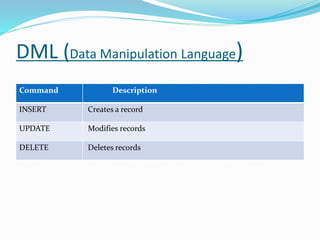
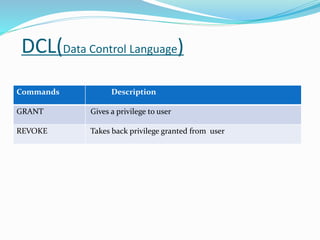
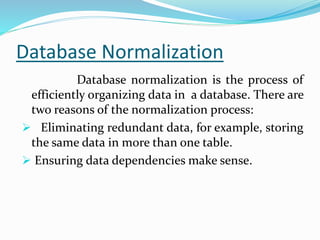
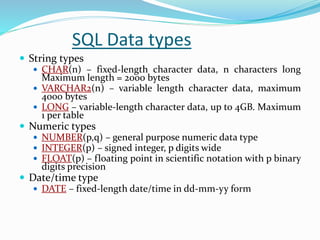
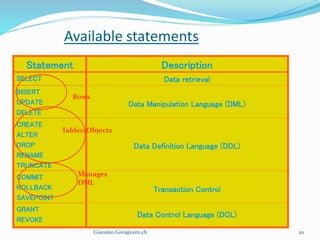
SQL is a language used to communicate with databases and manage data. It allows users to create, update, and retrieve data from databases. The document outlines the history of SQL and its evolution over time. It also describes key SQL concepts like data types, commands, primary keys, database normalization, and techniques for ensuring data integrity.