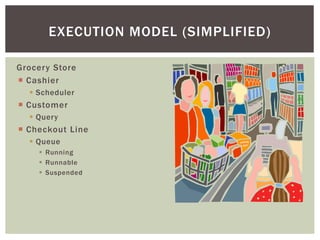
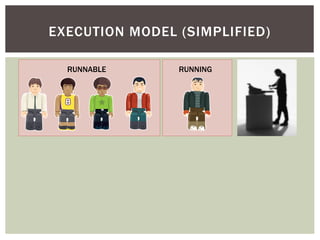
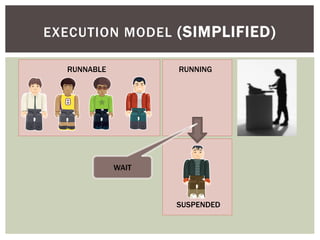
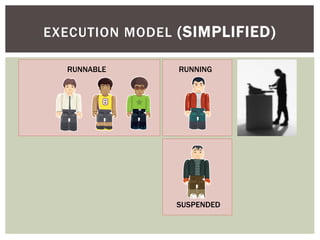
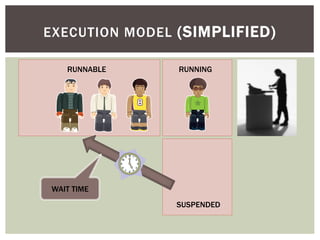
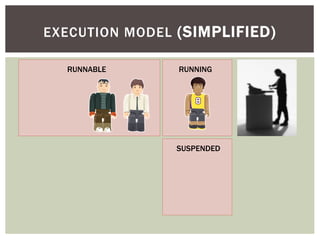
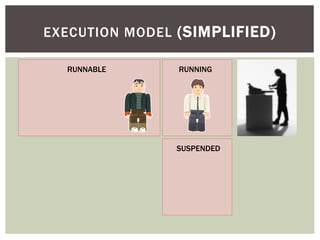
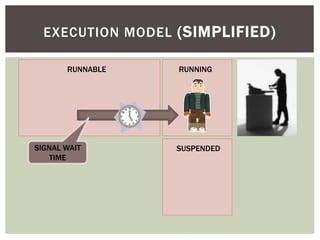
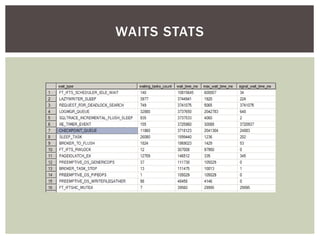
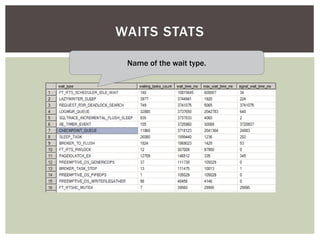
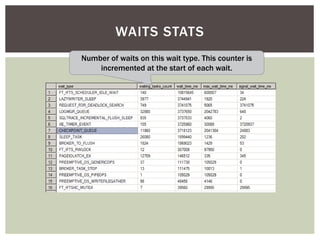
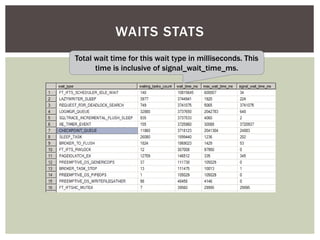
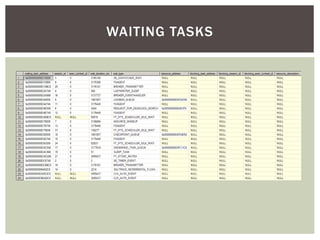
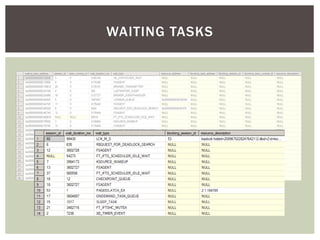
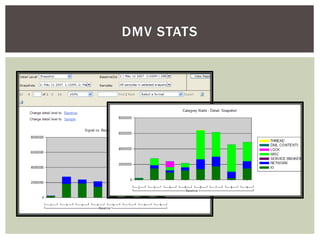
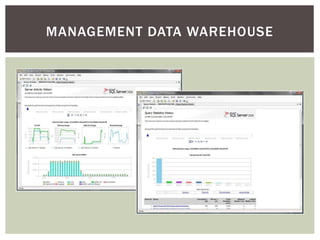
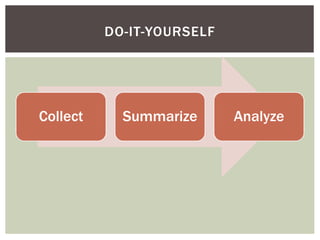
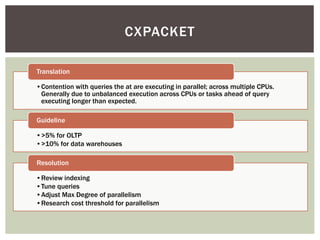
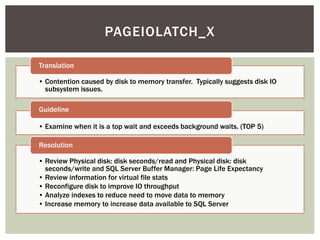
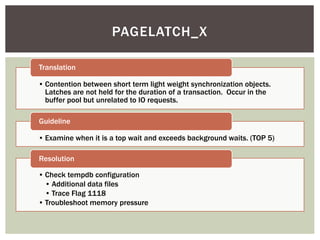
The document discusses wait statistics and wait types in SQL Server. It provides an overview of defining, viewing, collecting and reviewing wait data using dynamic management views and wait statistics. It also simplifies the SQL Server execution model using a grocery store checkout line analogy. Specific wait types are explained such as CXPACKET, OLEDB, PAGEIOLATCH_X, PAGELATCH_X and LATCH_X. Guidelines and potential resolutions are provided for analyzing and addressing top wait events.