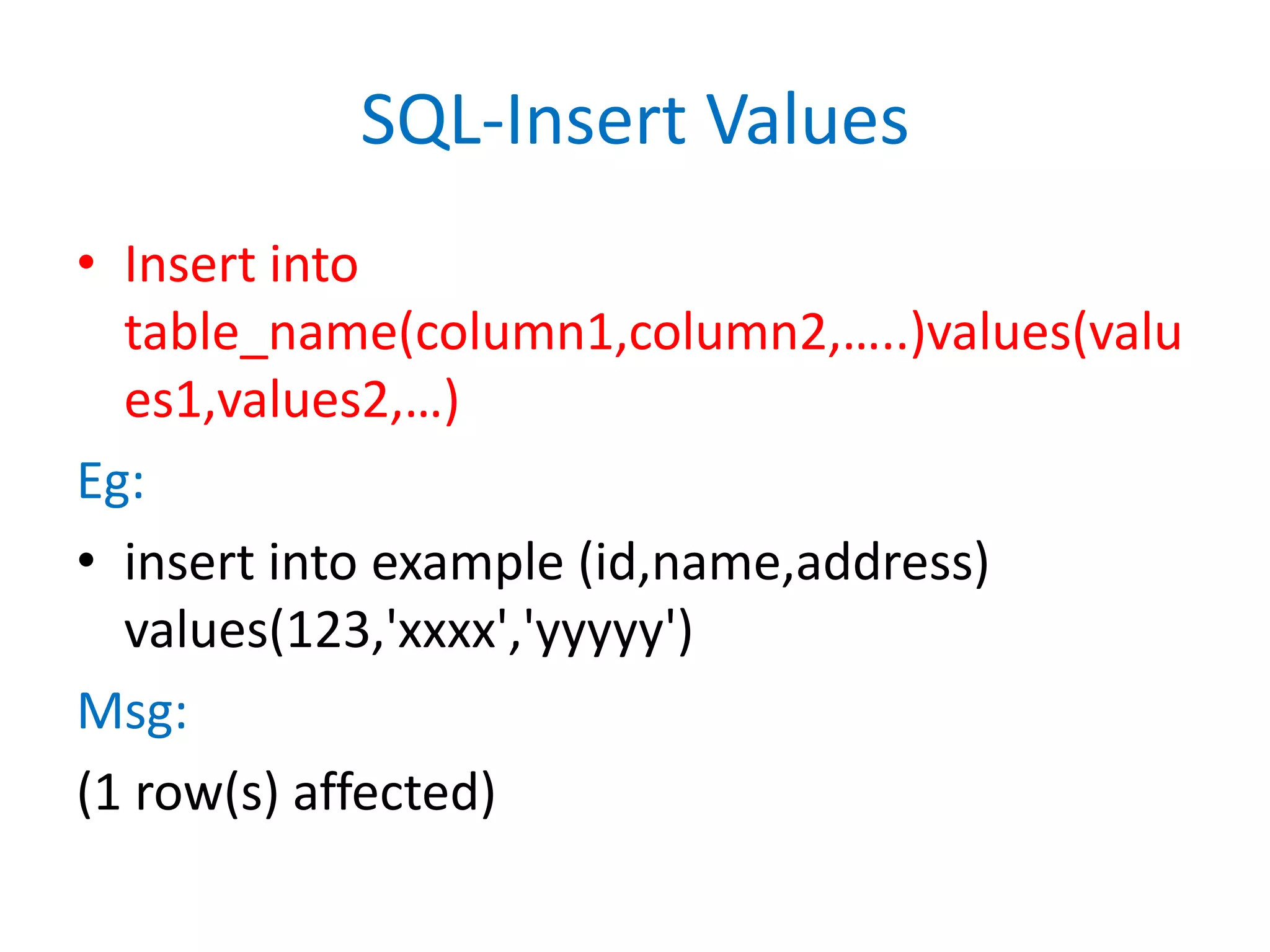
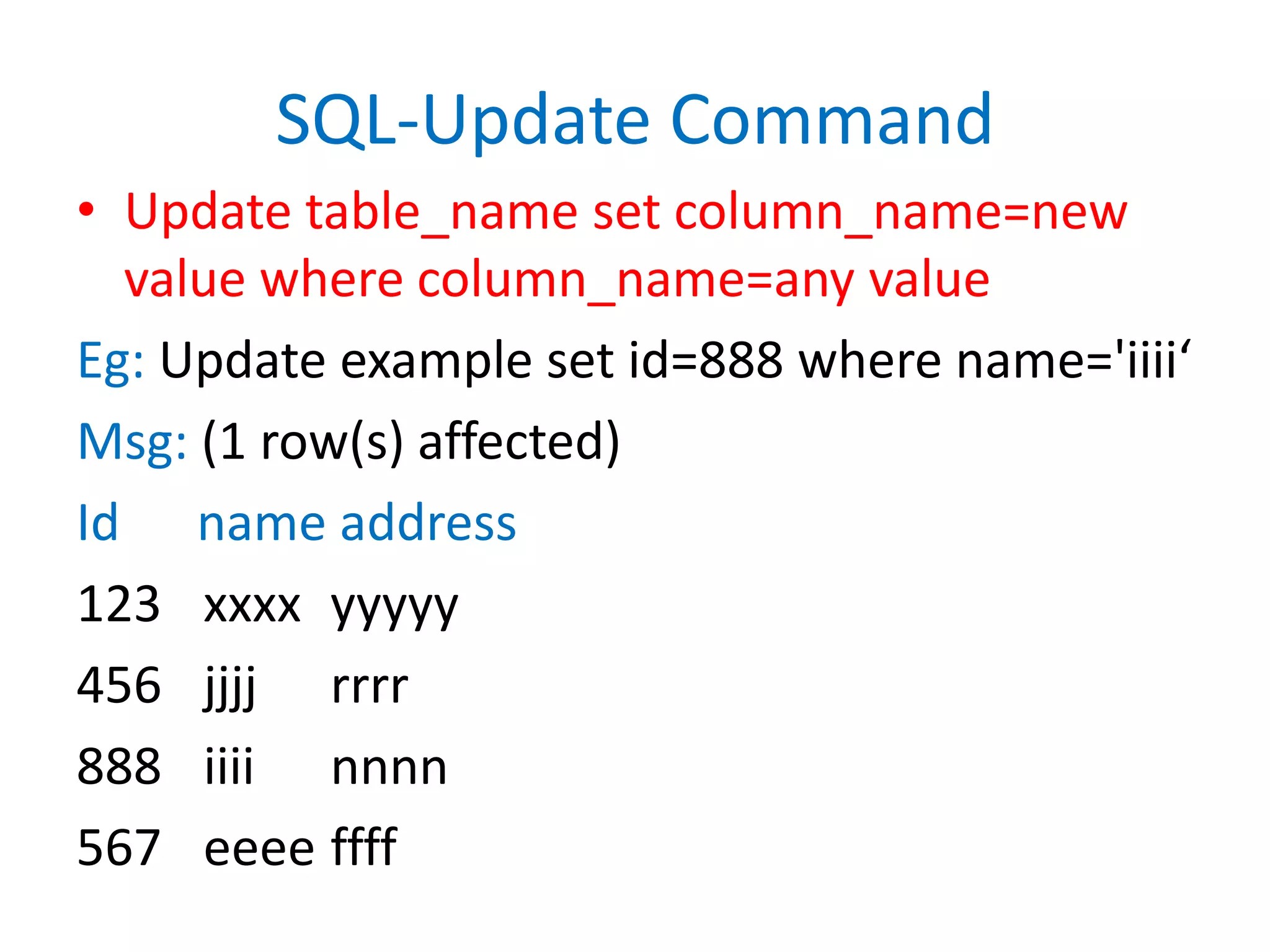
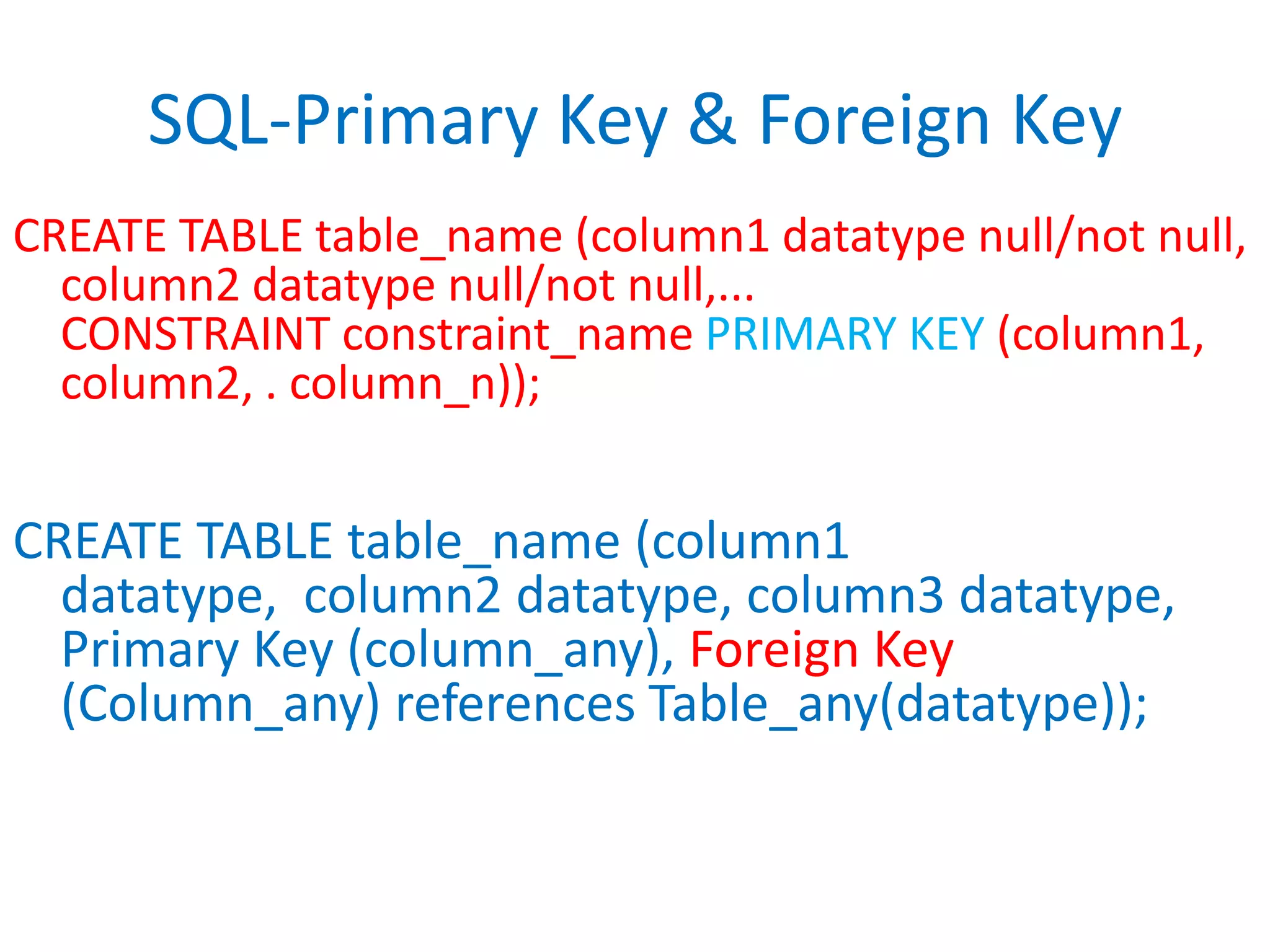
