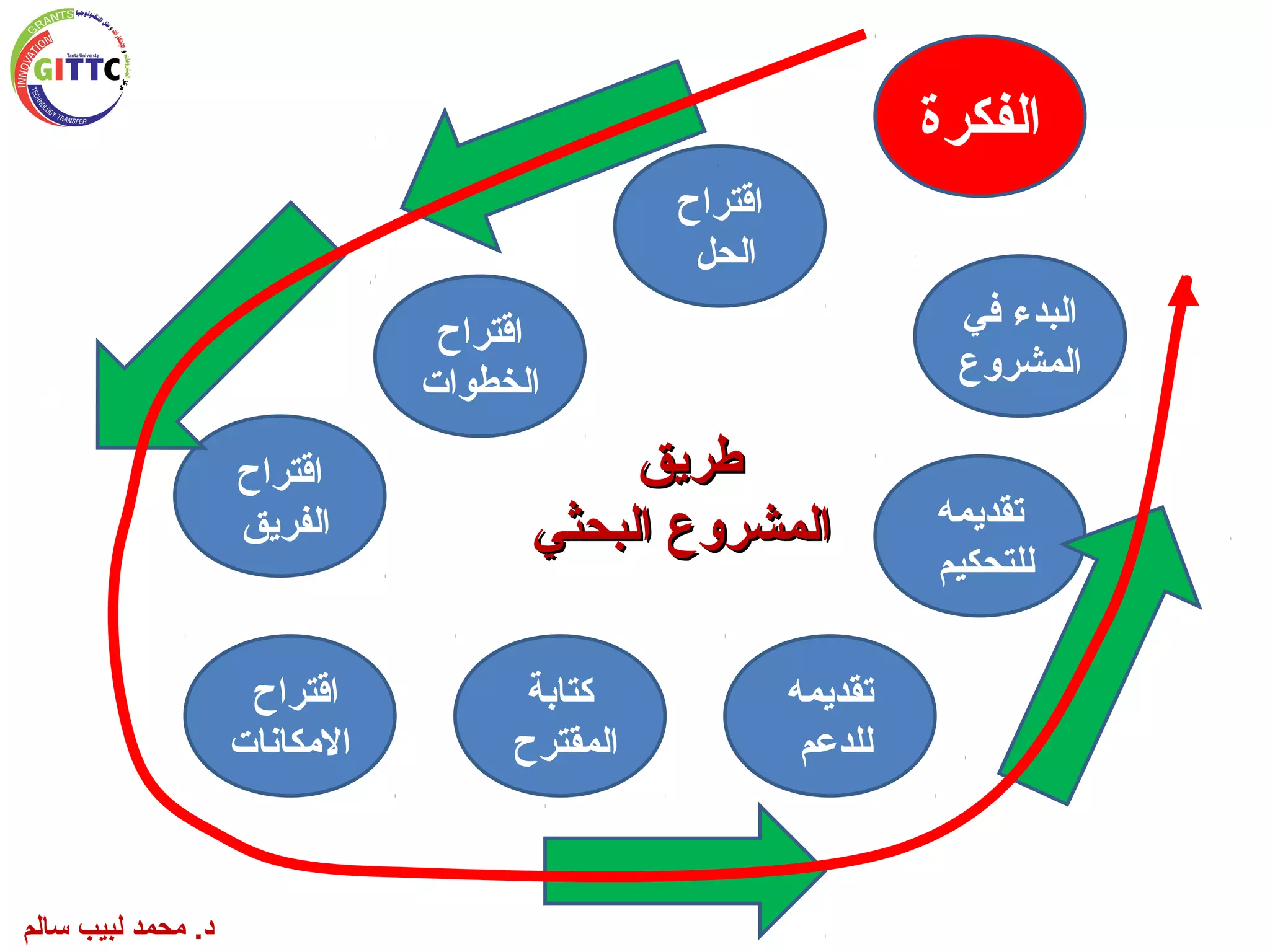
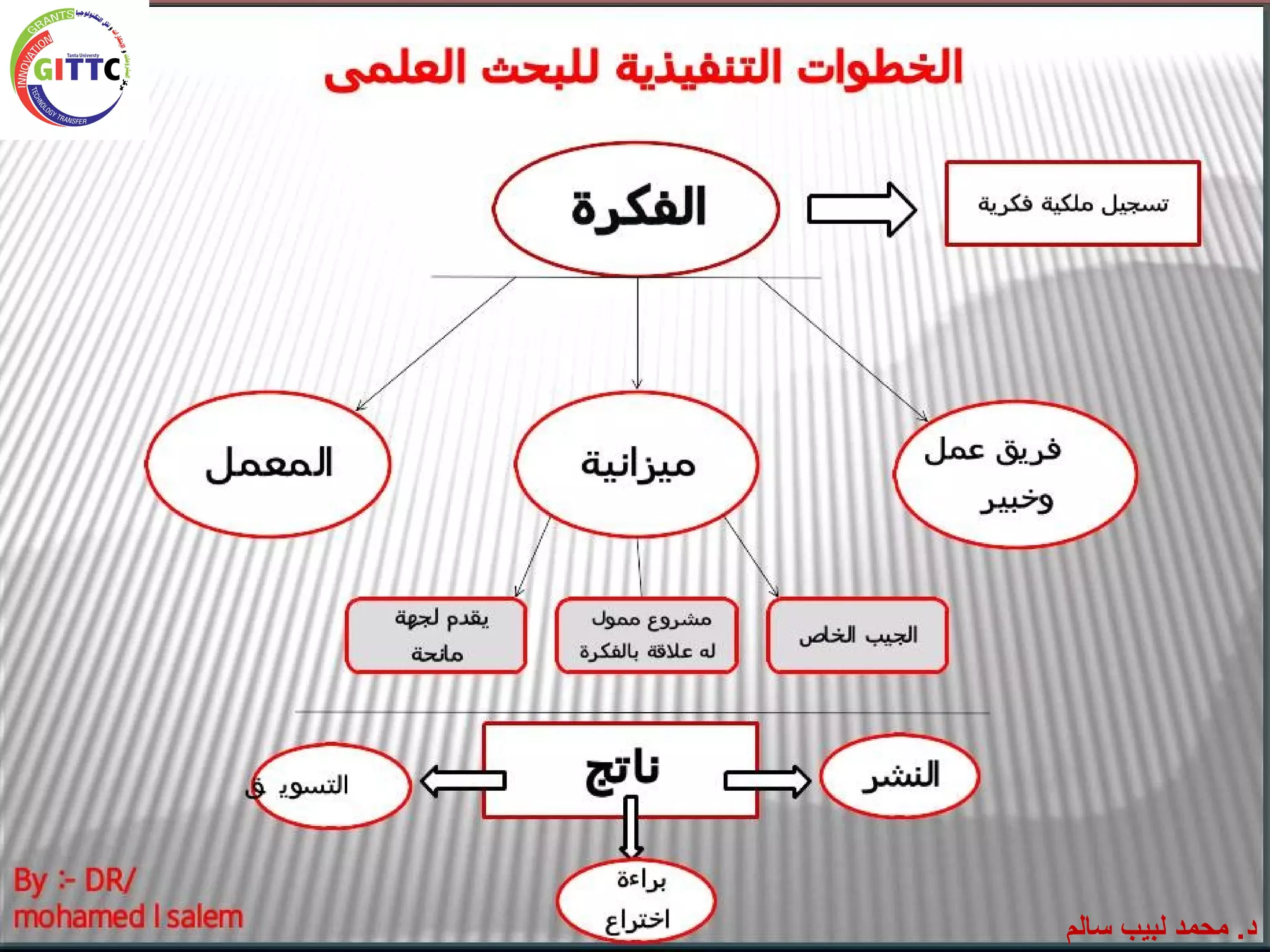
يتناول المستند كيفية كتابة مشروع بحثي في مجال العلوم، موضحًا أهمية البحث والمكونات الأساسية والمتطلبات الخاصة به. كما يشرح الخطوات اللازمة لتنفيذ البحث بما في ذلك صياغة الفكرة، أهداف المشروع، والأساليب التجريبية المطلوبة، بالإضافة إلى الميزانية والتحديات المحتملة. يُشير أيضًا إلى أهمية نشر النتائج بعد انتهاء المشروع وما يتطلبه ذلك من تخطيط جيد واستراتيجيات فعالة.