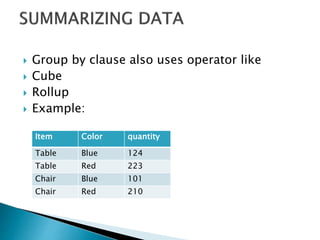
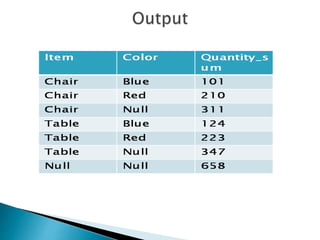
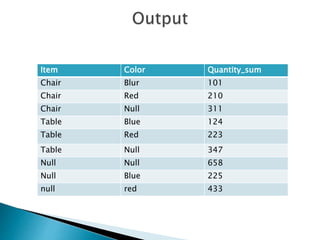
The GROUP BY clause is used to organize rows into groups and can be used with clauses like WHERE, HAVING, and operators like ROLLUP and CUBE. GROUP BY works with WHERE to restrict rows before grouping, groups null values separately, and ALL includes groups that don't meet search conditions. ROLLUP generates subtotals and totals, while CUBE shows aggregates for all column value combinations including totals.