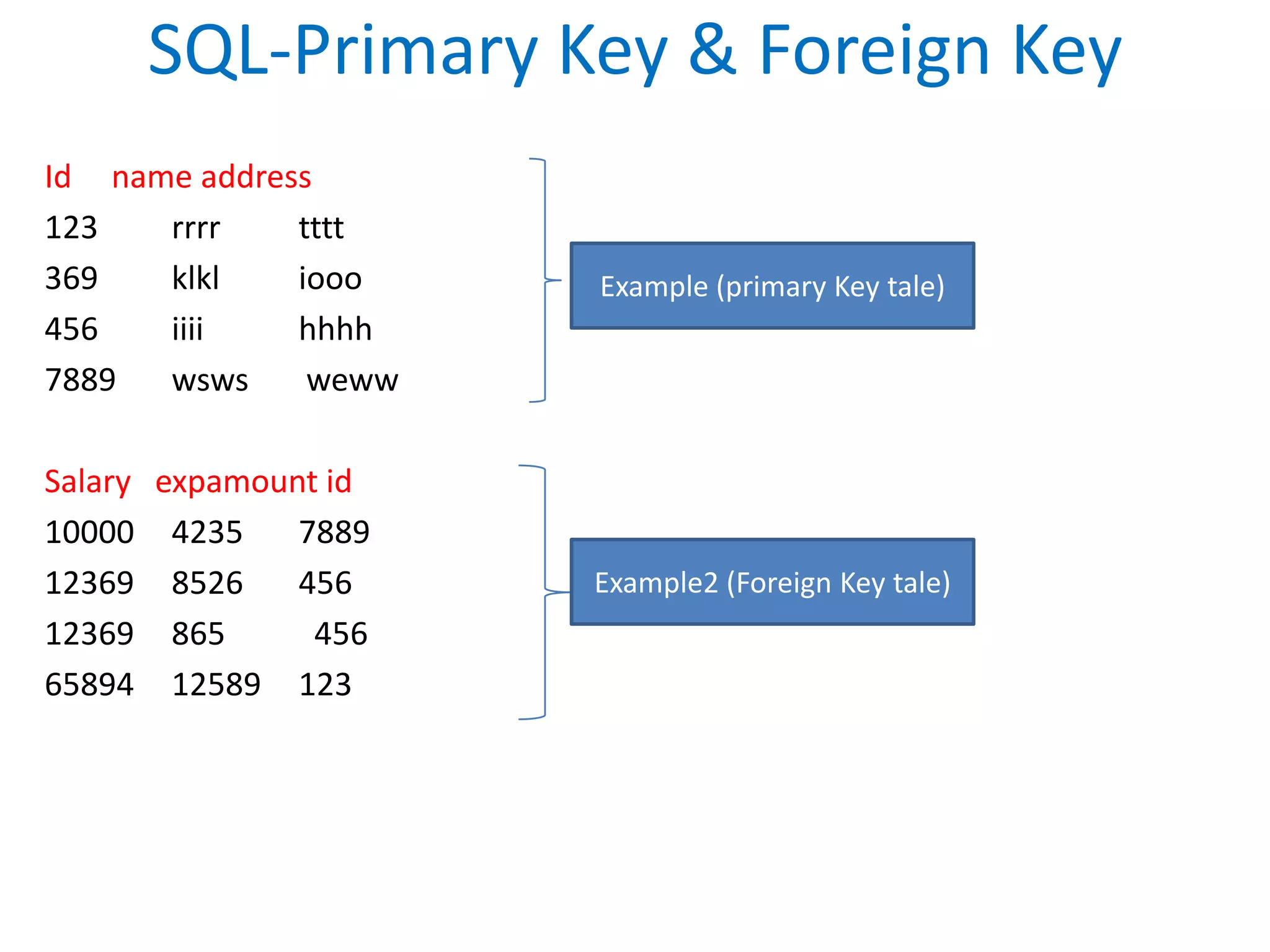
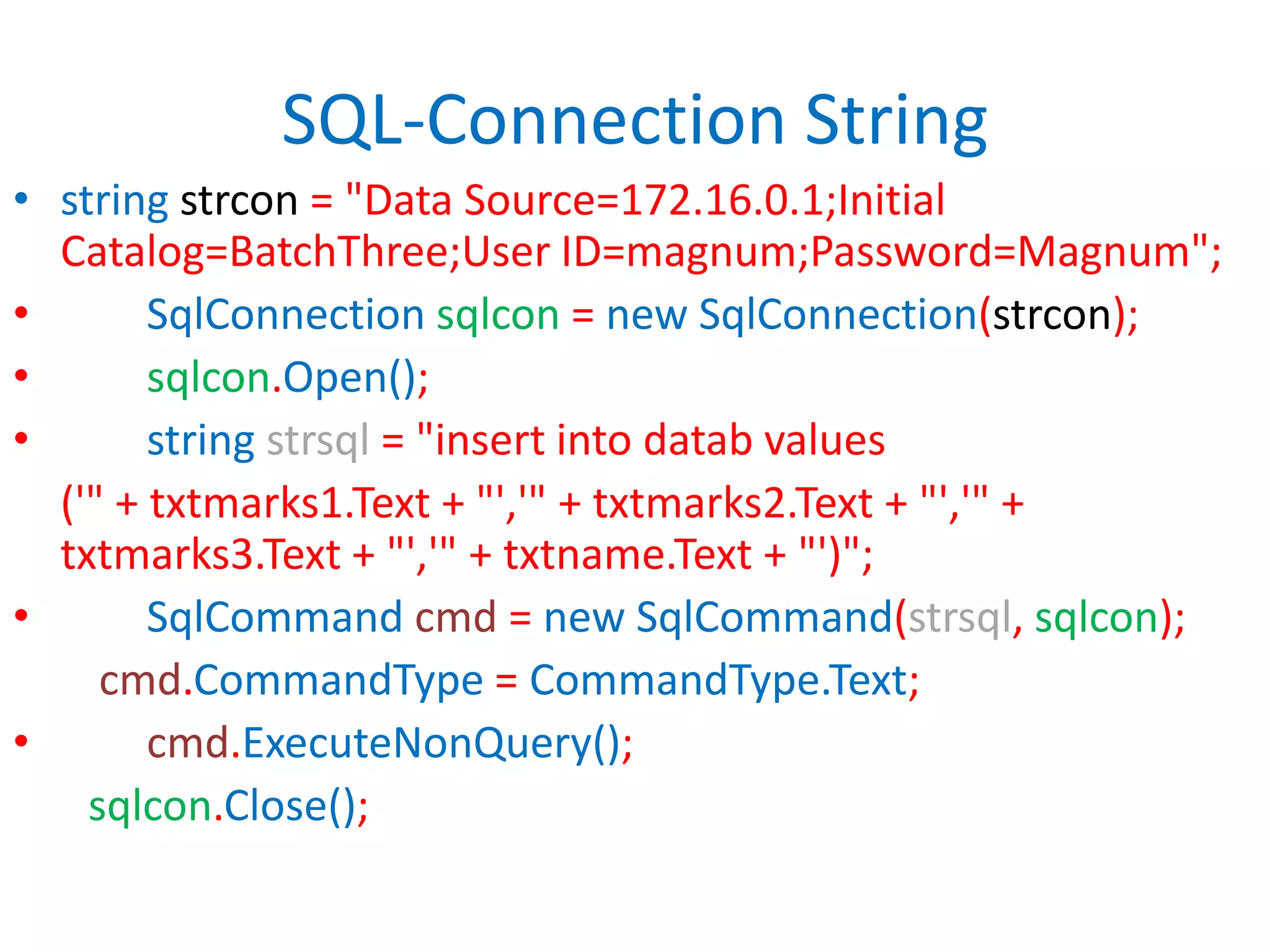
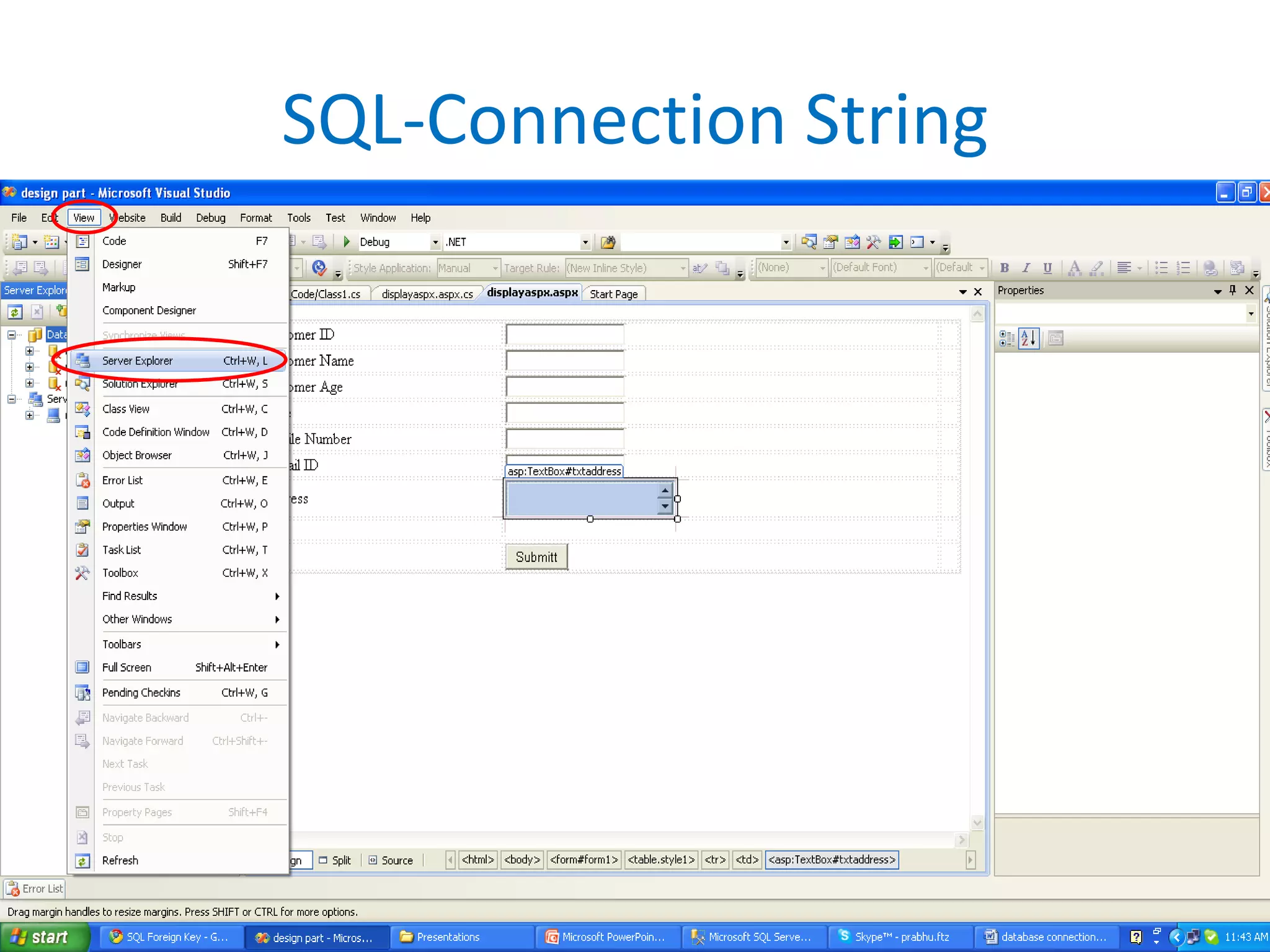
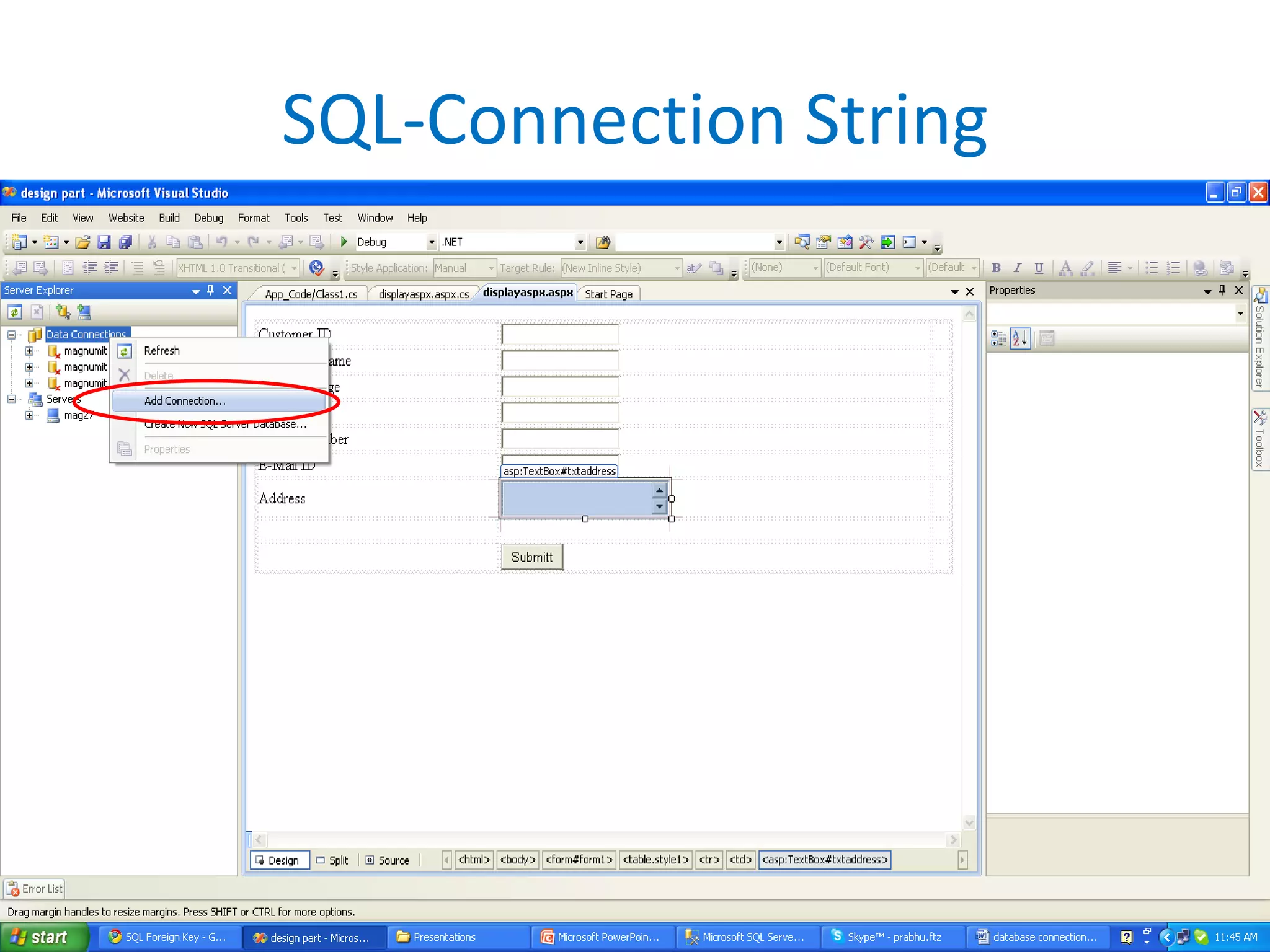
