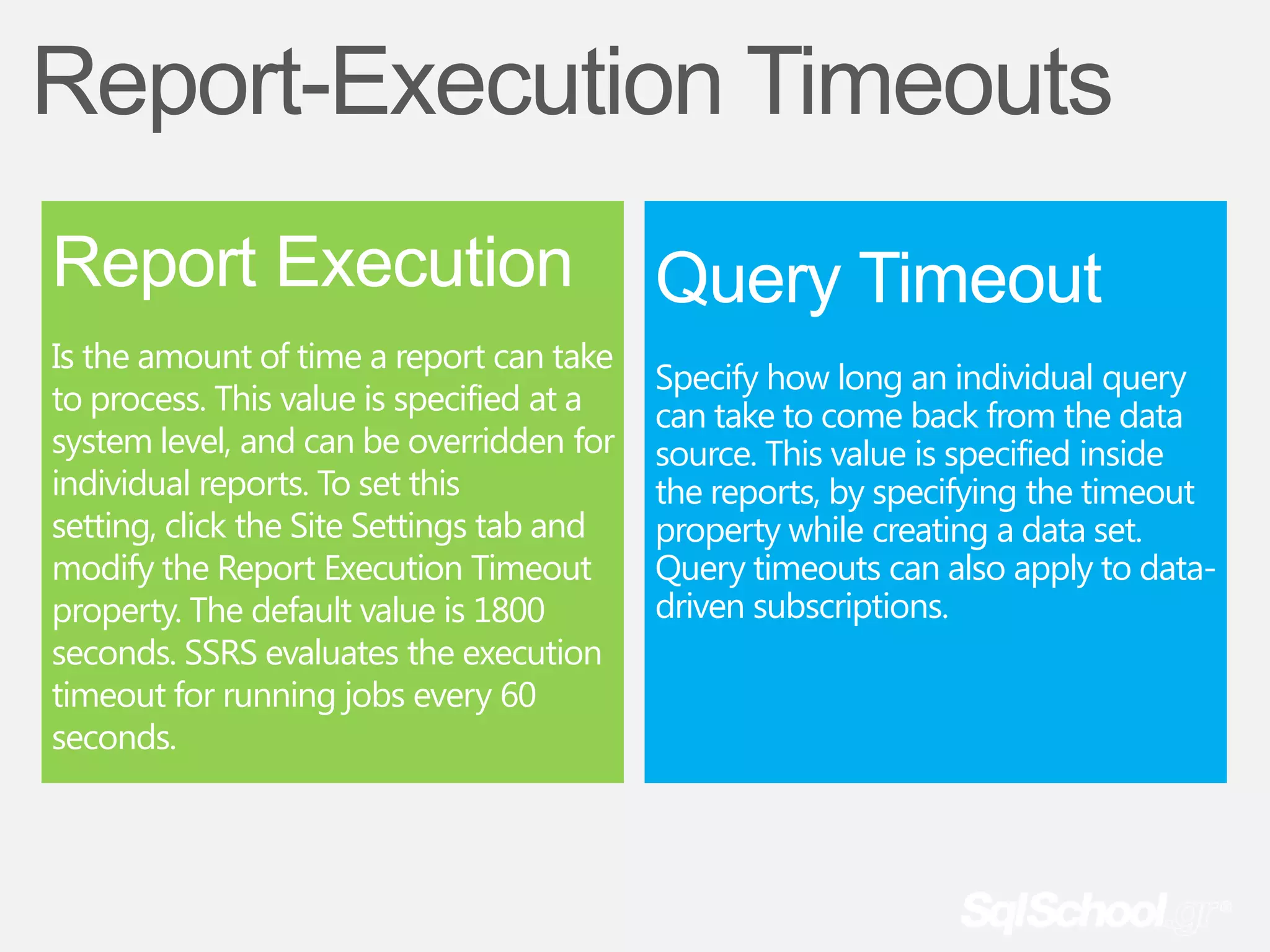
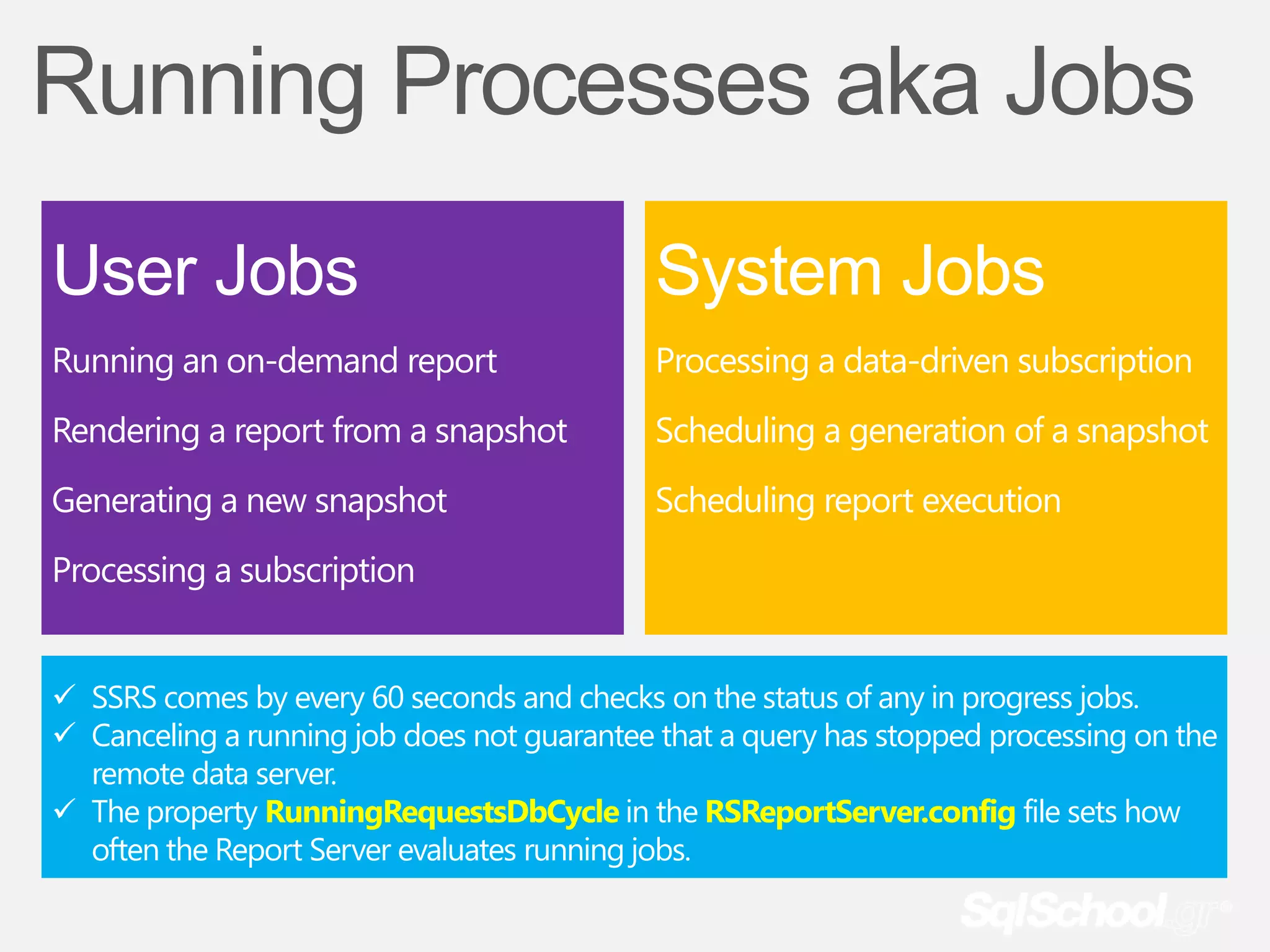
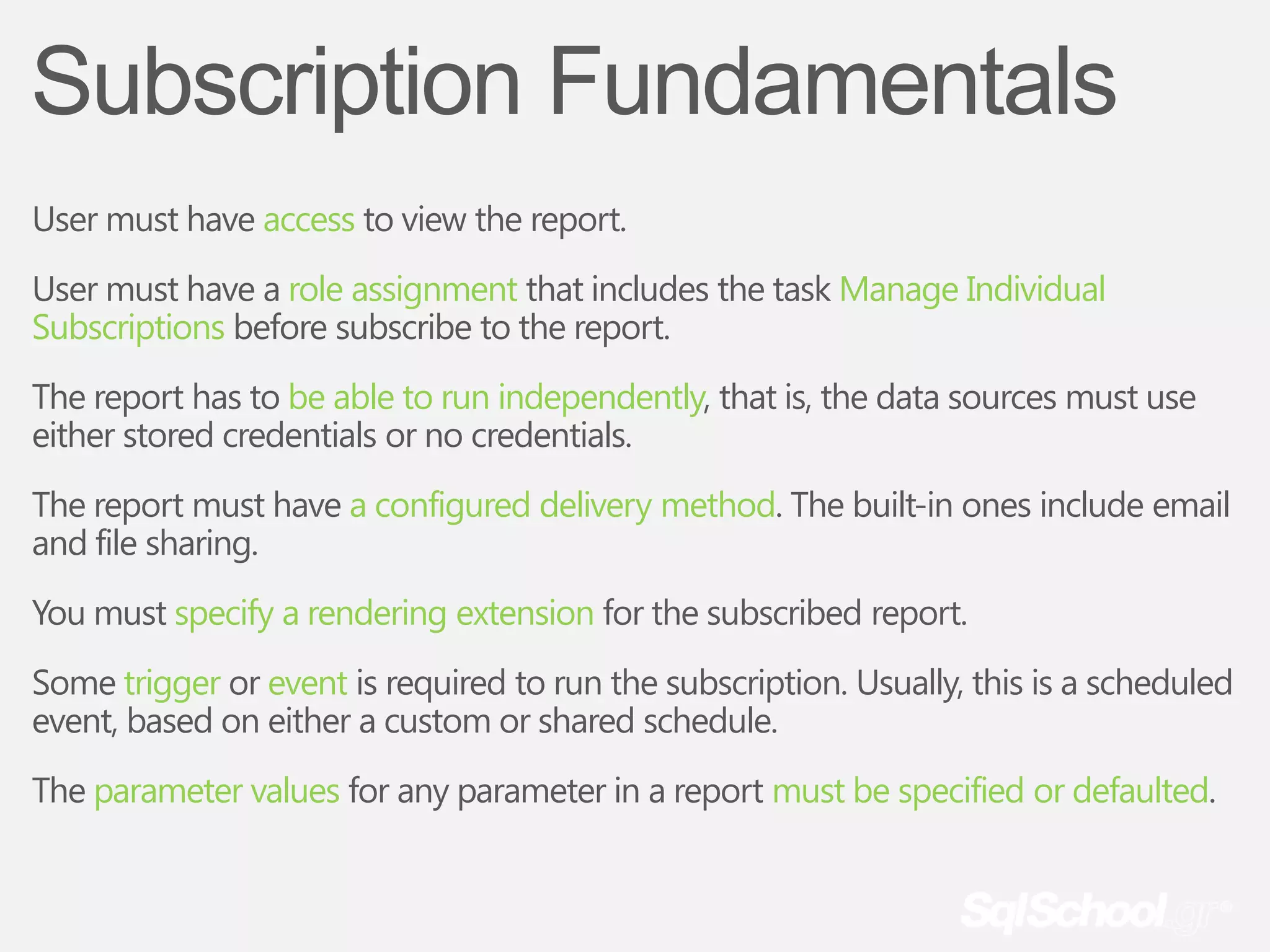
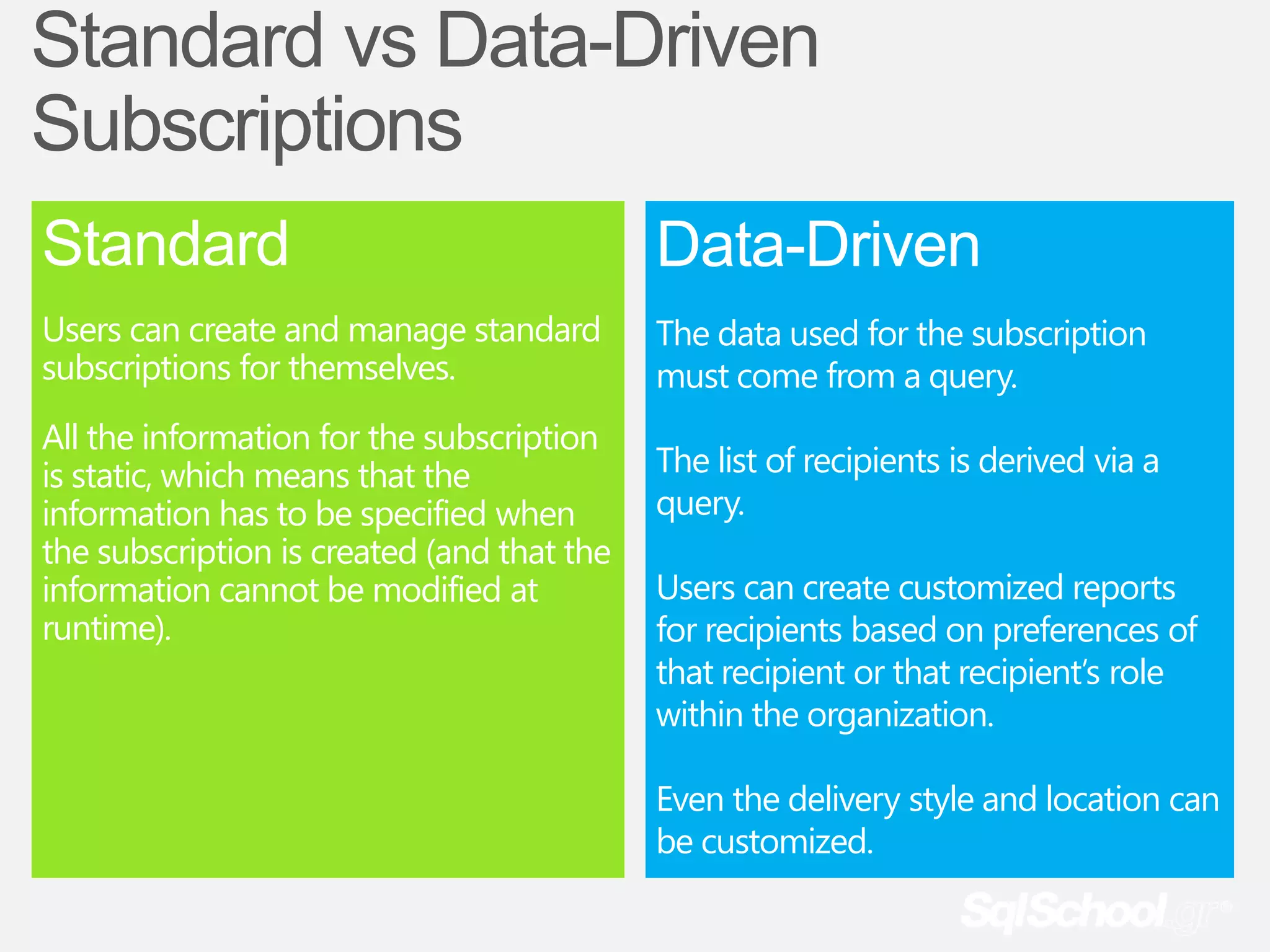
The document provides information about a presentation on Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Reporting Services Part II that will be recorded so that those who want to rewatch it or could not attend live have access. Attendees are asked to leave immediately if they have any issues with being recorded. The presentation is free and will begin in 1 minute. The presenter is currently speaking and asking attendees to confirm they can hear him, and if not, to change their card color so he is notified. Thank you is provided for cooperation.