This document provides an overview of SQL Server for developers, covering topics such as:
- SQL Server architecture, services, and administrative tools like SQL Server Management Studio.
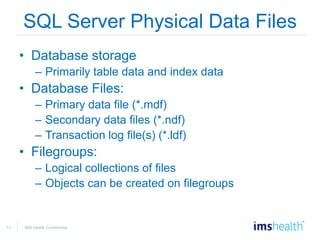
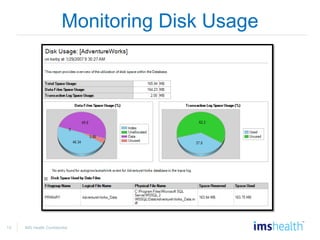
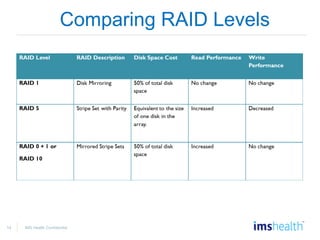
- Managing databases, including designing data storage, monitoring disk usage, and moving/copying databases.
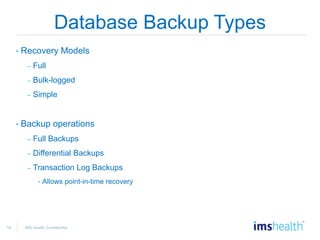
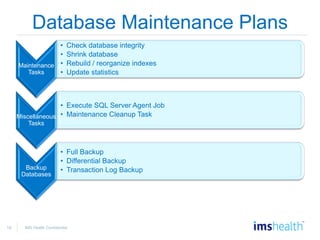
- Database maintenance and data protection, including different backup types and recovery processes.
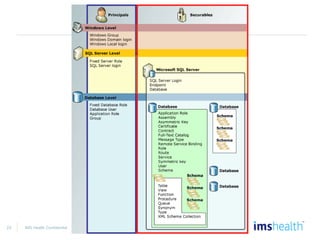
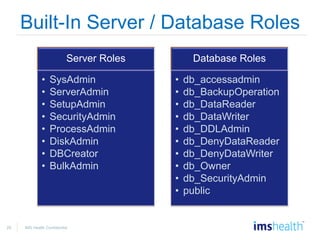
- Securing SQL Server, including configuring permissions for logins, users, roles, and service accounts.
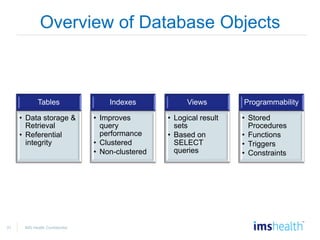
- Managing database objects like tables, indexes, views, and stored procedures.