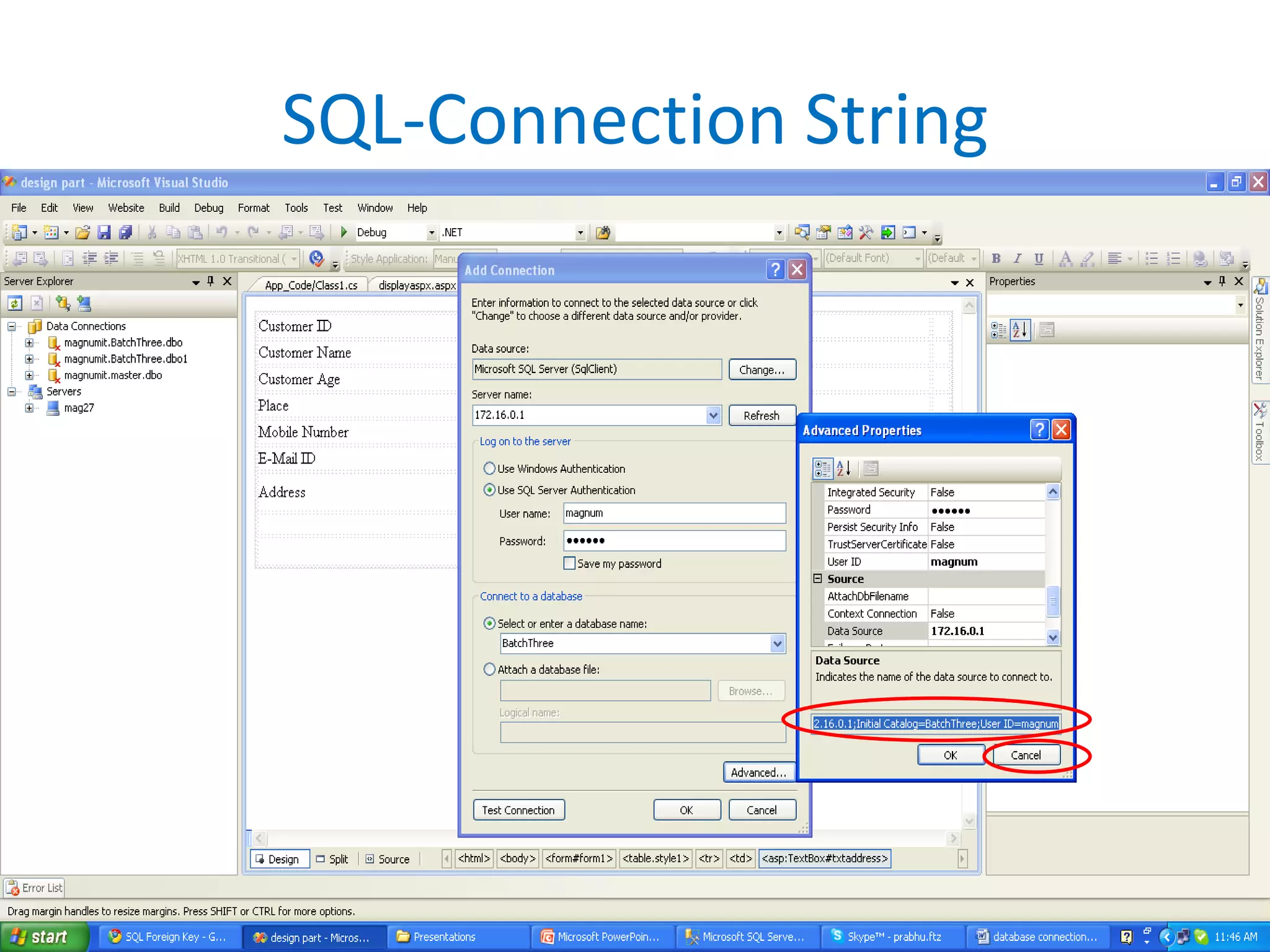
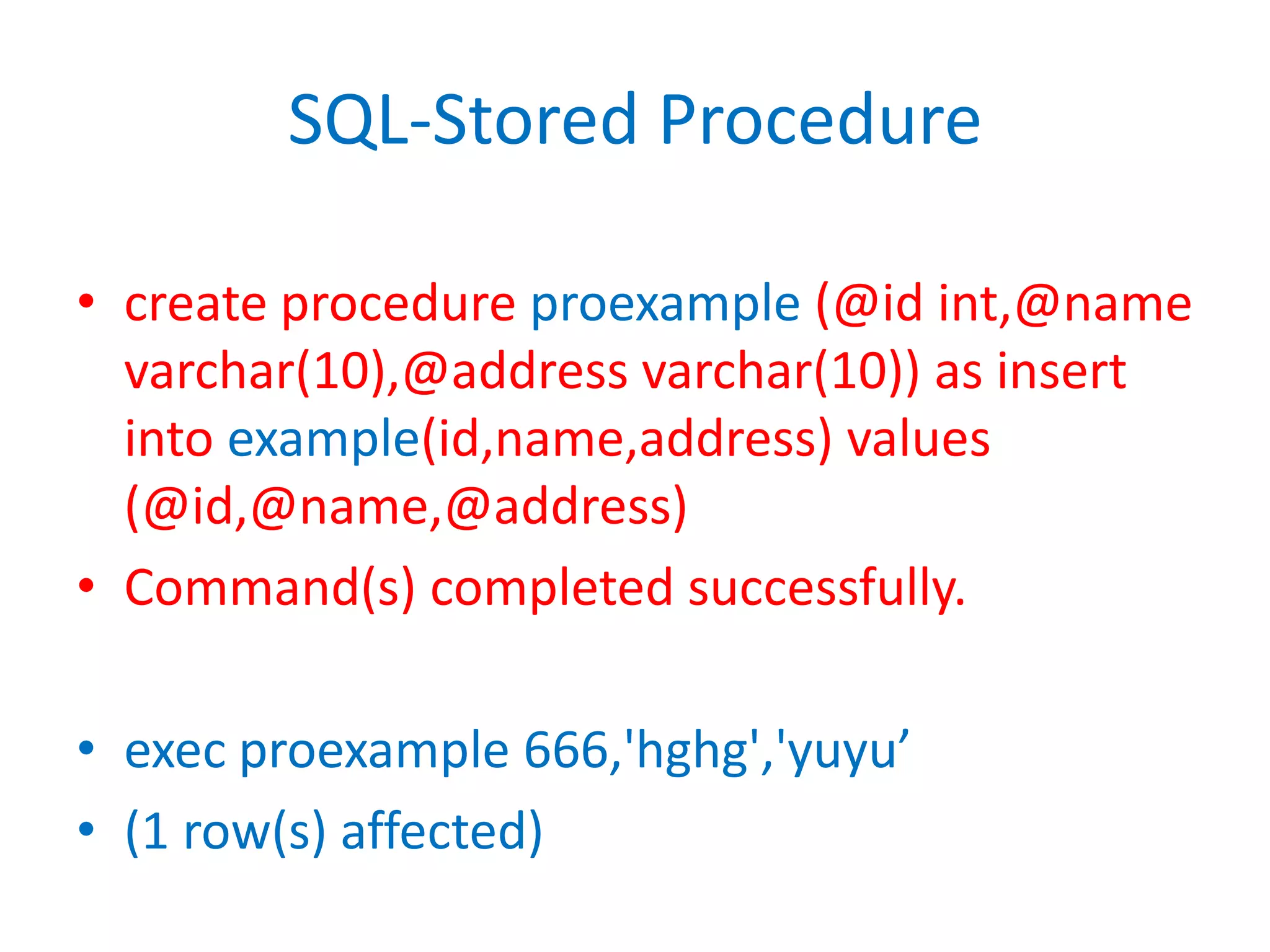
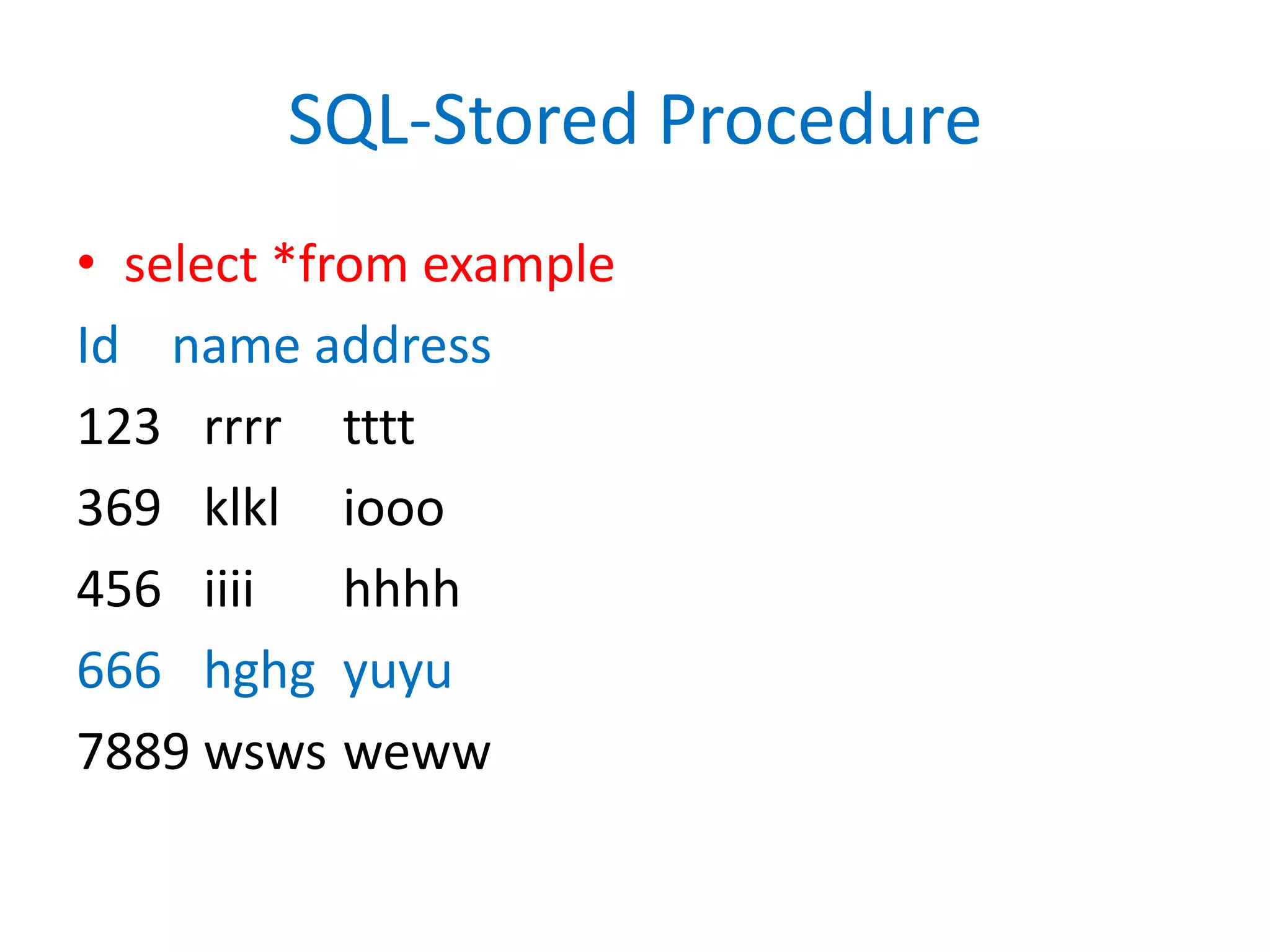
