Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times

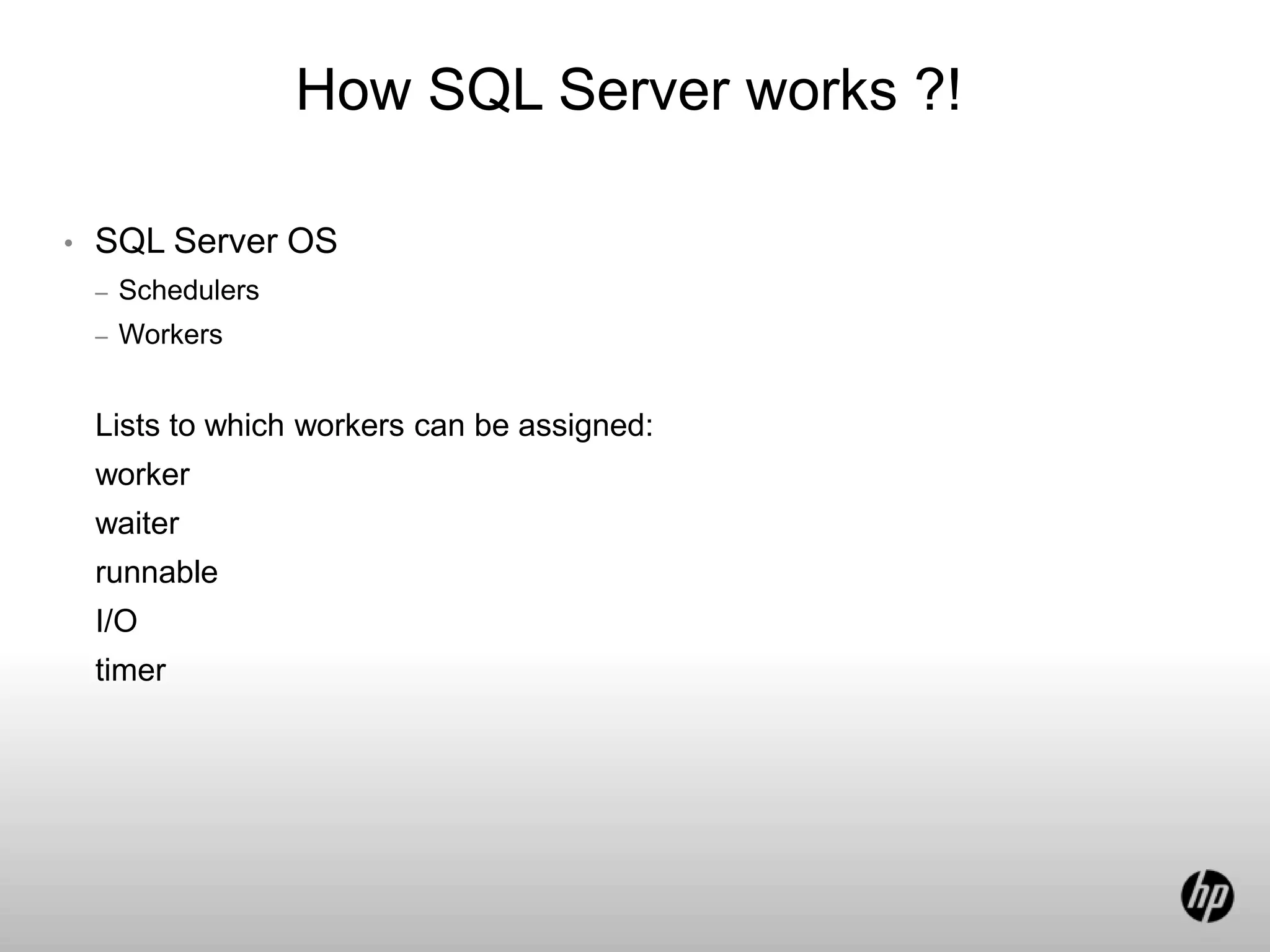
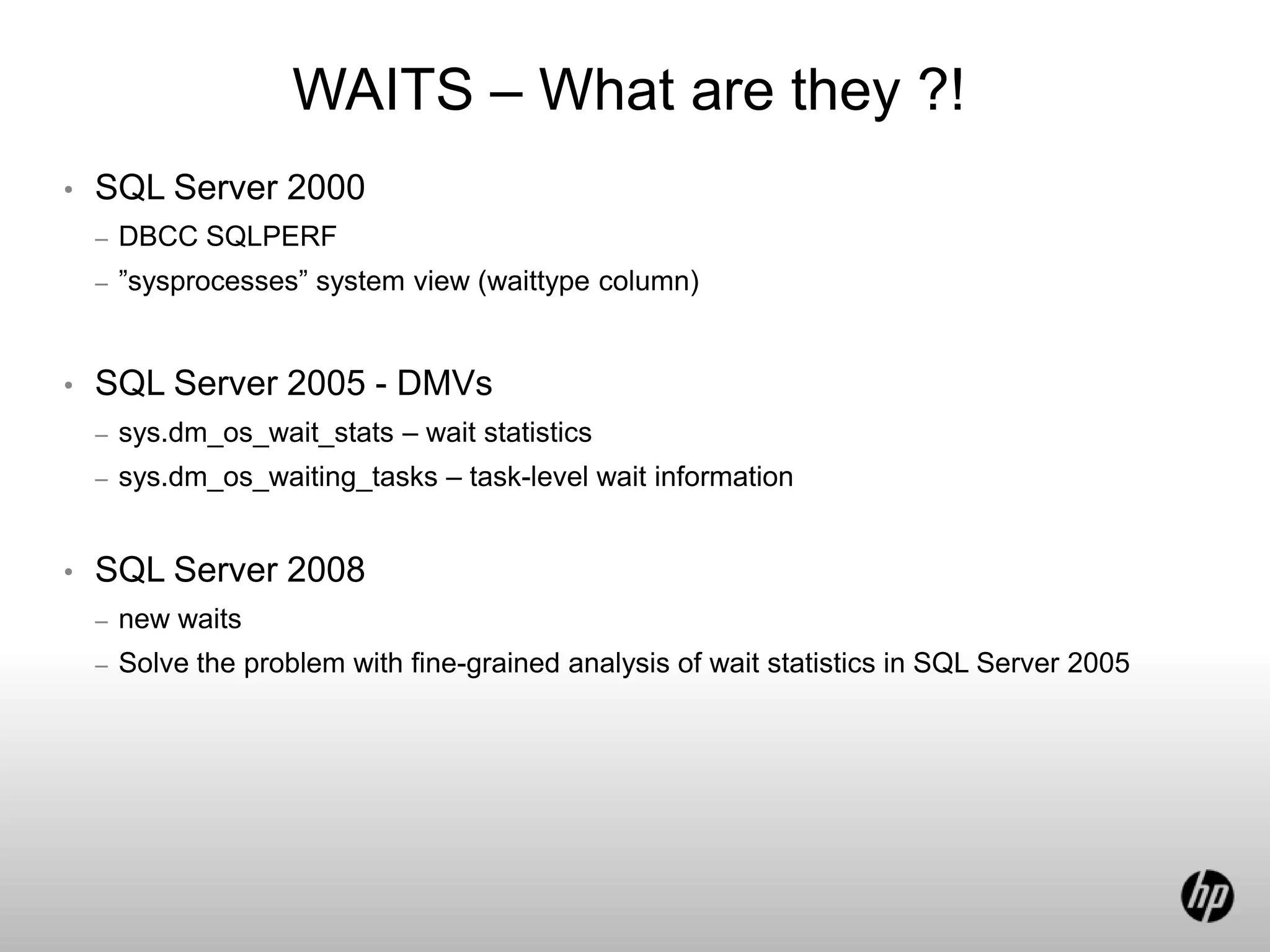






This document discusses waits in SQL Server 2008. It explains that waits occur when a SQL Server worker thread is waiting for a resource to become available, such as waiting for memory, disk I/O, or to stop blocking on a lock. The document lists common wait types including memory, disk I/O, blocking, CPU, and network waits. It also discusses dynamic management views introduced in SQL Server 2005 that provide wait statistics and extended events for monitoring waits.