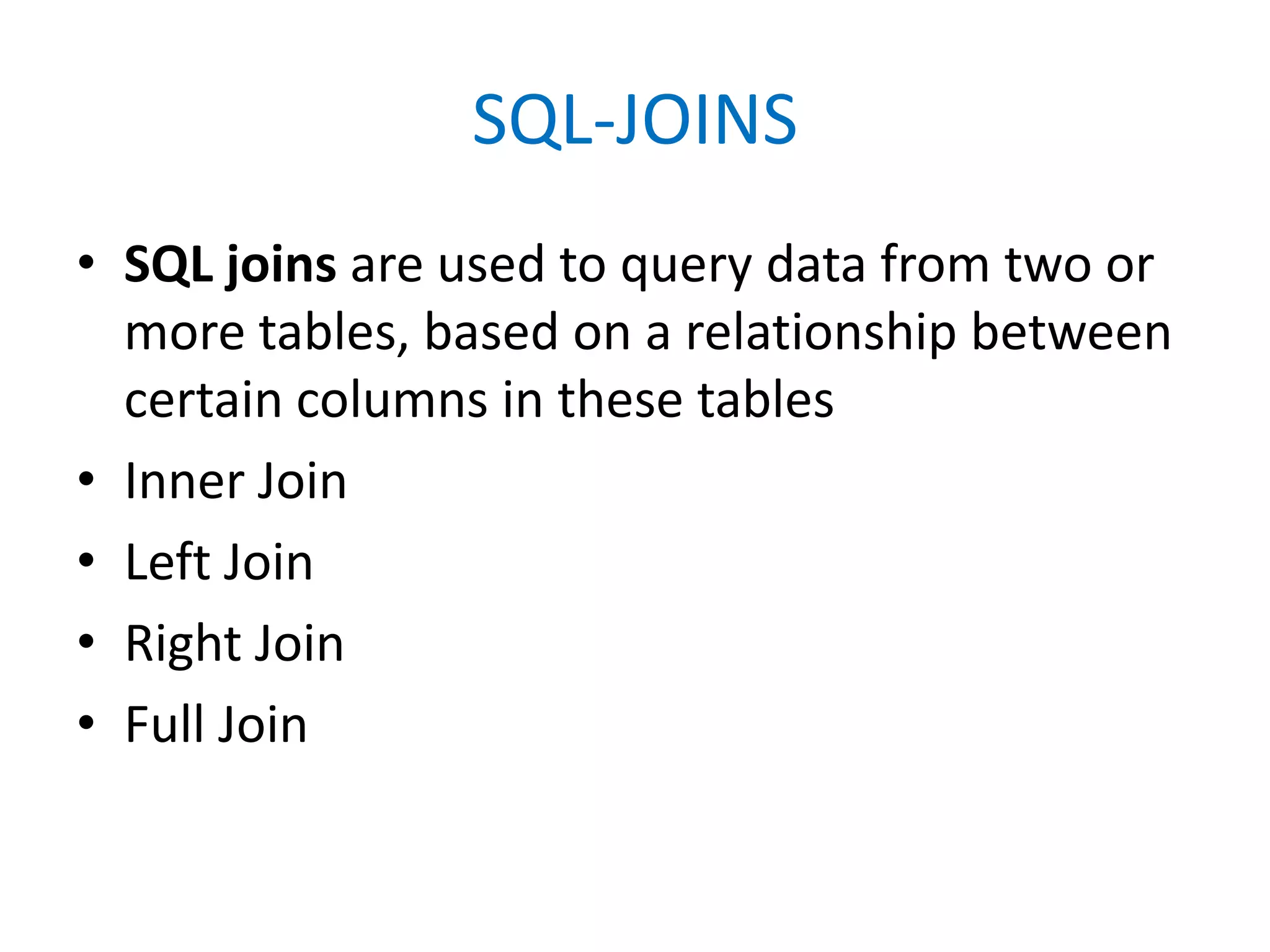
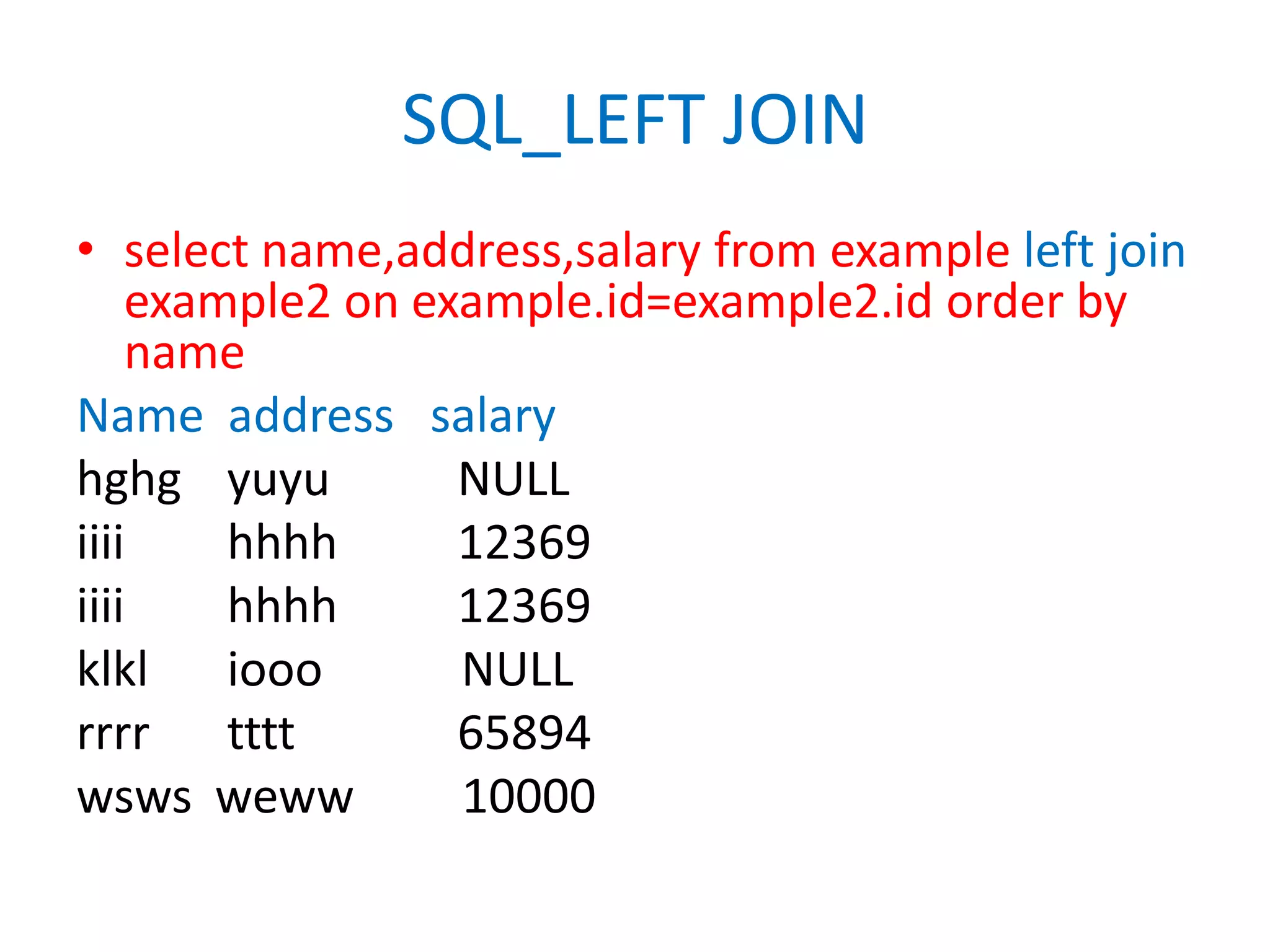
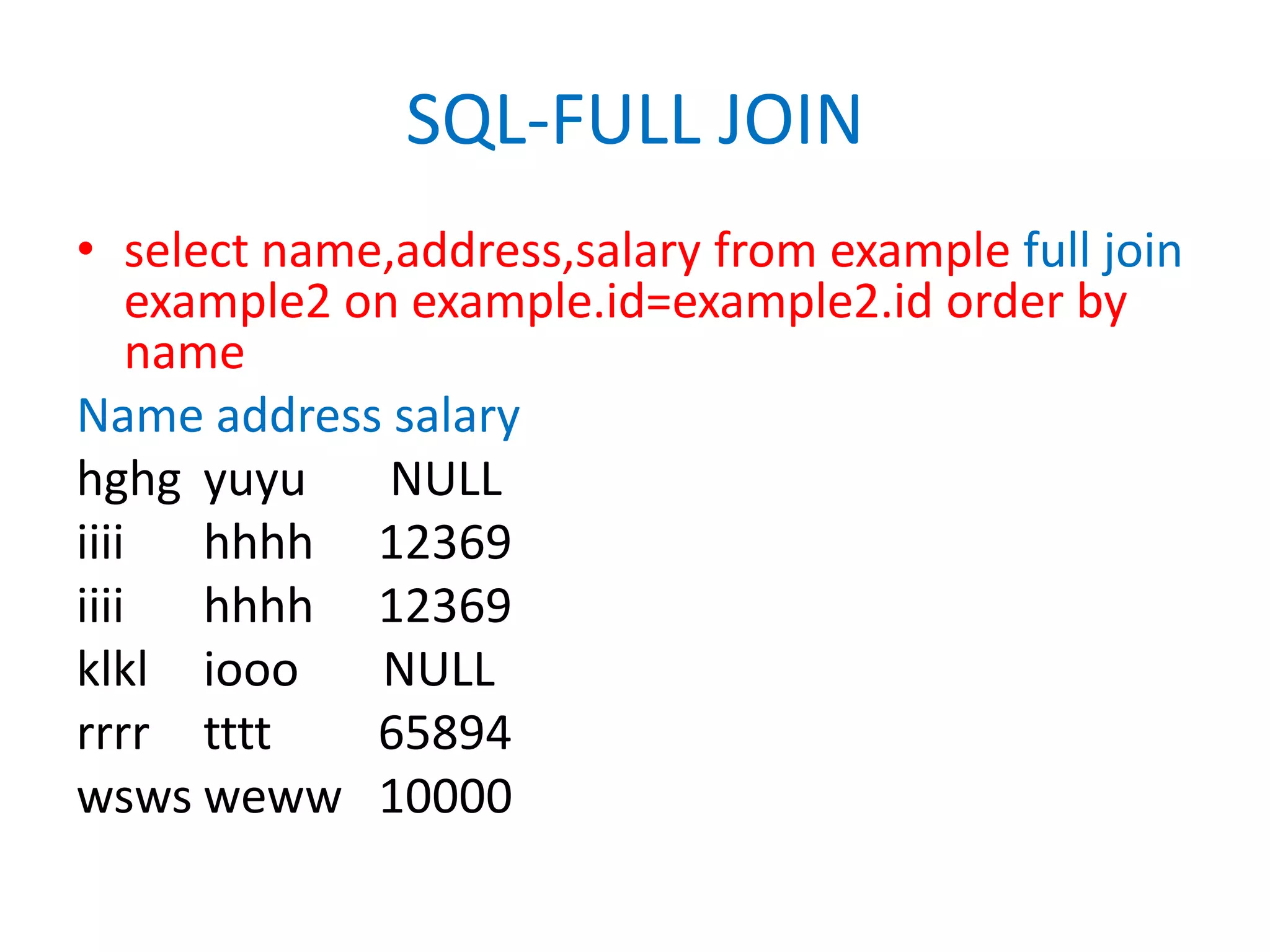
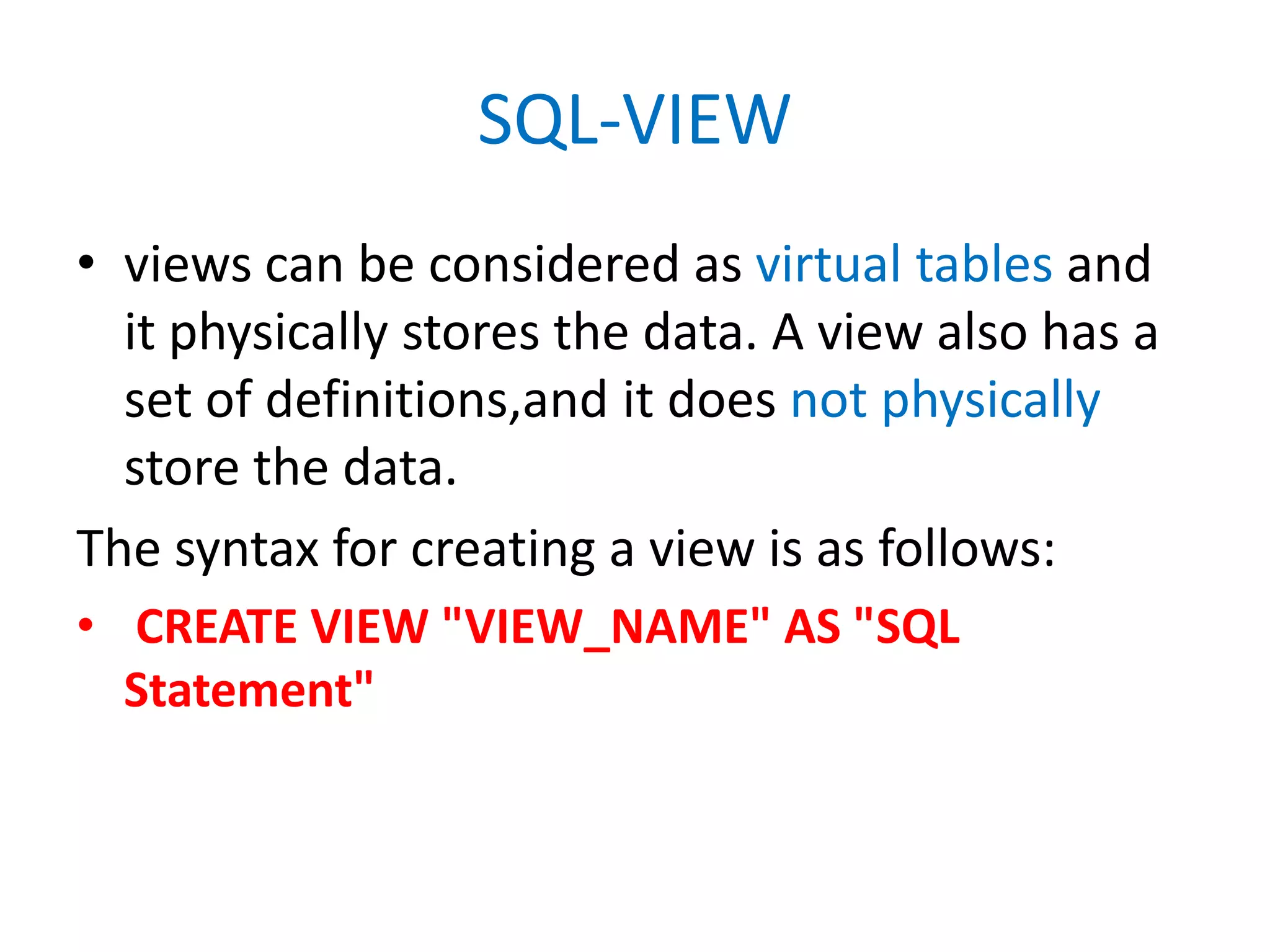
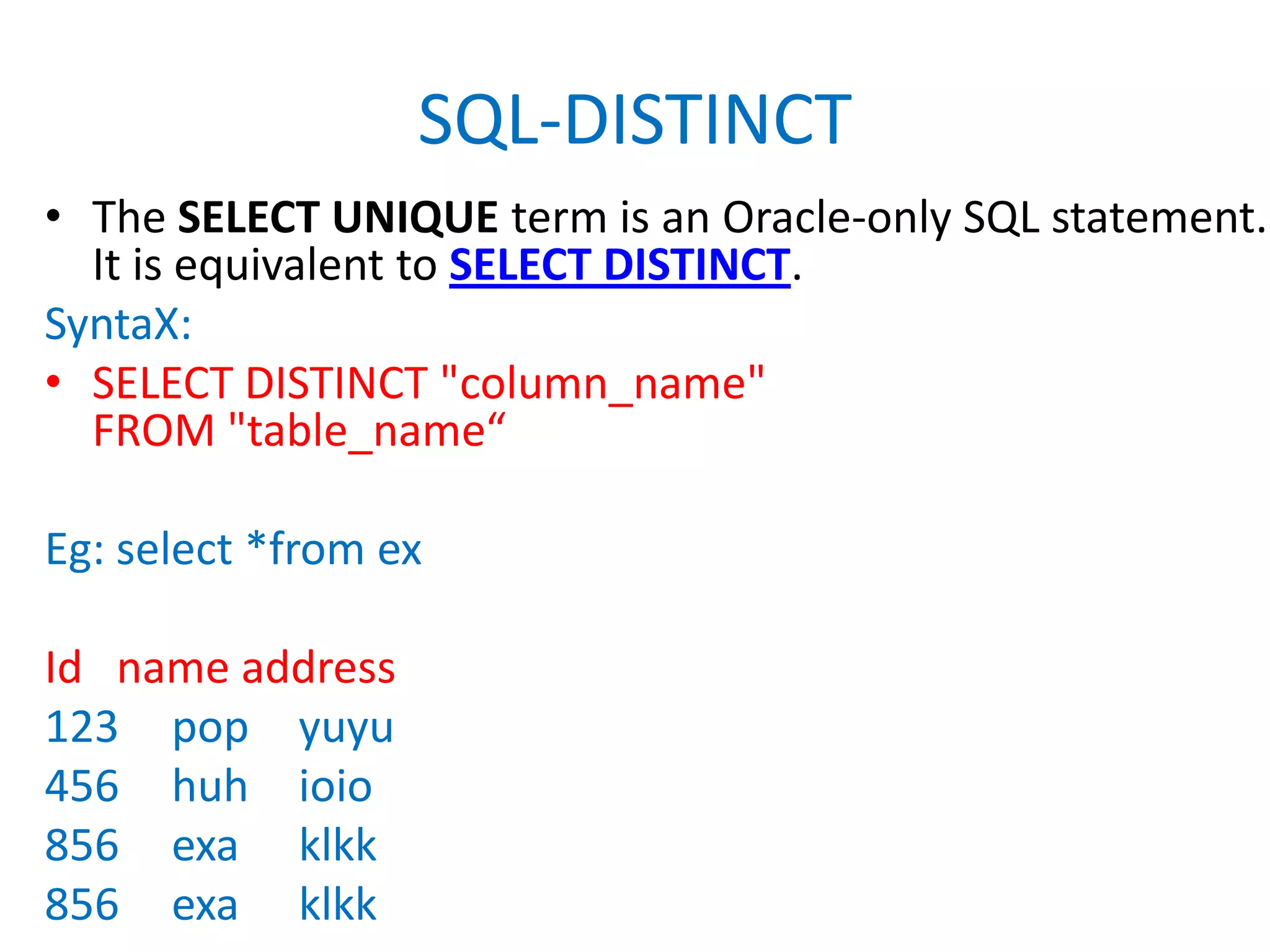
This document provides an overview of SQL commands including CREATE, INSERT, SELECT, ALTER, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP, DISTINCT, WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY, HAVING, JOIN, VIEW, STORED PROCEDURES. It includes examples of creating tables, inserting data, selecting data, updating data, deleting data, adding/dropping columns and tables. It also covers primary keys, foreign keys and relationships between tables.